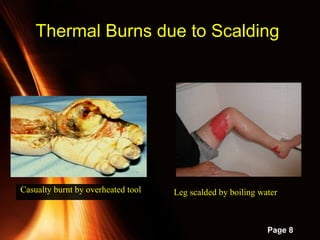
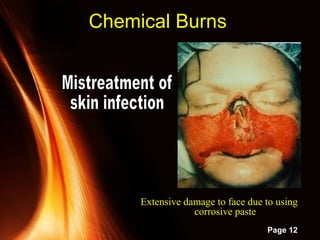
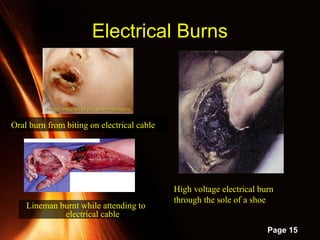
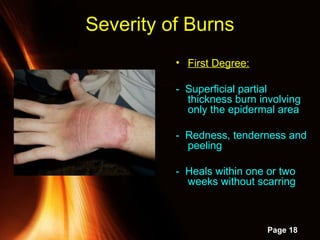
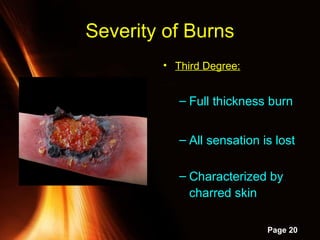
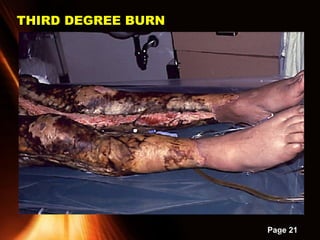
This document provides information on powerpoint slides about burns. It defines burns as injuries caused by heat, cold, chemicals or electricity. It describes the three types of burns as thermal, chemical and electrical burns. It explains how to assess the severity of burns based on depth, with first, second and third degree burns. It provides guidance on first aid treatment for burns, including cooling the burned area, covering it, and seeking prompt medical attention for severe burns. The overall document aims to educate on classifying and treating different types of burn injuries.