This document provides an overview of material science and engineering, including:
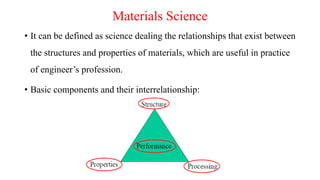
1) It discusses the historic development of materials from the Stone Age to modern times and defines materials science as relating the structure and properties of materials.
2) Materials are classified into metals, ceramics, polymers, composites, semiconductors, and biomaterials based on their atomic structure and properties.
3) Advanced materials either have enhanced traditional materials properties or are newly developed with high performance capabilities for applications like integrated circuits.