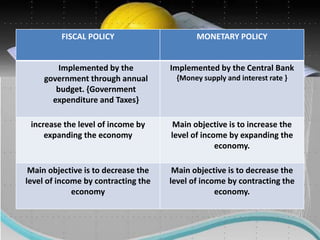
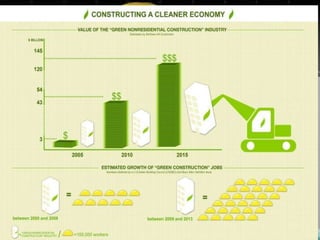
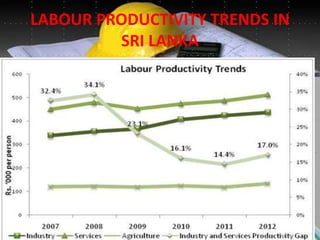
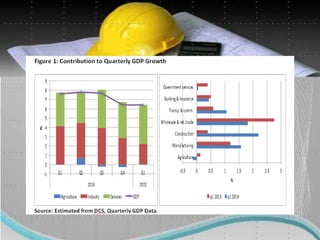
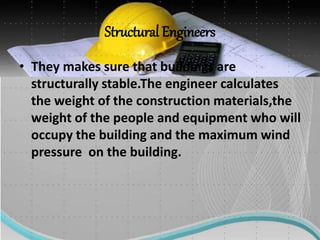
The document discusses several factors that affect the construction industry, including local and global environments, its relationship to the economy and employment. It outlines objectives to regulate and standardize construction activities. The construction industry is influenced by various local codes and regulations. It also discusses the roles of various professionals that make up the building team, such as architects, engineers, contractors and material suppliers. The construction industry impacts economies through government fiscal and monetary policies. It is an important source of employment but also faces issues like worker safety and disputes.