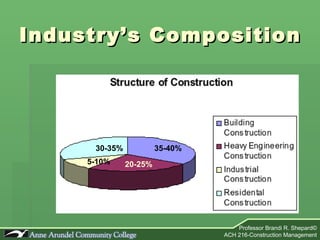
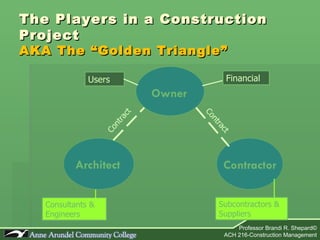
The document provides an overview of the construction industry, including definitions of construction management, an explanation of construction technology and administration, and descriptions of the key players involved in a construction project. It discusses the nature and composition of the construction industry, challenges it faces, and its future direction. It also outlines the roles and responsibilities of the main participants in a construction project: the architect, owner, and construction manager.