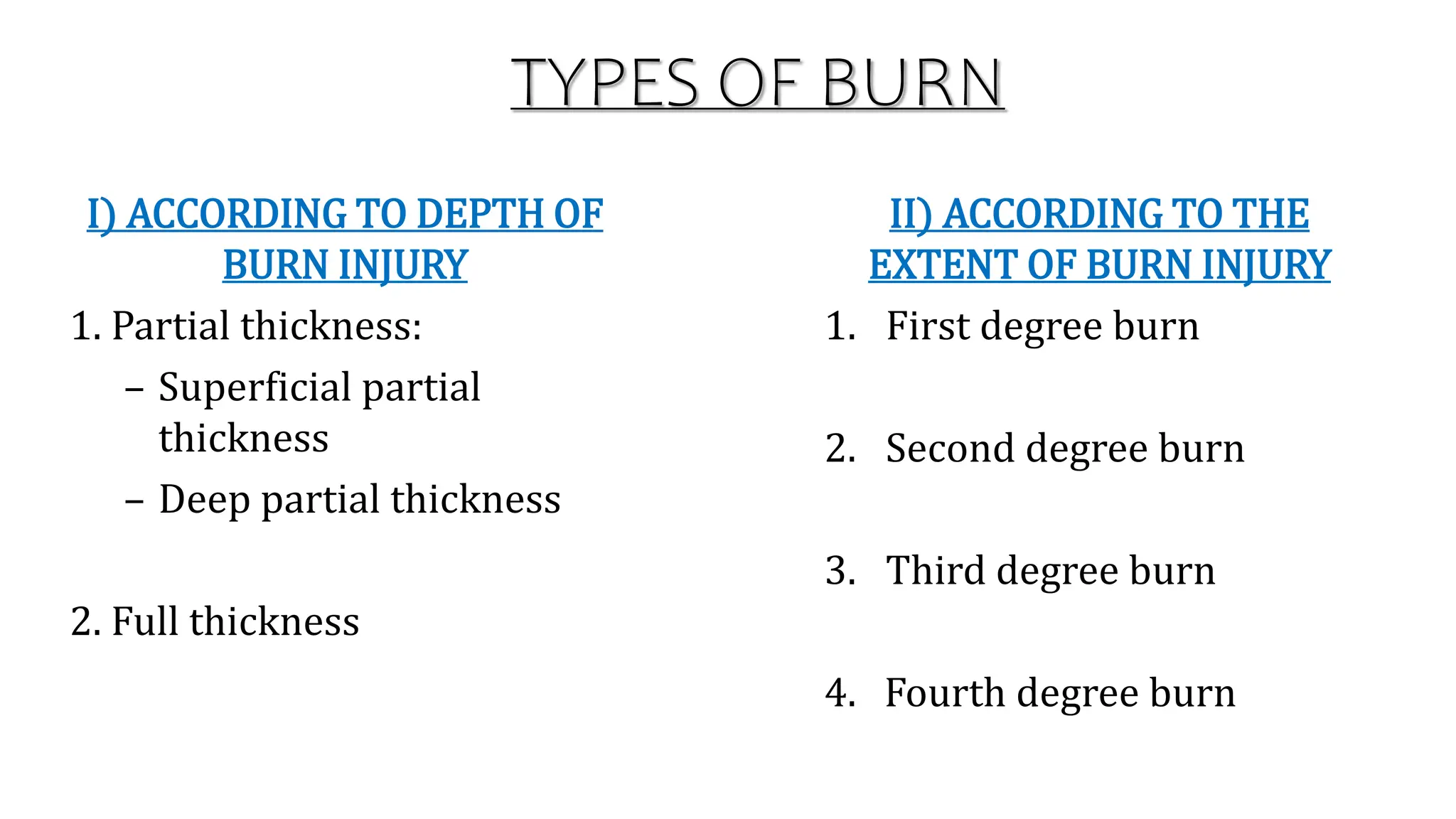
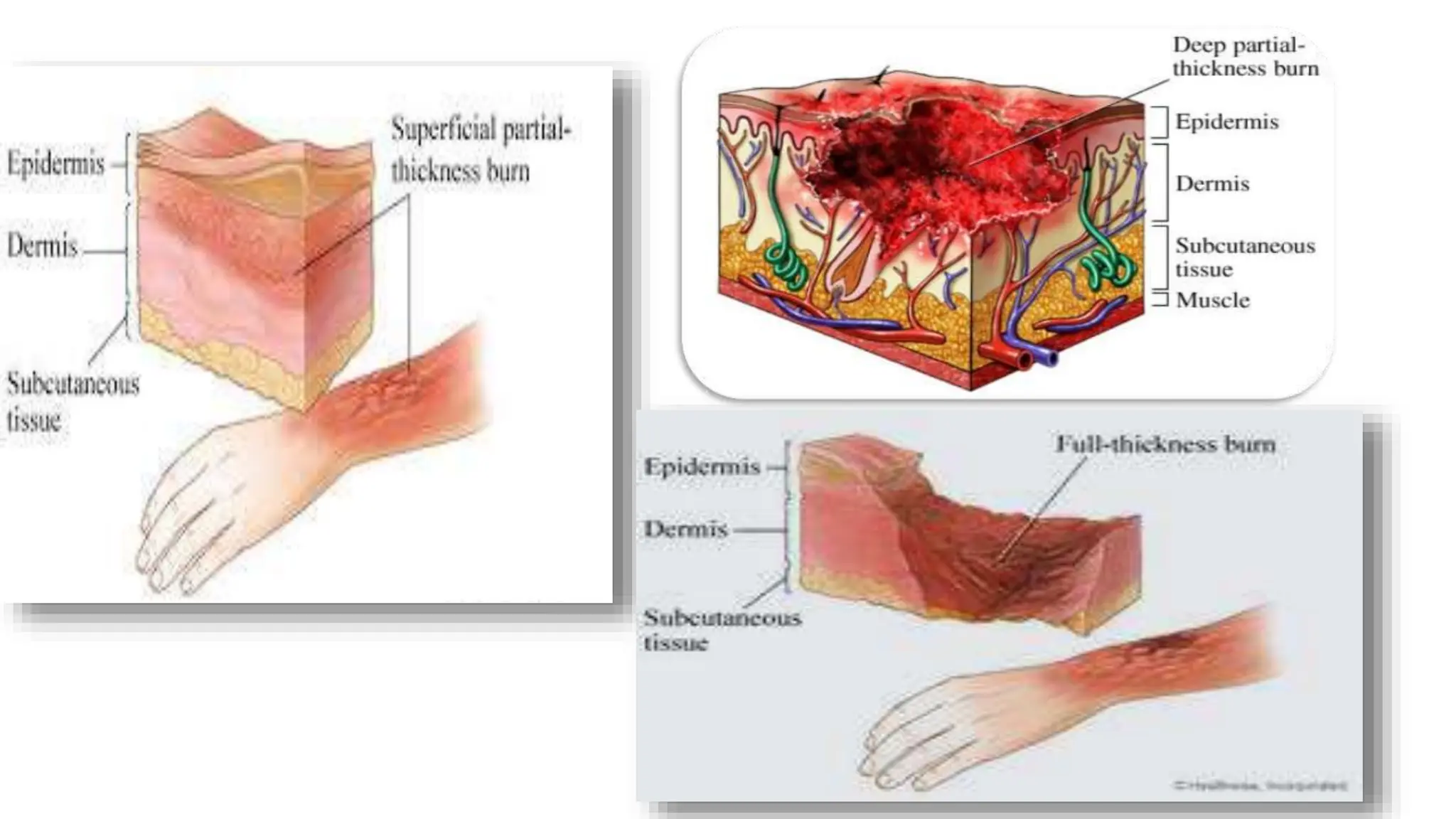
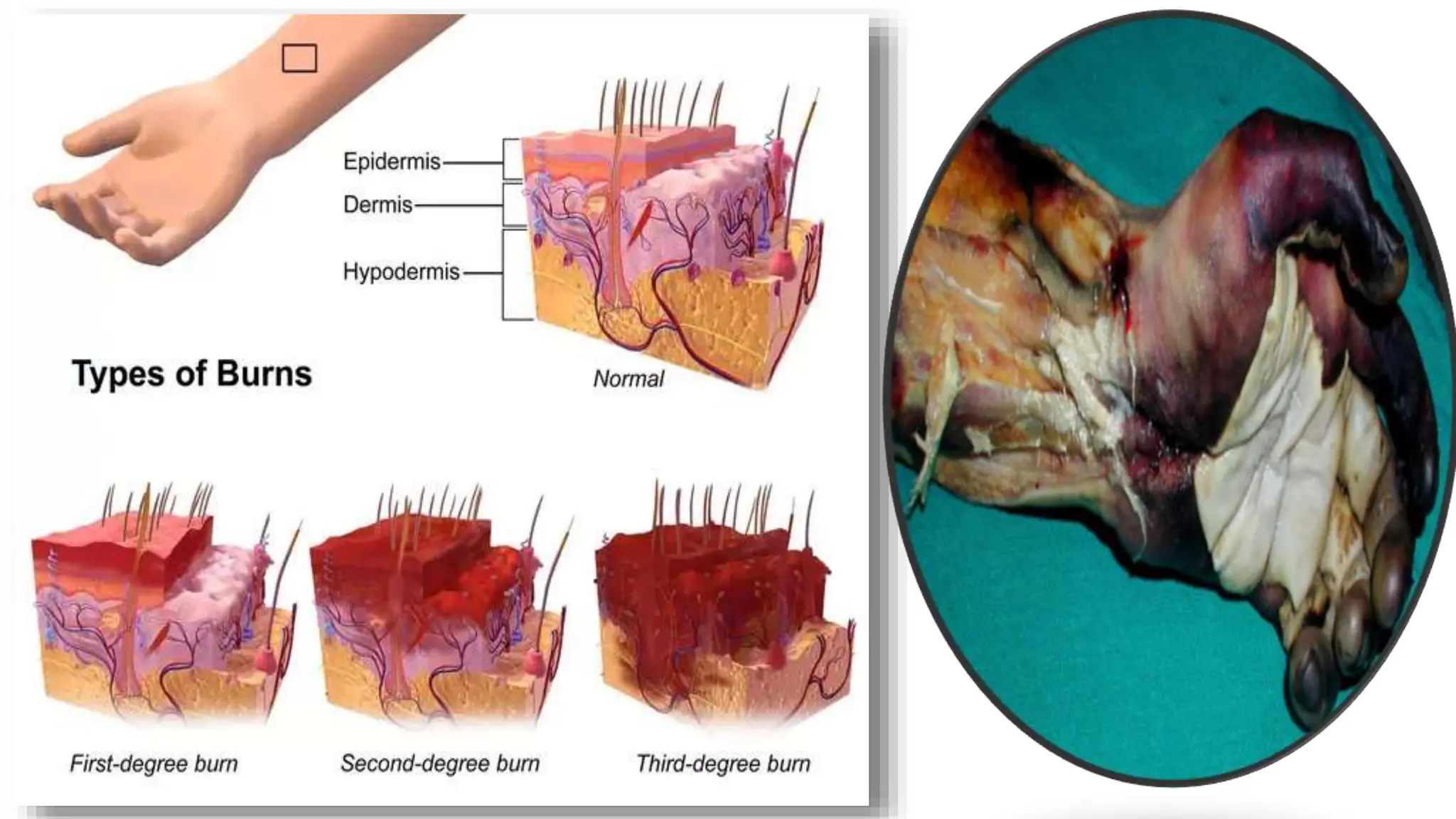
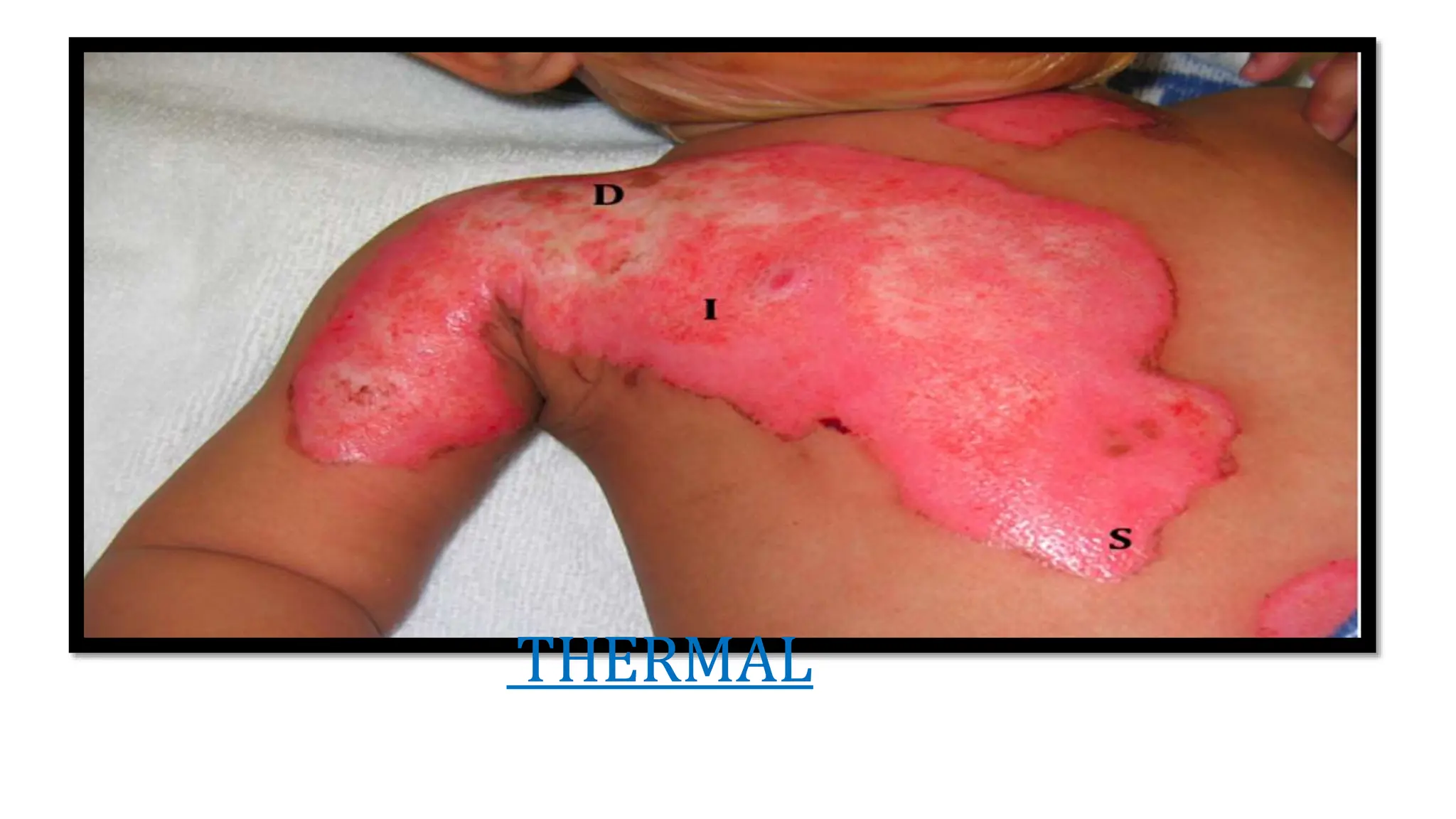
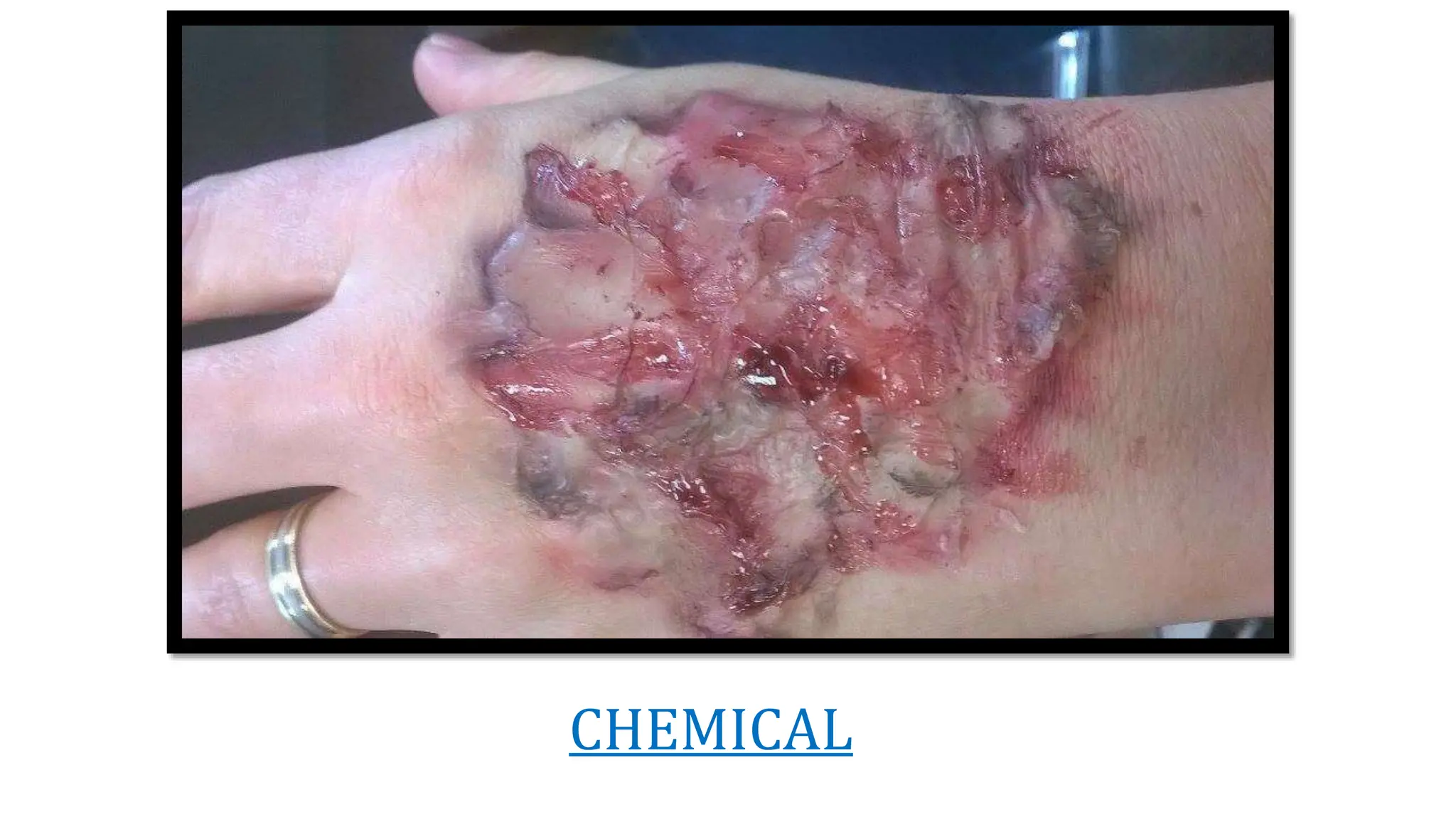
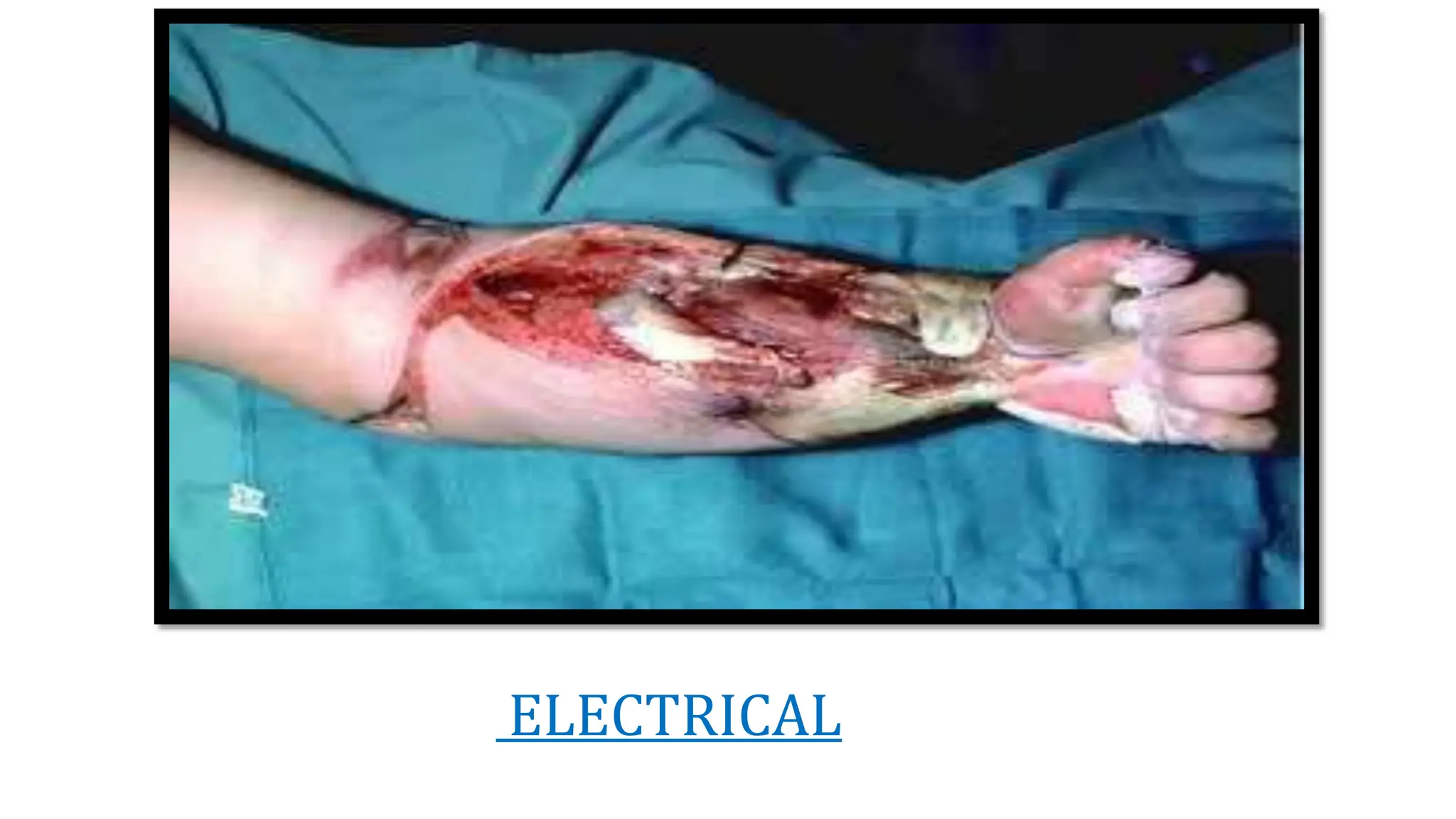
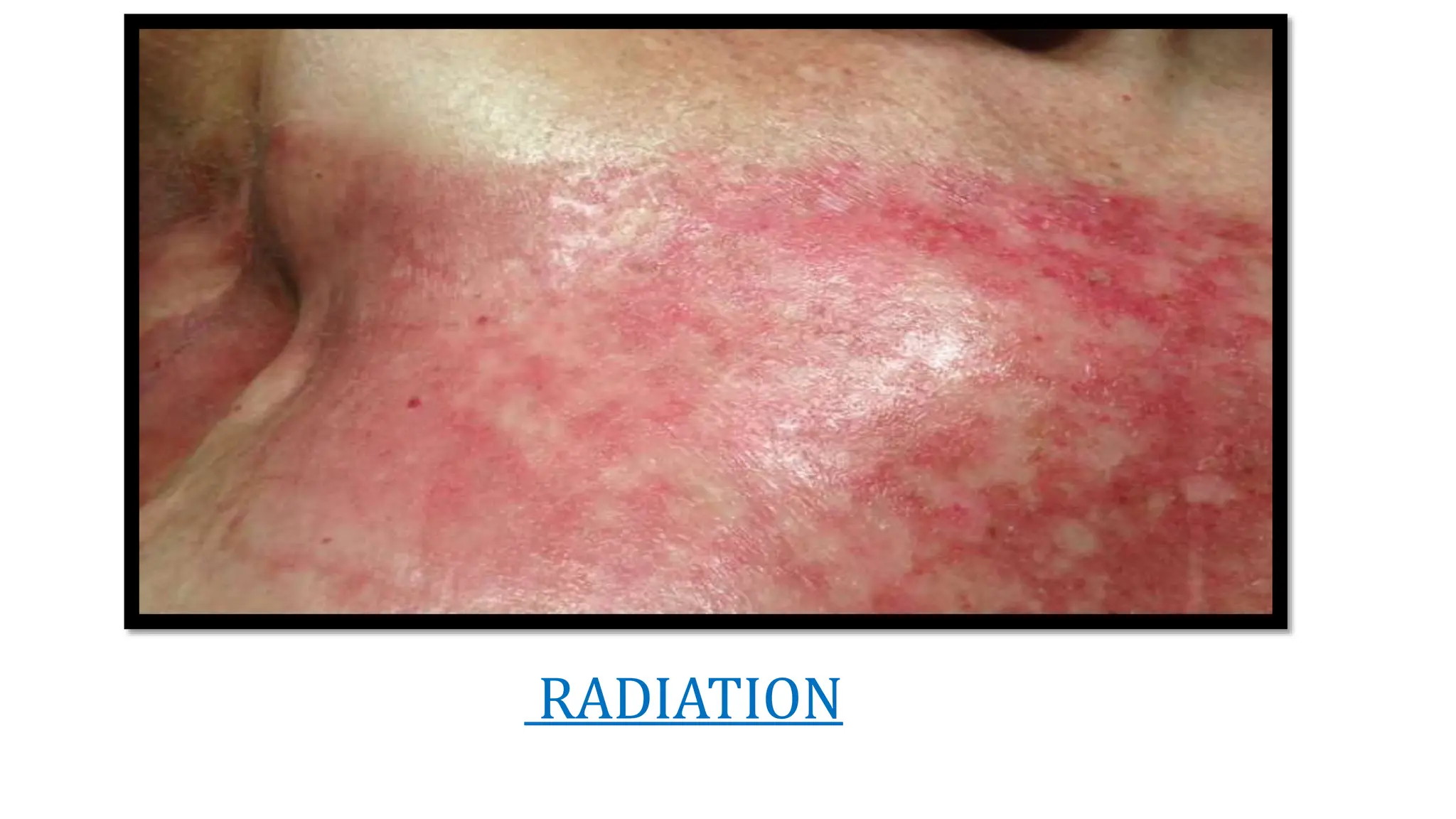
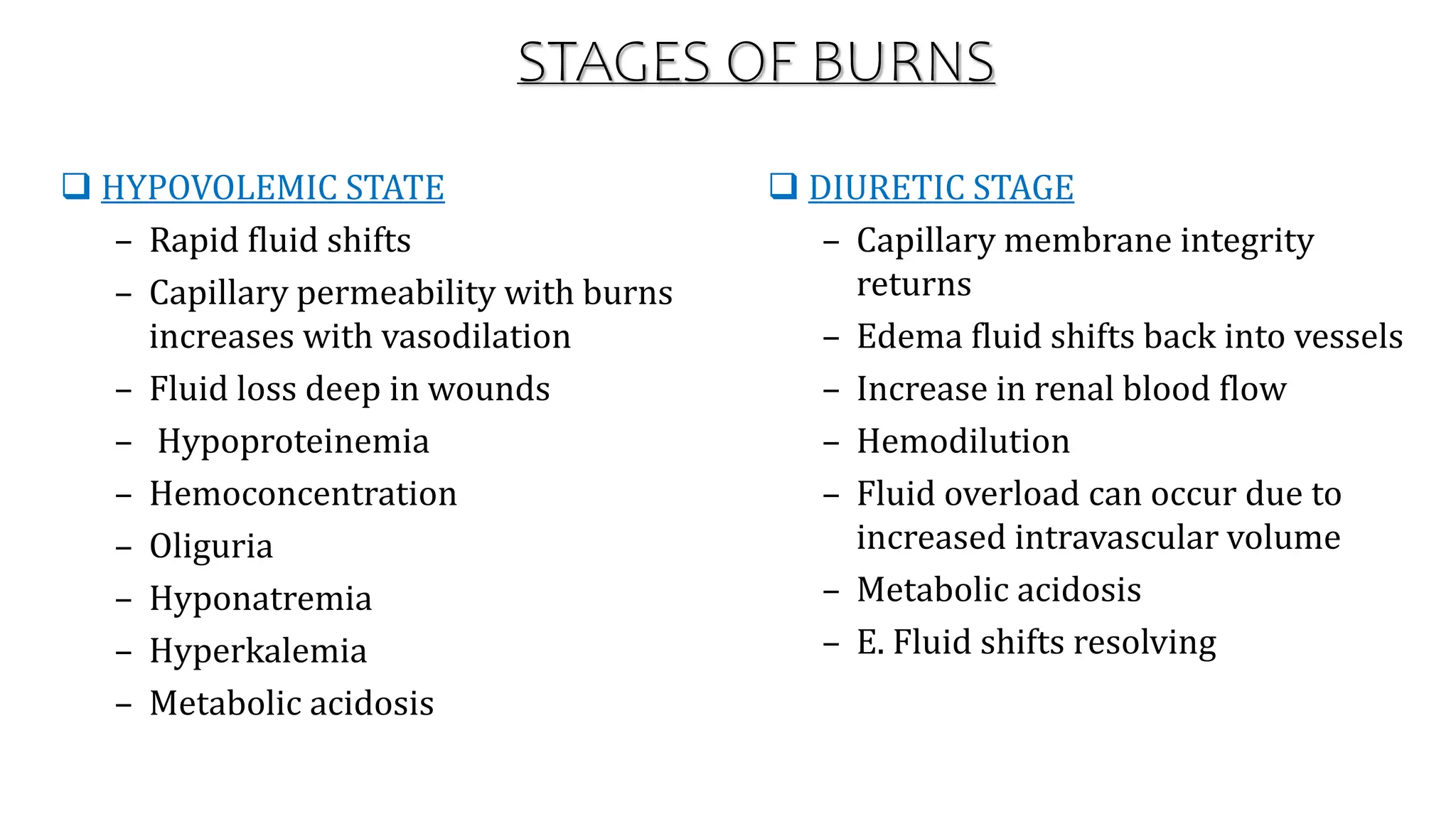
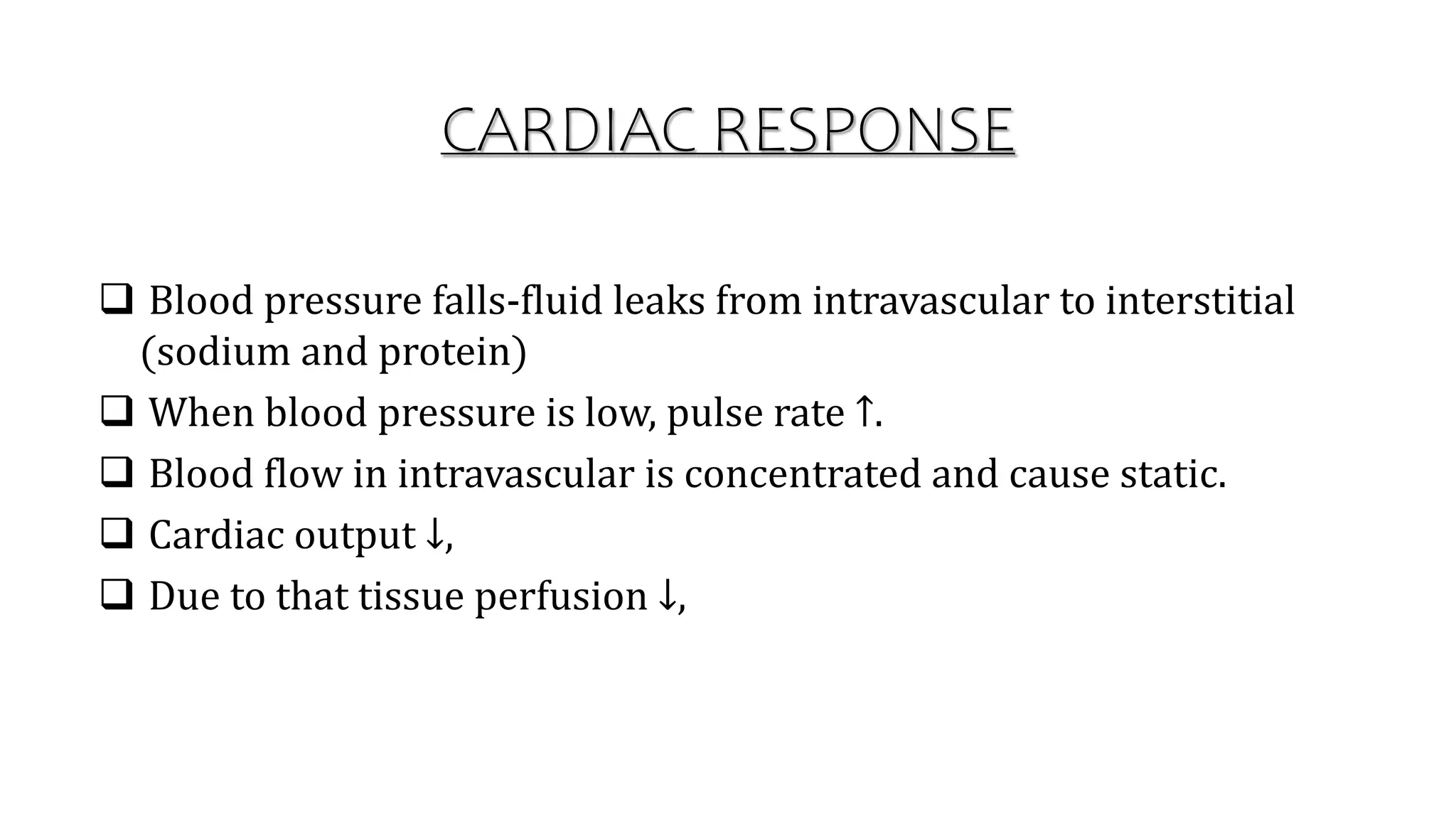
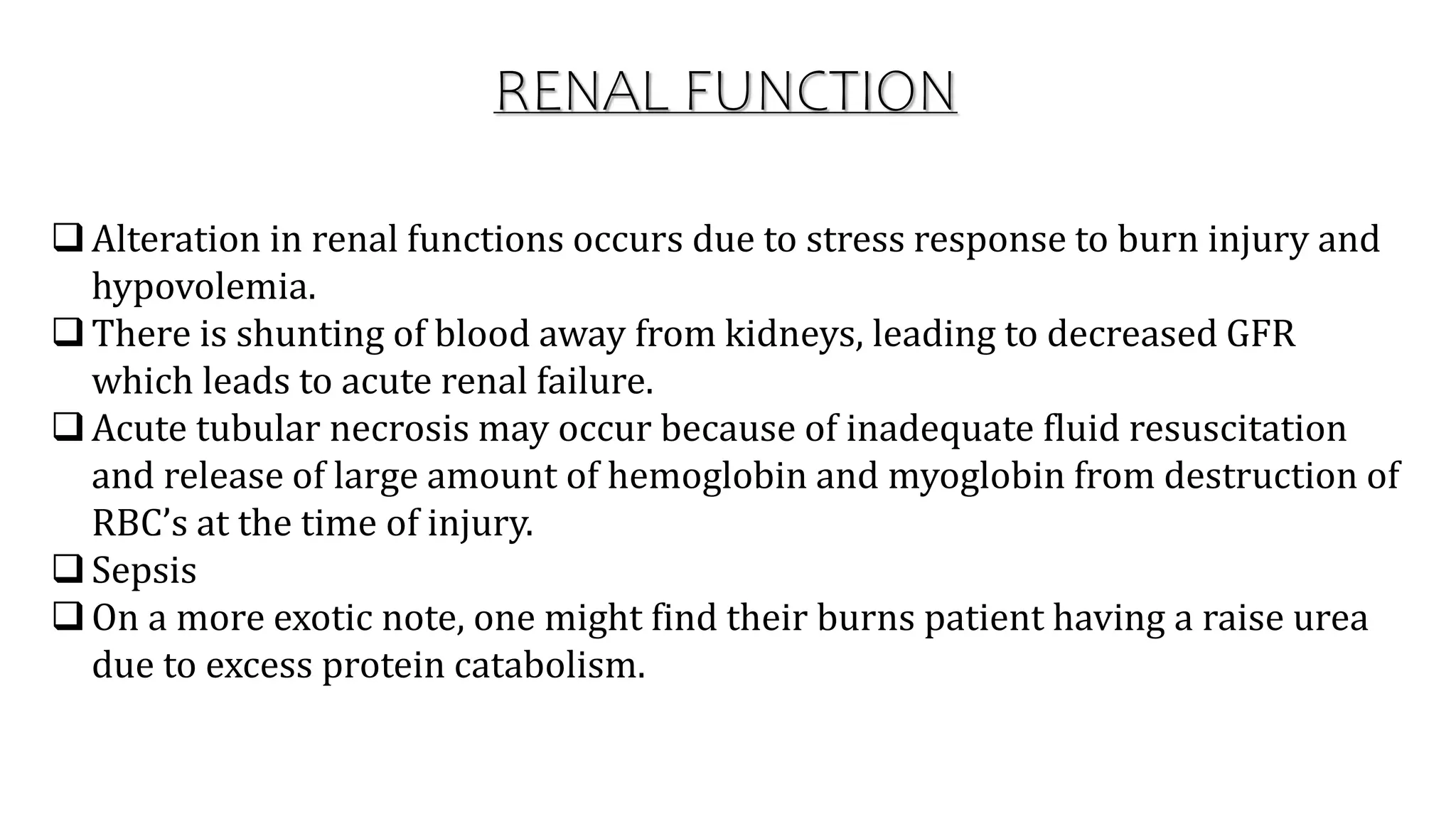
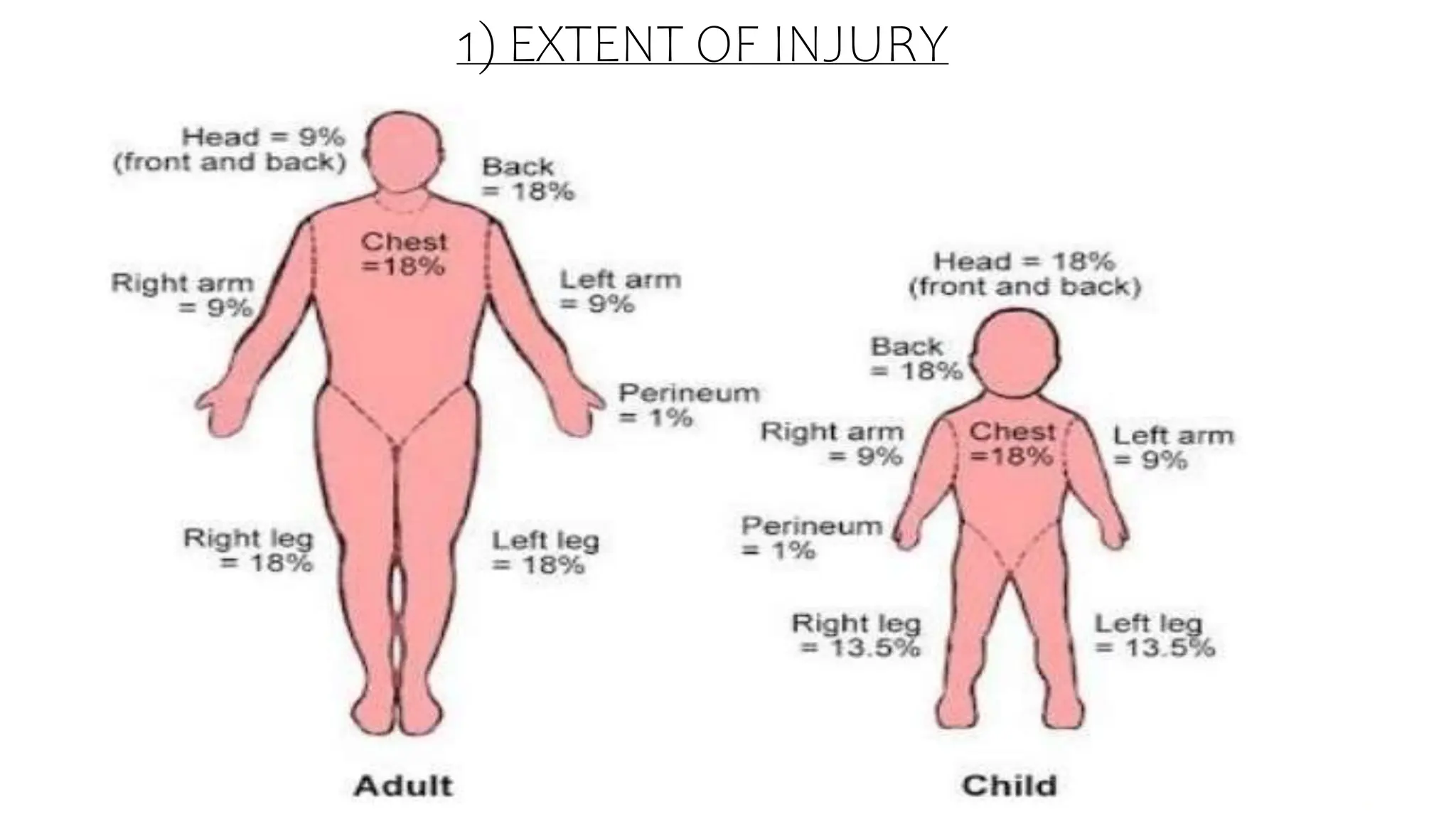
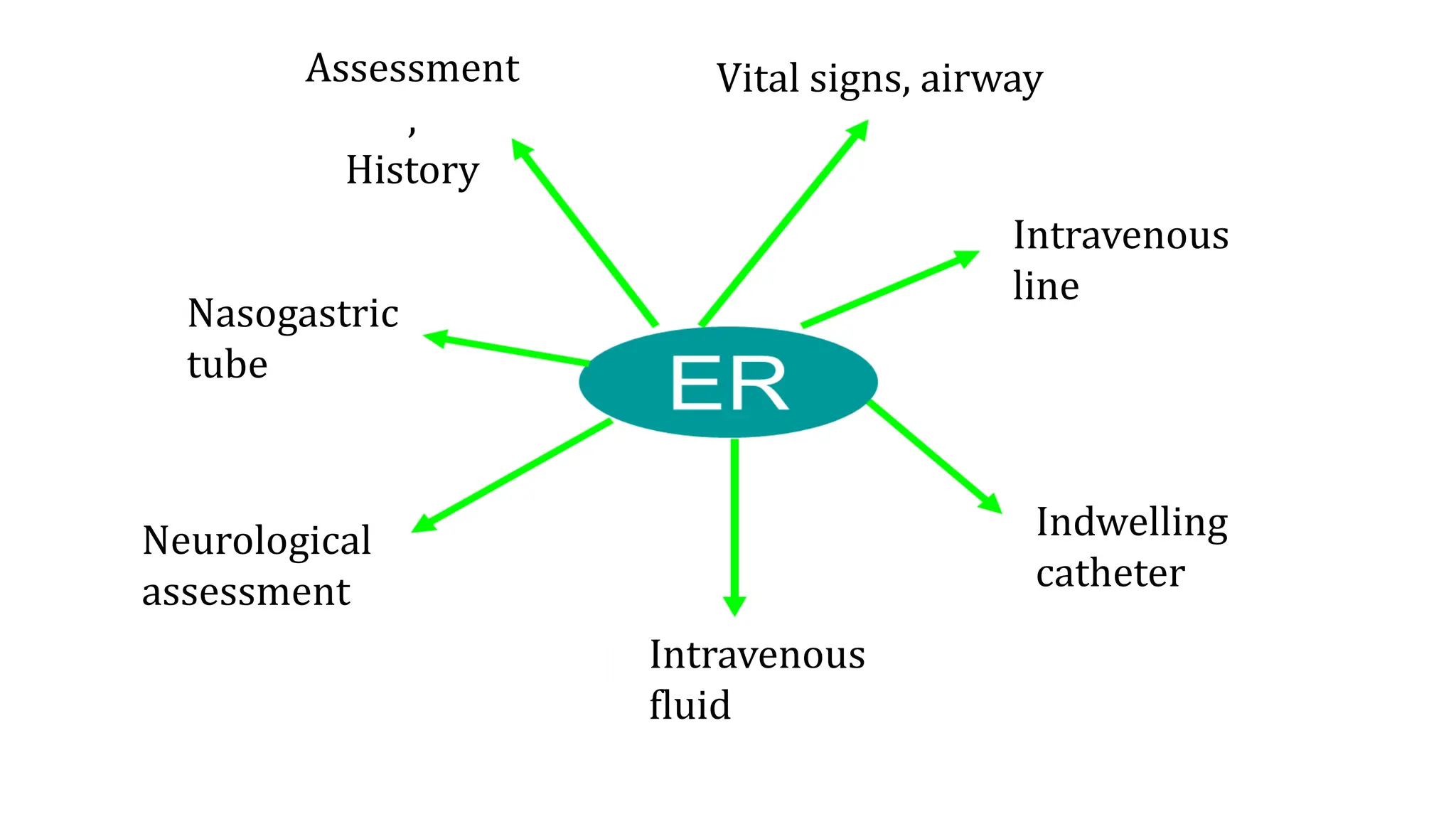
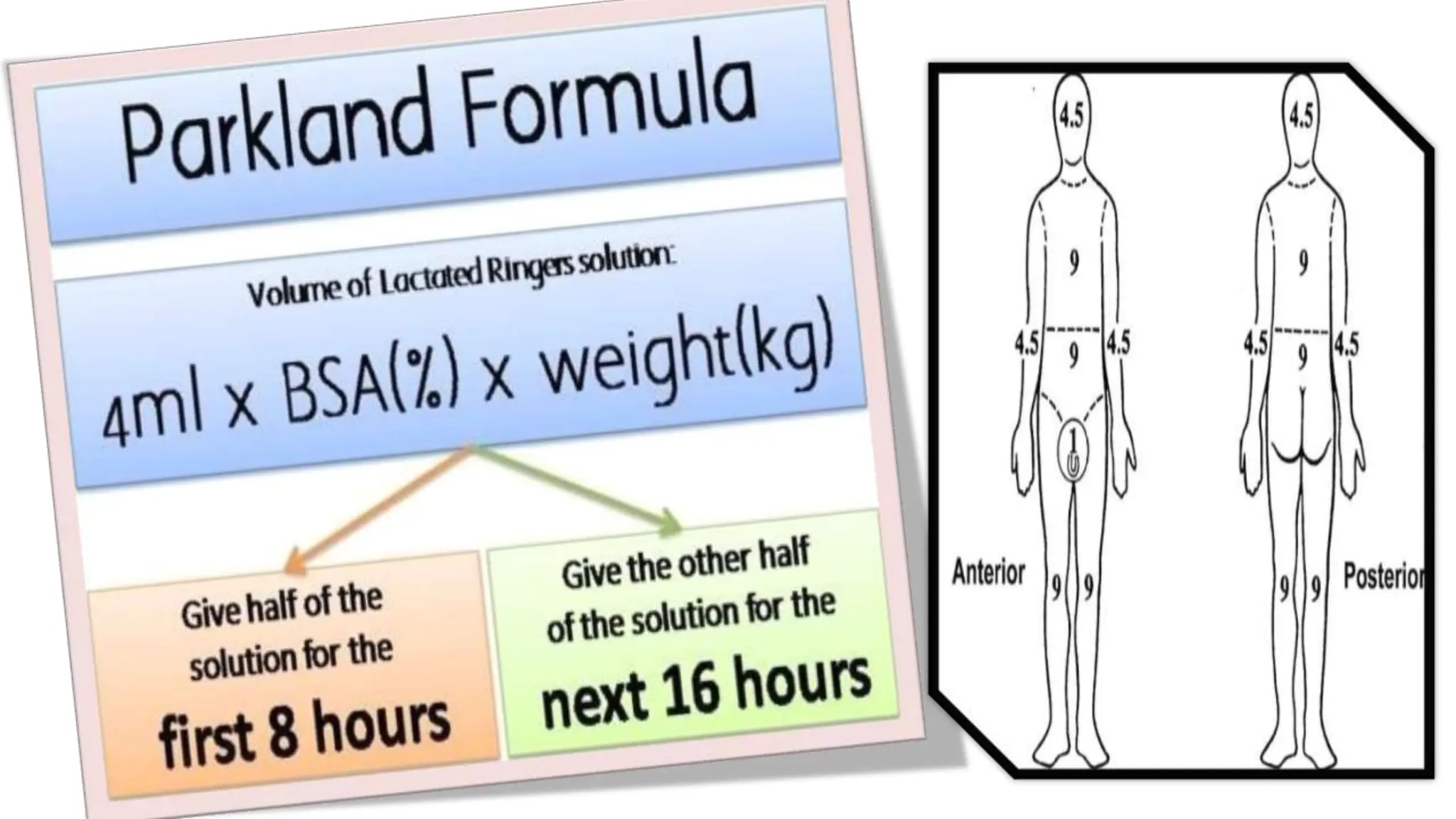
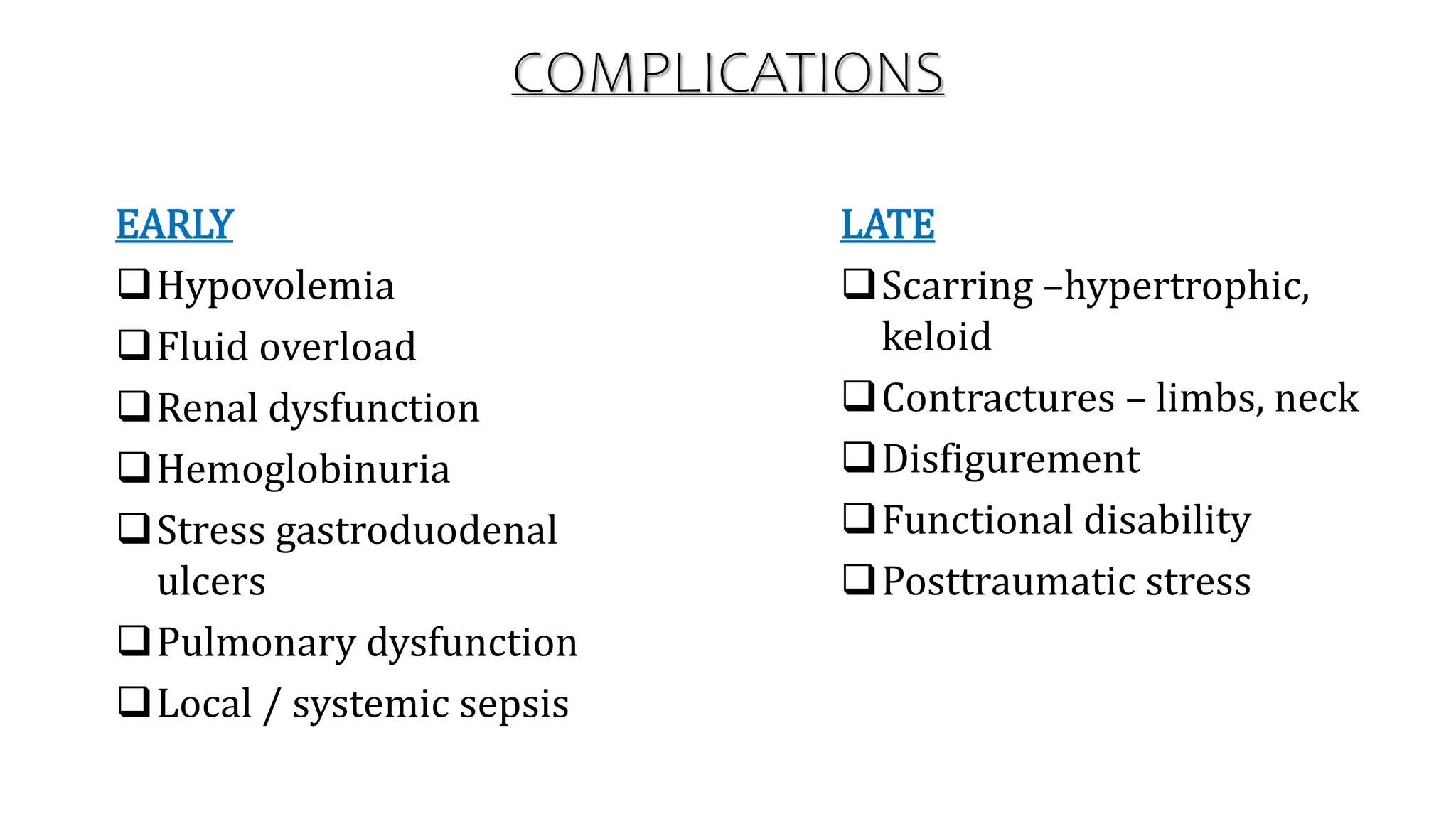
Burns are injuries caused by heat, cold, electricity, chemicals, friction or radiation. They can range from superficial partial thickness burns to full thickness burns. The main causes of burns are thermal burns from hot liquids, solids or fire, as well as chemical and electrical burns. Burn injuries lead to local skin damage and systemic physiological changes due to fluid shifts, metabolic changes, and increased risk of infection. Treatment involves stopping the burning process, assessing the extent and depth of the burn, fluid resuscitation, wound care, infection control and rehabilitation.