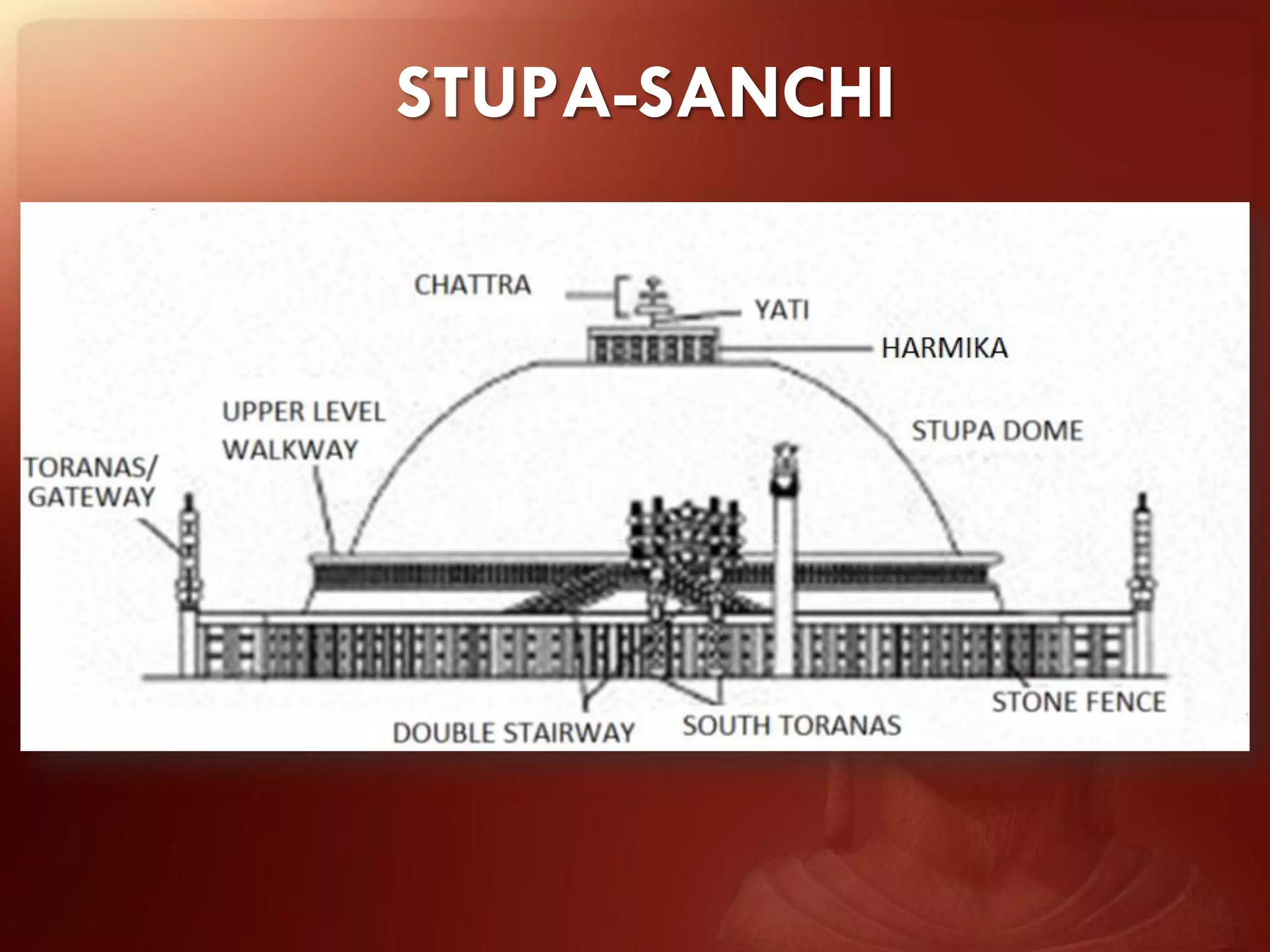
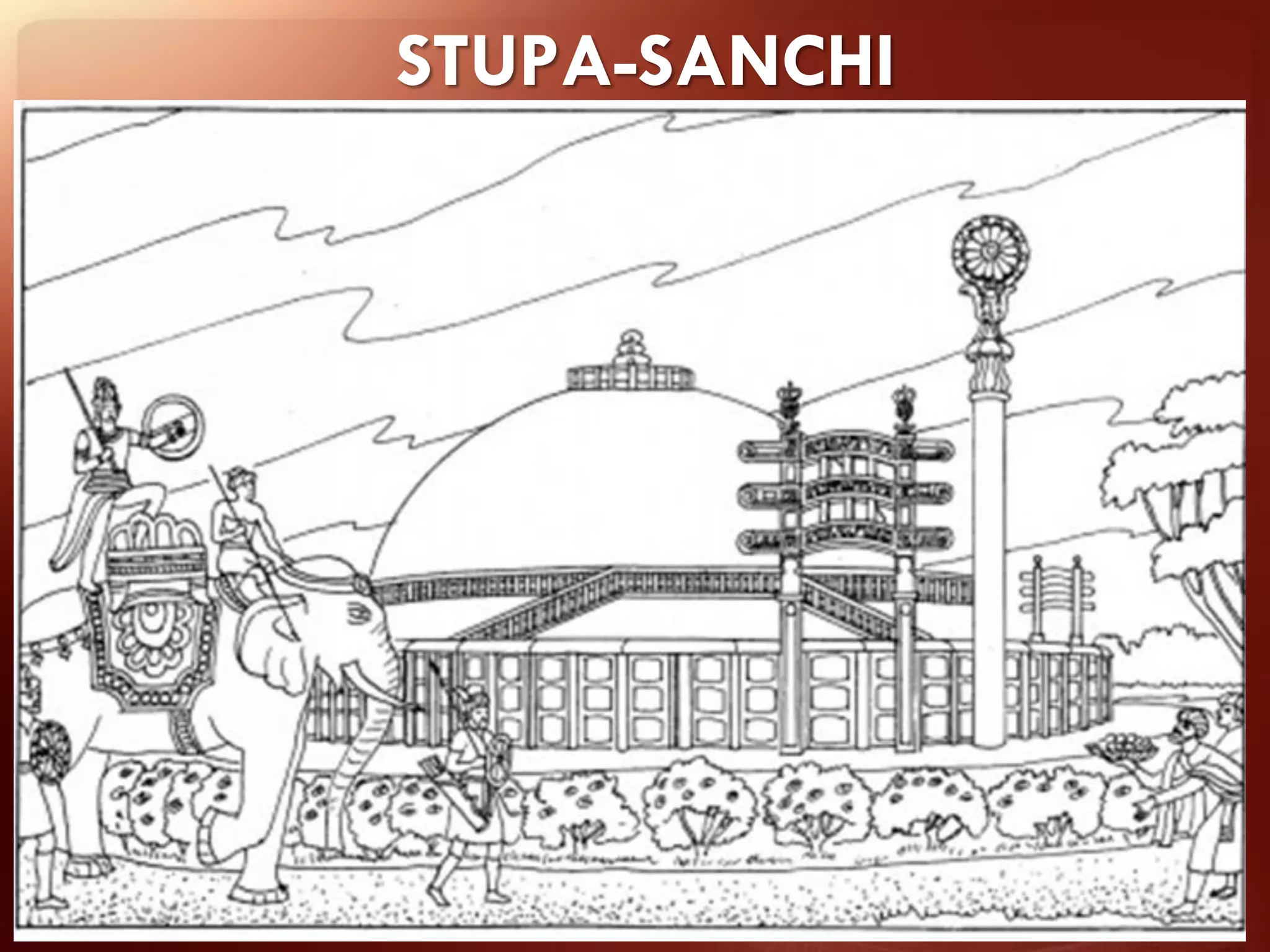
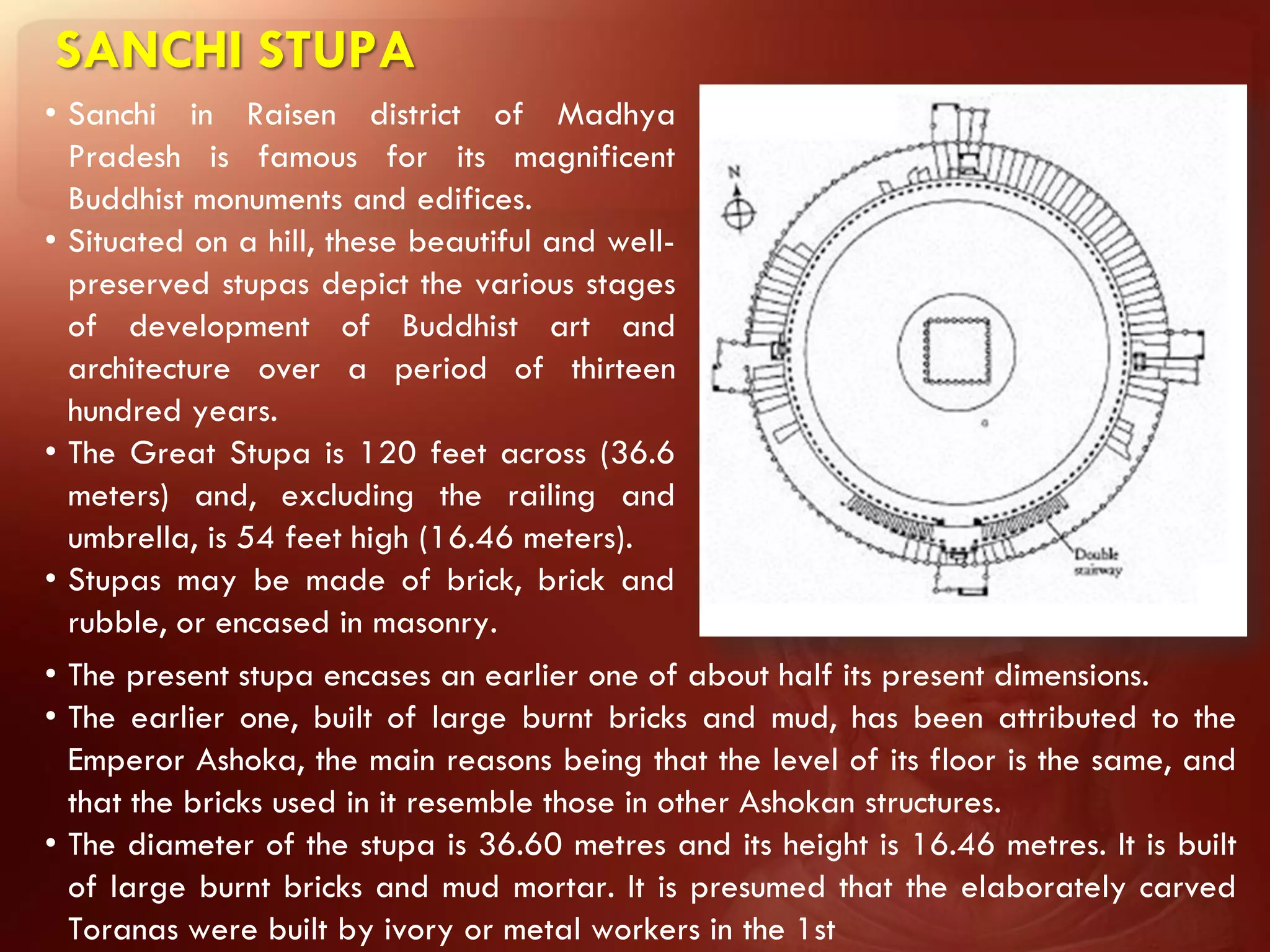
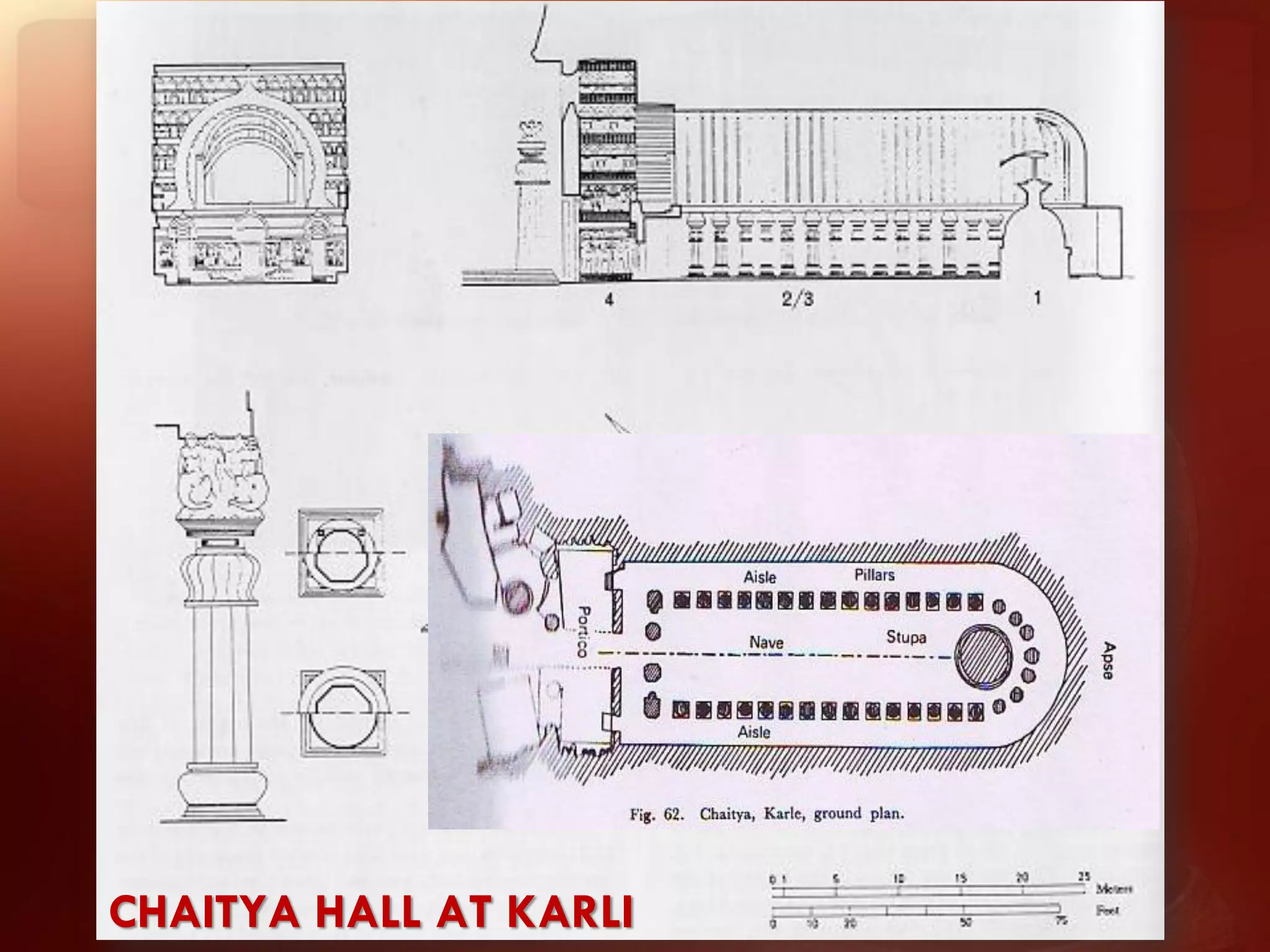
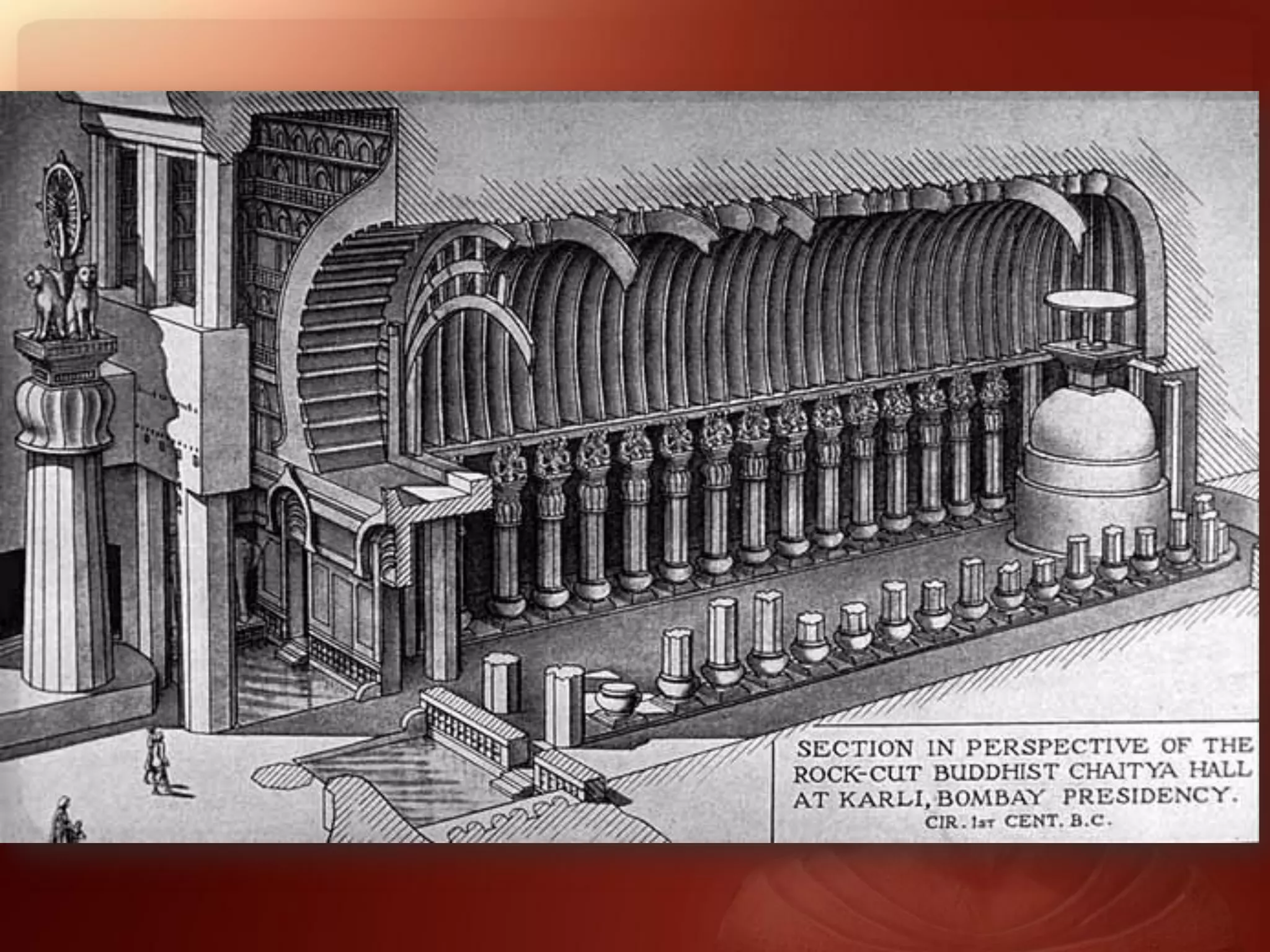
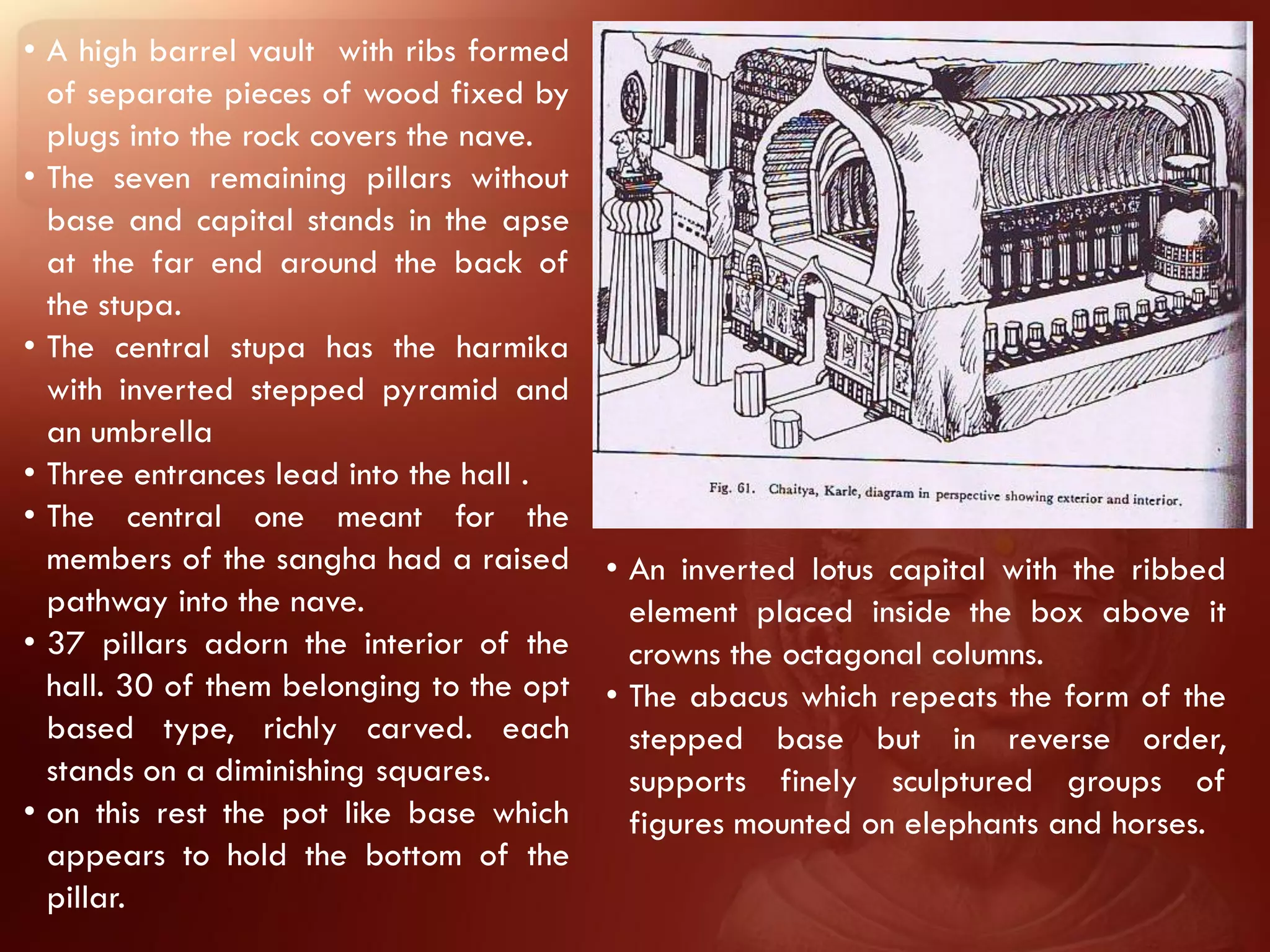
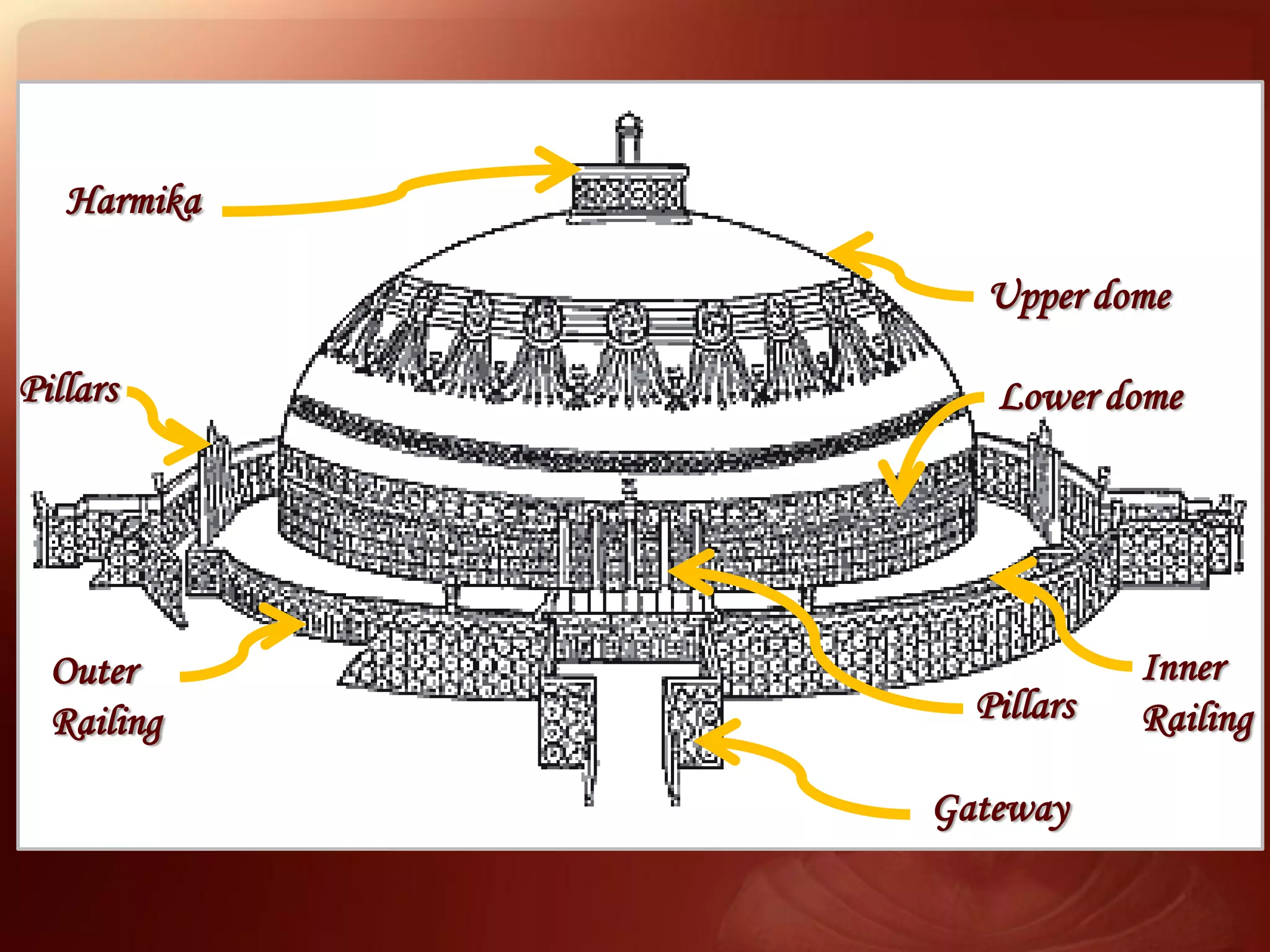
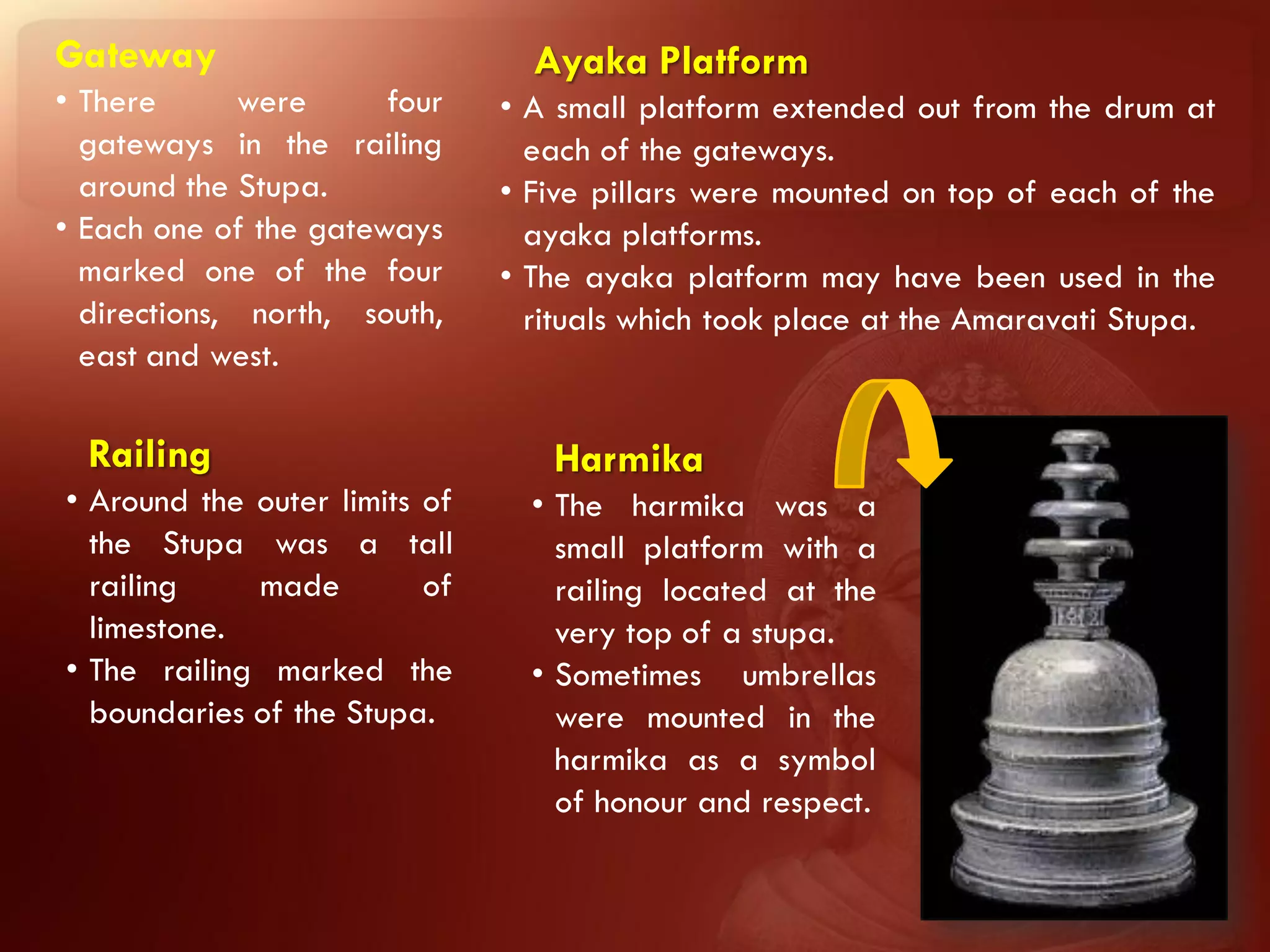
Buddhism originated from the teachings of Siddhartha Gautama, known as the Buddha. The two main branches are Theravada and Mahayana. Theravada is prominent in Southeast Asia while Mahayana is found in East Asia. Early Buddhist architecture included stupas to house relics and mark important sites. The Great Stupa at Sanchi, built in the 3rd century BC, exemplifies the architectural elements of stupas including a hemispherical dome, circular terraces, and carved gateways. Monasteries like Takht-i-Bahai featured courtyards, stupas, chapels, and residential quarters for monks. Chaitya halls provided worship spaces