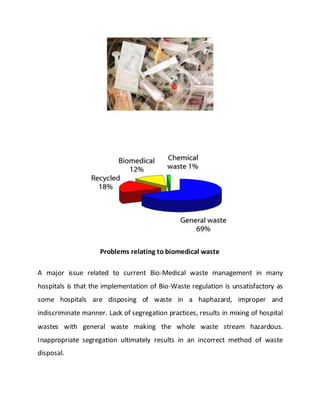
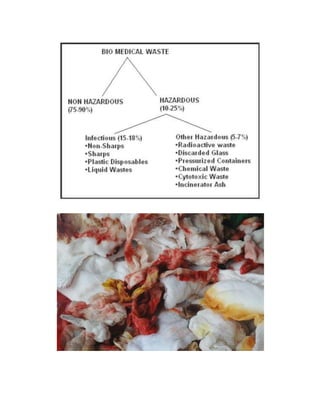
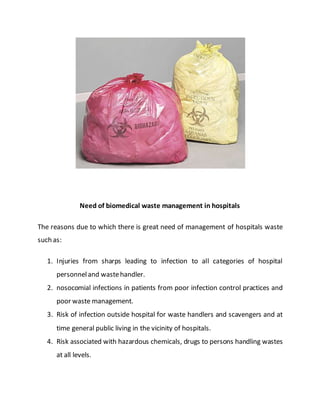
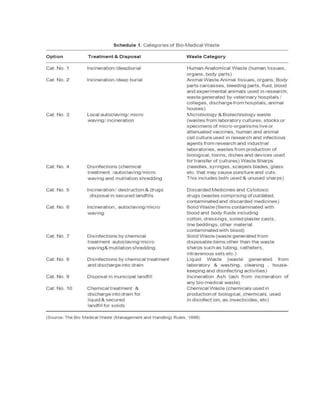
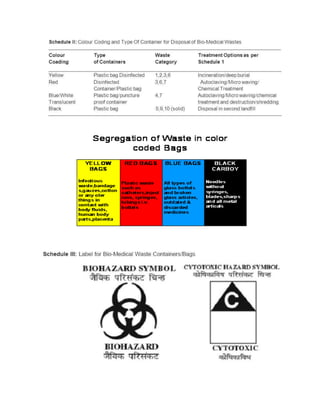
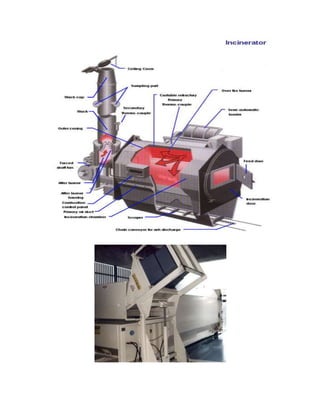
This project report summarizes Rochan Banga's investigatory project on biological waste management. The report discusses the need for proper biological waste management in hospitals to prevent the spread of diseases and environmental pollution. It provides classifications of biomedical waste, sources of waste, and the problems caused by improper management. It also outlines the key steps in biological waste management processes, including collection, segregation, transportation, treatment, and disposal. Common treatment methods like incineration and autoclaving are also summarized.