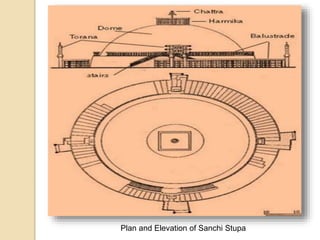
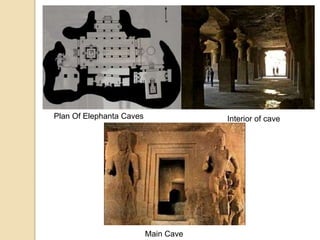
The document discusses Buddhist architecture. It provides an overview of key architectural features associated with Buddhism such as pillars, stupas, and rock-cut caves that were developed during the reign of Emperor Ashoka to spread Buddhism. It then describes the architectural developments during the early Mahayana phase, including masonry stupas, wooden chaitya halls, and rock-cut monasteries. Specific examples of notable Buddhist architectural structures are highlighted such as the Sanchi stupas, Ajanta caves, and Borobudur temple. In conclusion, it notes how Buddhist communities decided to promote their religion through architectural monuments that reflected the preachings of Buddha and spread Buddhism across many countries through a variety of styles