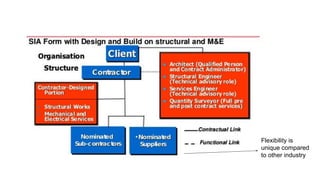
Building economics is the application of economic principles to construction projects. It involves studying client requirements, project costs, and ensuring efficient use of resources. Construction resources include materials, equipment, labor, finance, and subcontractors. The construction industry differs from others in its project-based nature, temporary multi-organization structure, unique pricing methods depending on location, and inability to reuse completed projects elsewhere. The four factors of production are land, labor, capital, and enterprise. The construction industry is important to the economy through its scale, employment opportunities, investments, role for government, and ability to attract international investors through improved infrastructure. Government policies like RUMAWIP and mortgage interest tax relief influence housing supply and demand.