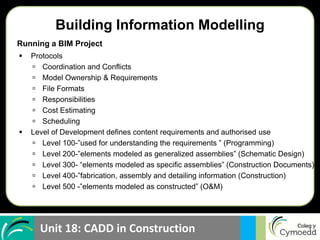
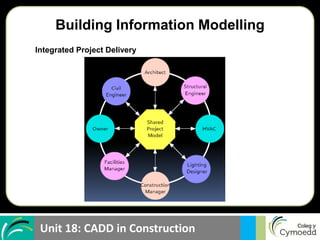
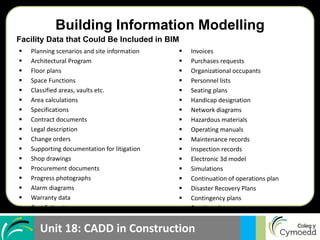
BIM allows for:
- Clash detection and coordination between designs to reduce errors.
- Simulation of designs before construction to improve quality.
- Sharing of information across disciplines and teams to improve communication and productivity.
However, BIM requires:
- Investment in new software and training which increases costs initially.
- Strict guidelines and standards to be followed for effective collaboration.
2D CAD is:
- Familiar to many in the industry so requires less training.
- Less expensive than transitioning to new BIM software.
But 2D CAD lacks: