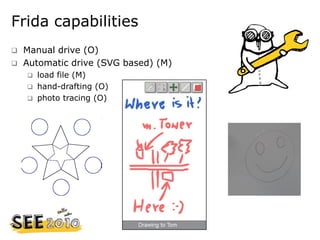
This document provides an overview of a project to build a mobile robot named Frida that can draw vector graphics using colored markers controlled by a Symbian smartphone over Bluetooth. A team of 3 engineers and 1 project manager built Frida over 3 months with a budget of 672 euros using Lego Mindstorms parts. Frida uses servos, sensors, gears and software to allow manual and automatic drawing of files sent from a Symbian phone application. The application filters photos into vector drawings and transmits movement instructions over Bluetooth while the robot precisely draws the images.































![Bitmap filtering and vectorizing
Gradients computing
edge detection by gradient mask
[ 1 2 1] [1 0 -1]
[ 0 0 0] and [2 0 -2]
[-1 -2 -1] [1 0 -1]
Non-maximum suppression
clearing all pixels that are not extremal in
their local neighbourhood
edges are thinner and more clear rather
than but thick and blurred](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buildingyourfirstwowsymbianapplication-101123061319-phpapp02/85/Building-Your-First-WOW-Symbian-Application-33-320.jpg)






