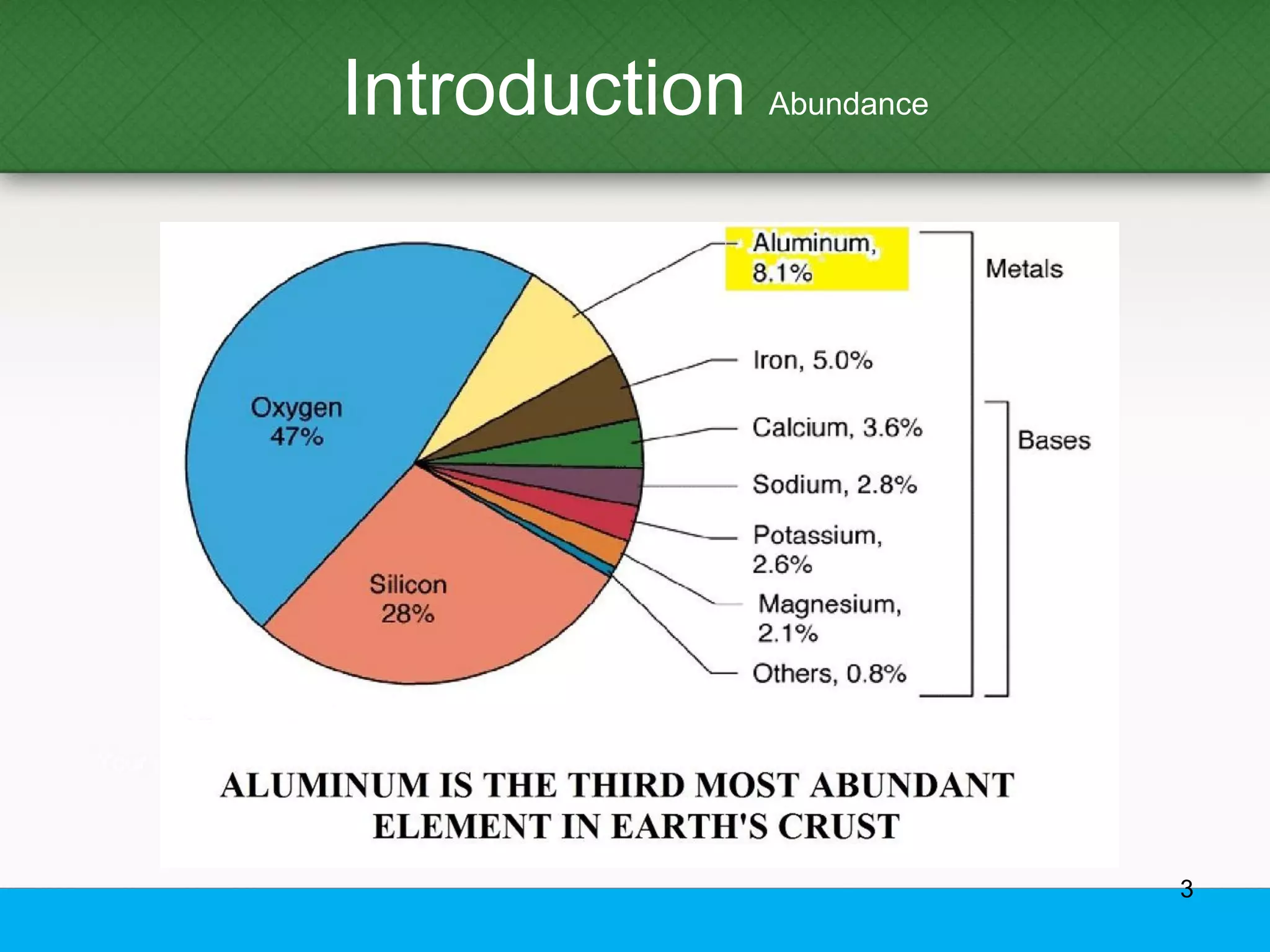
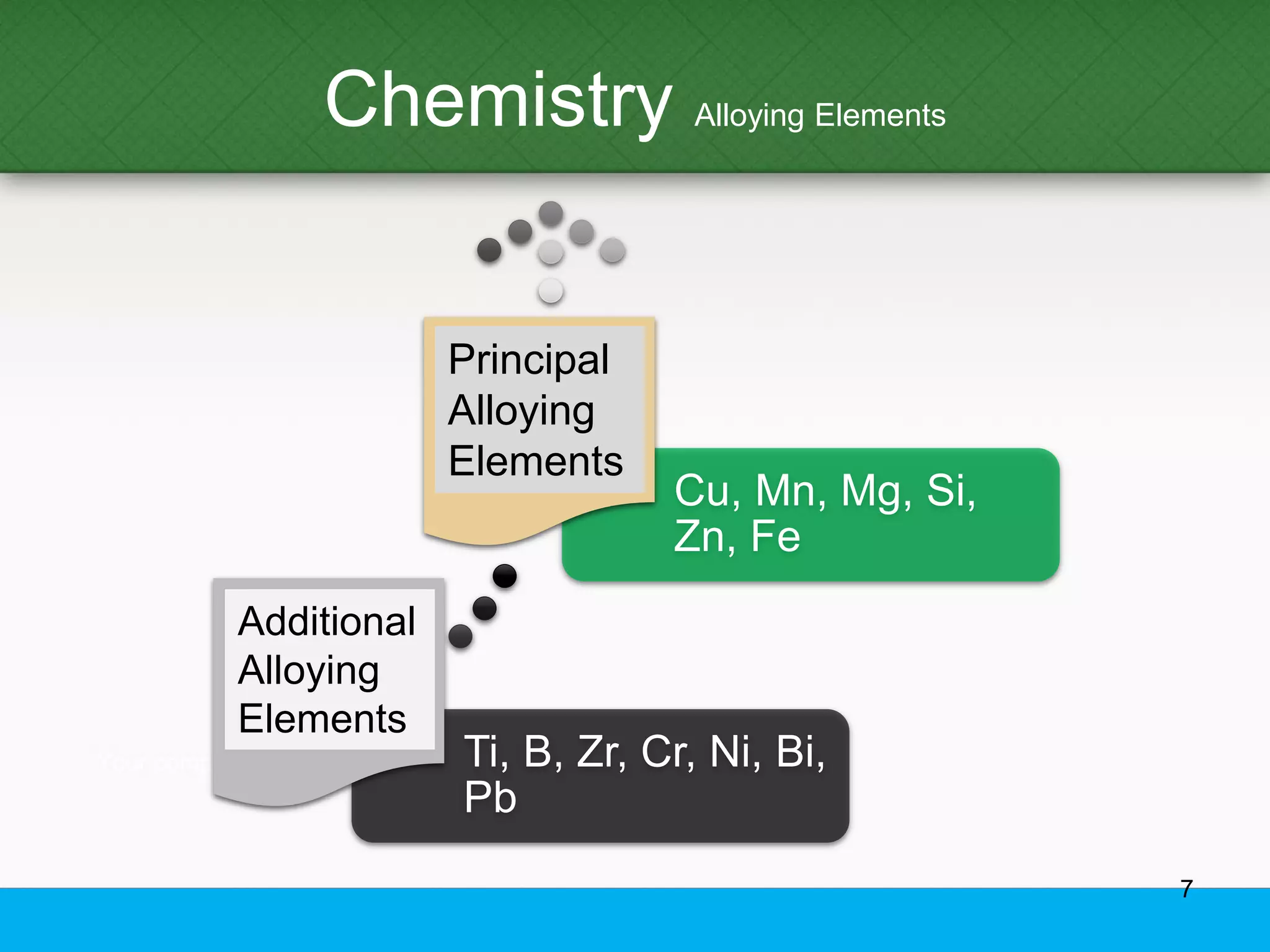
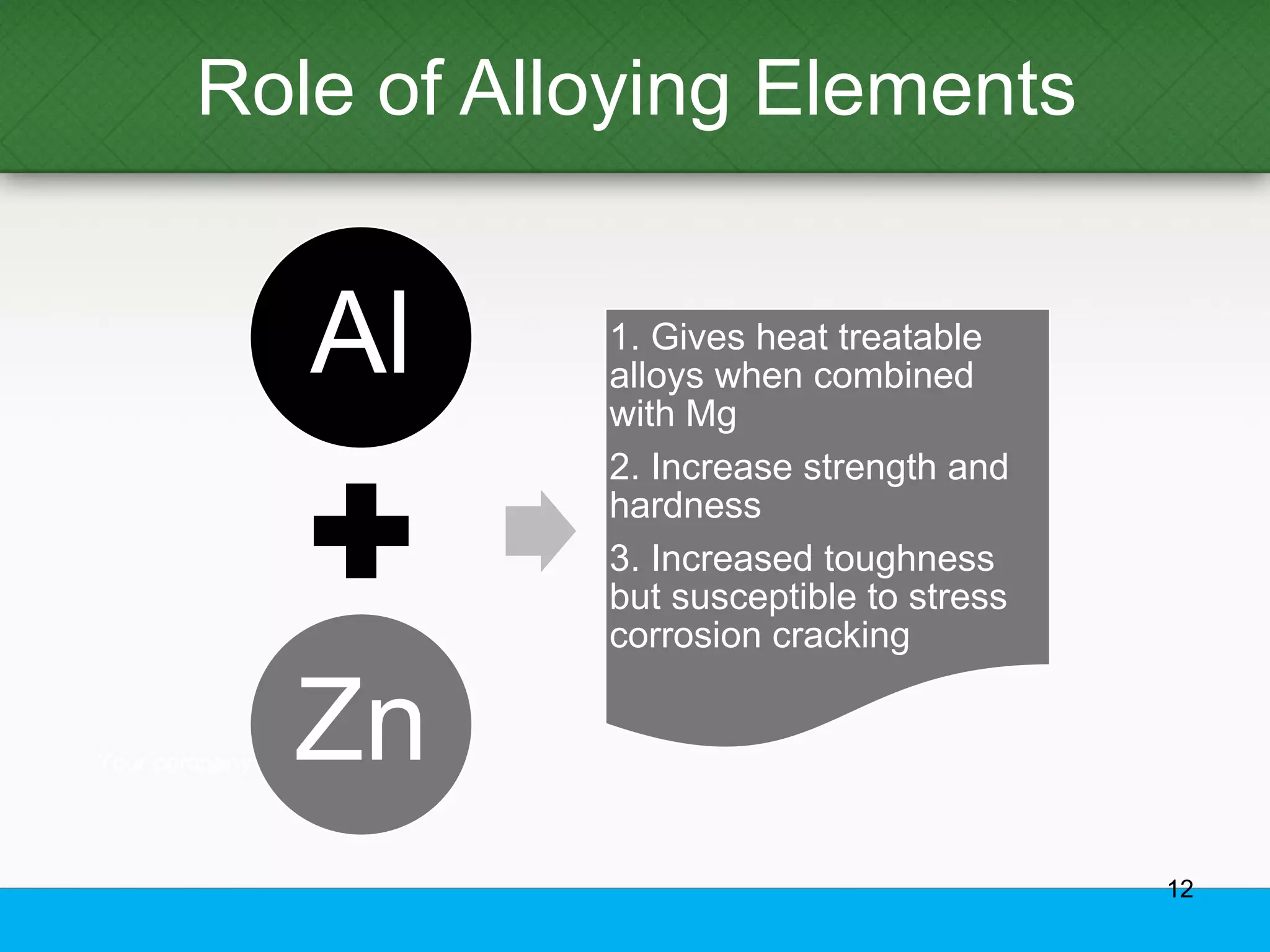
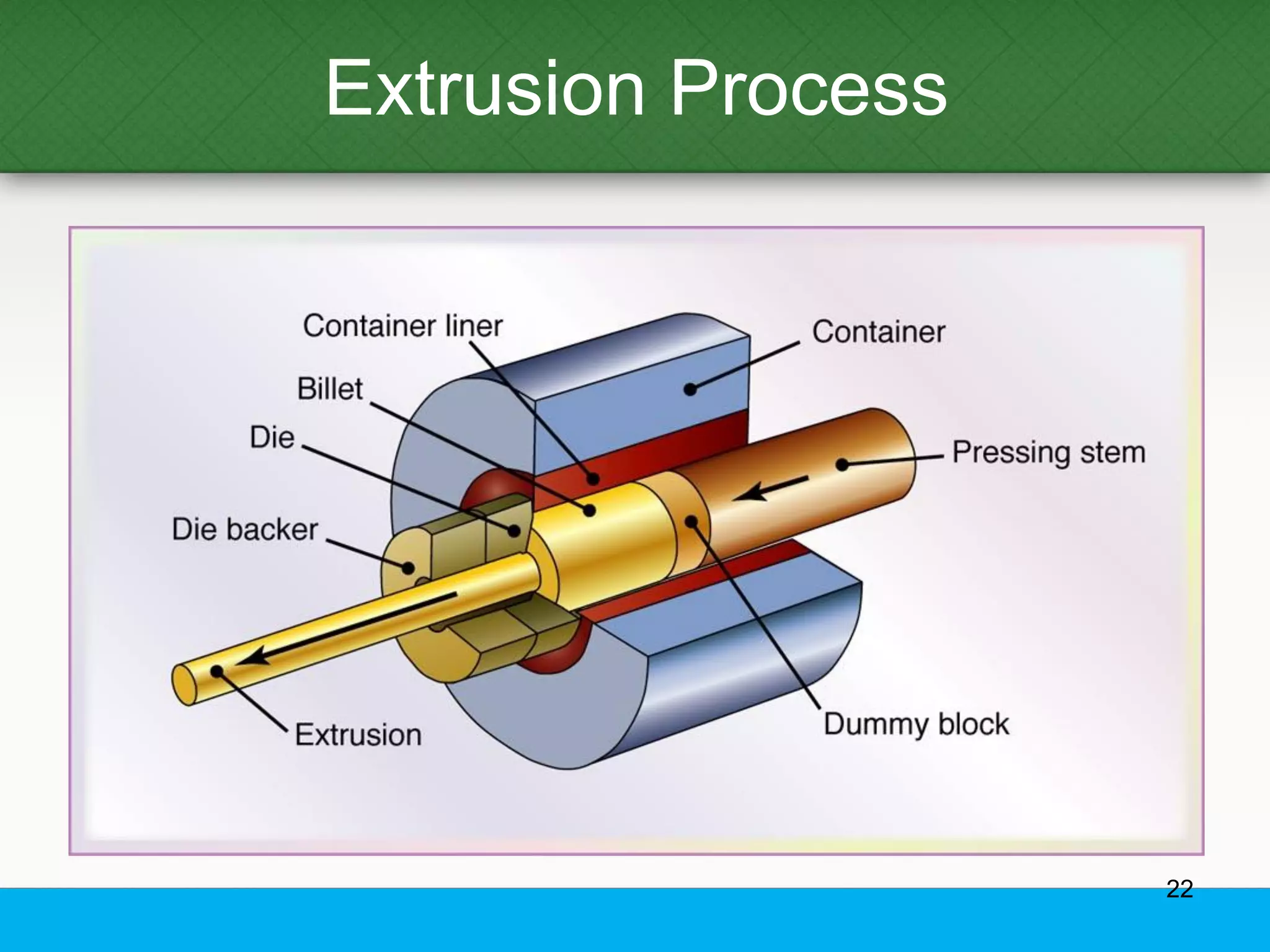
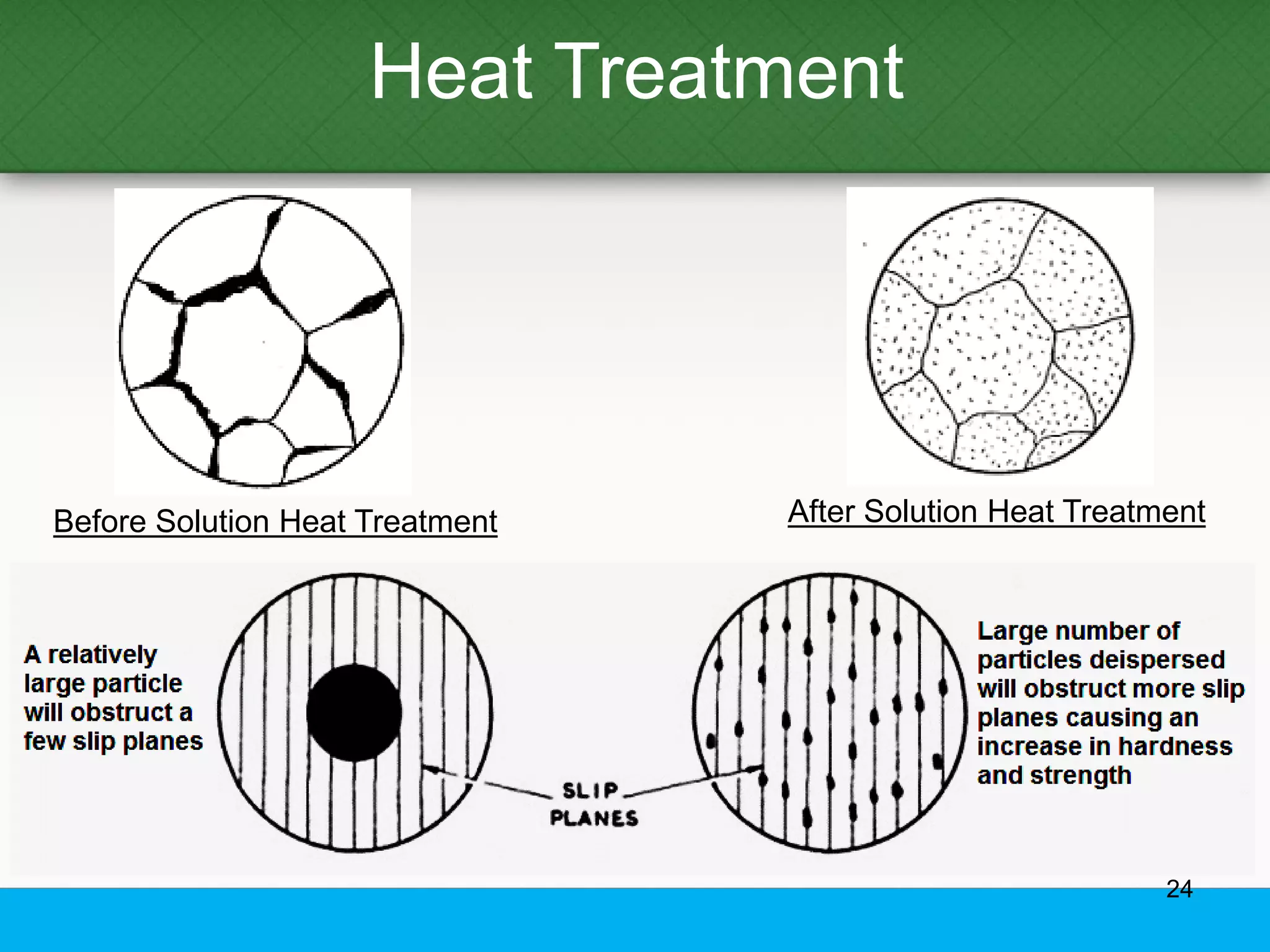
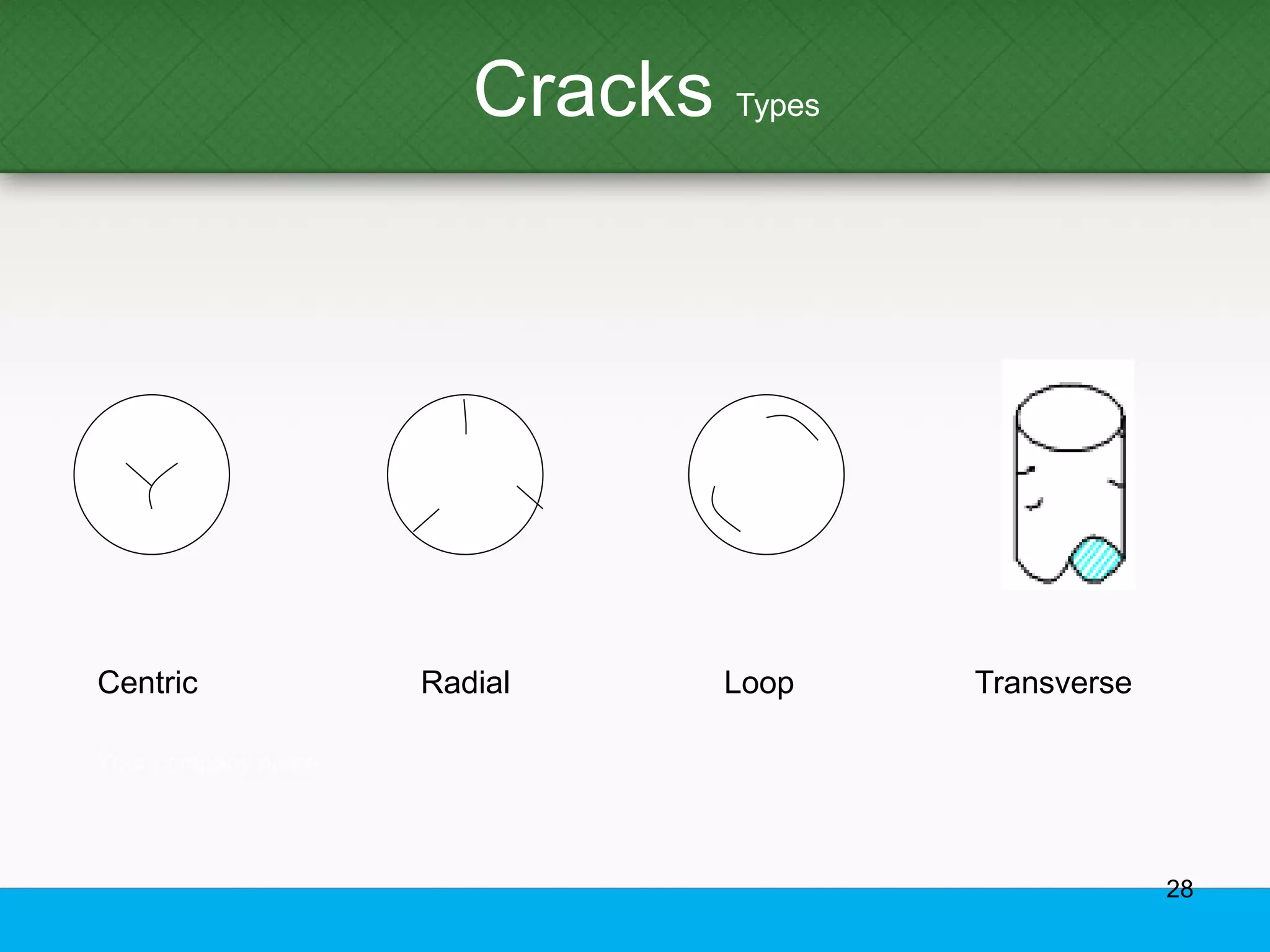
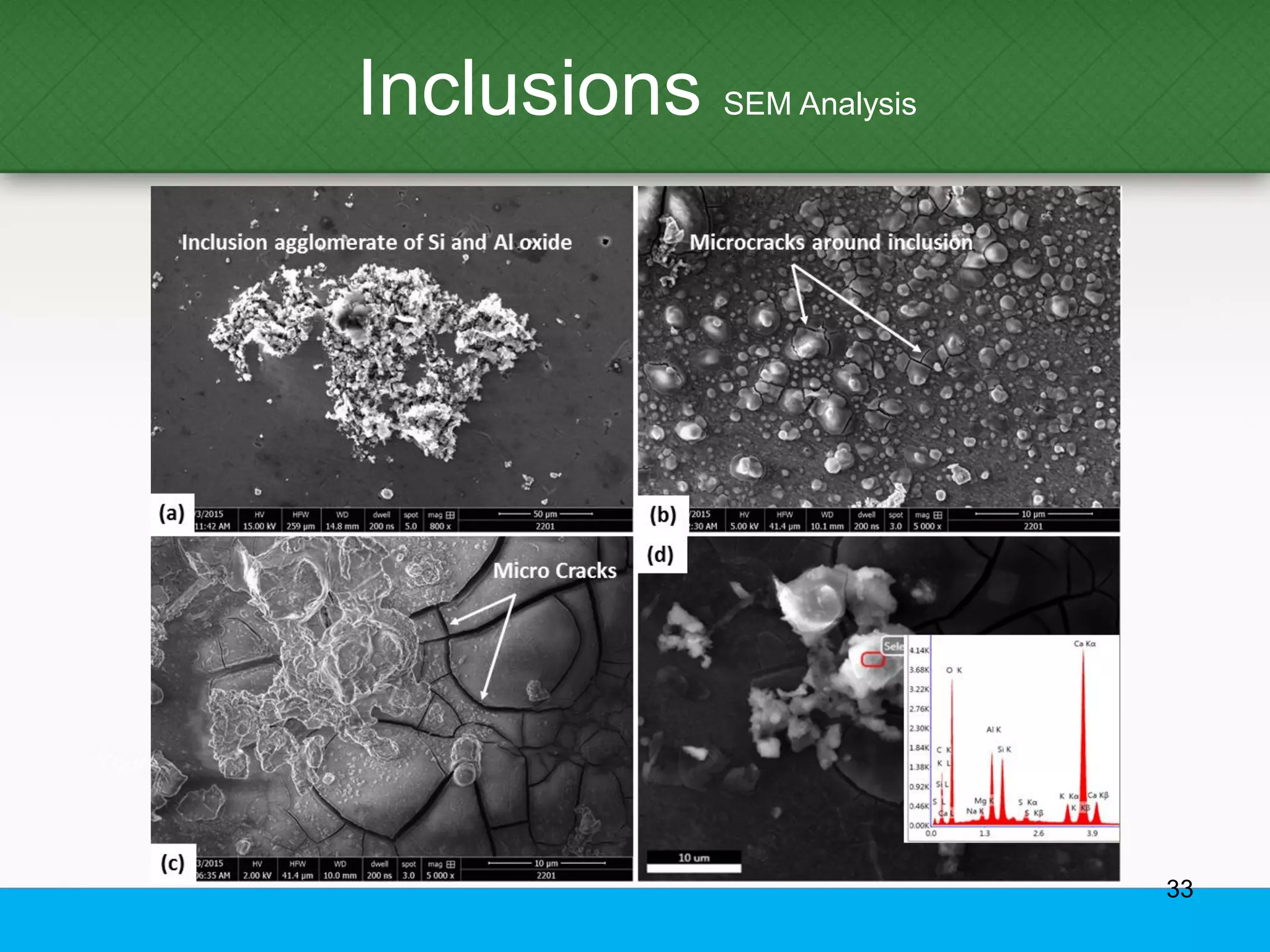
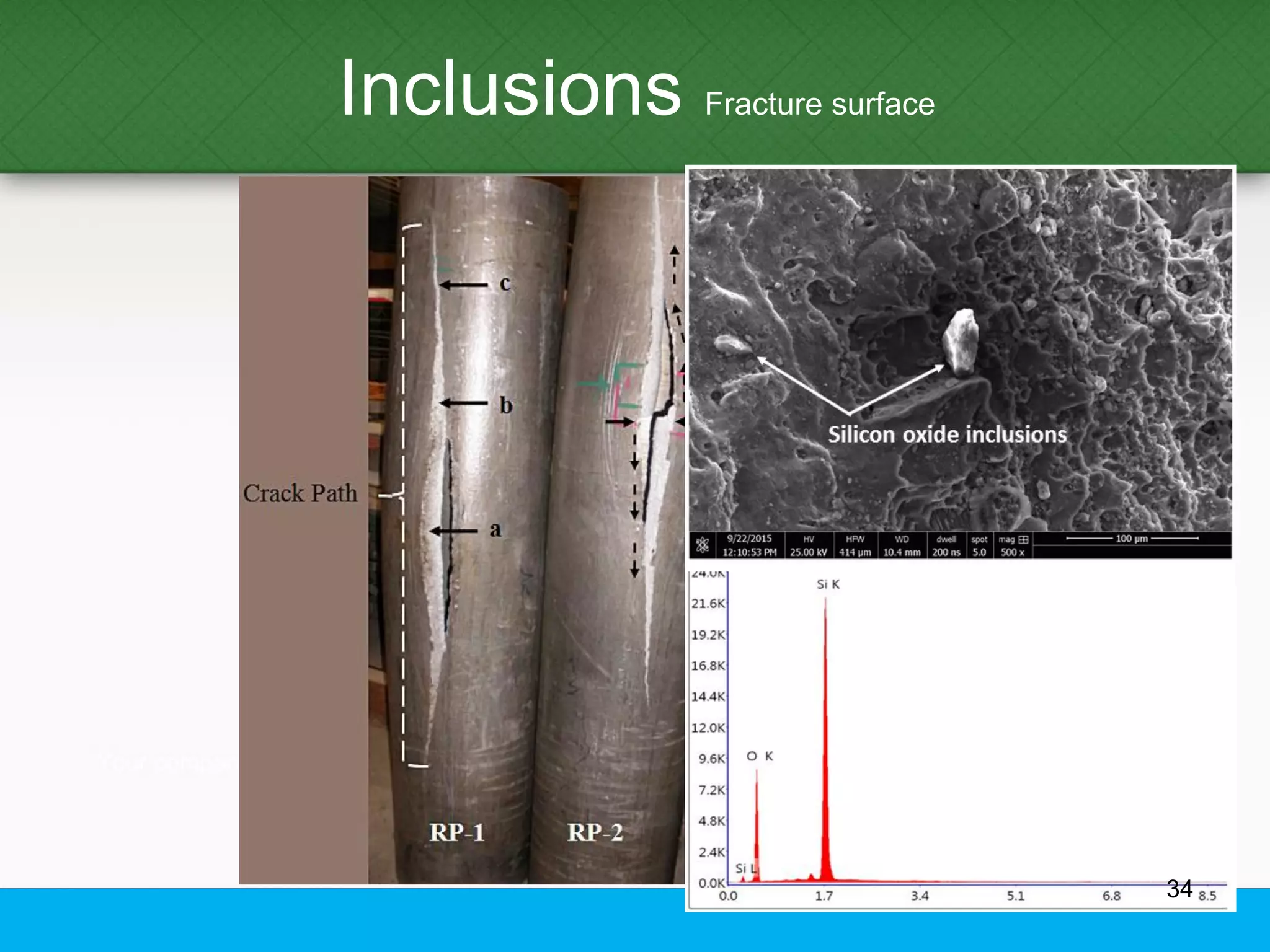
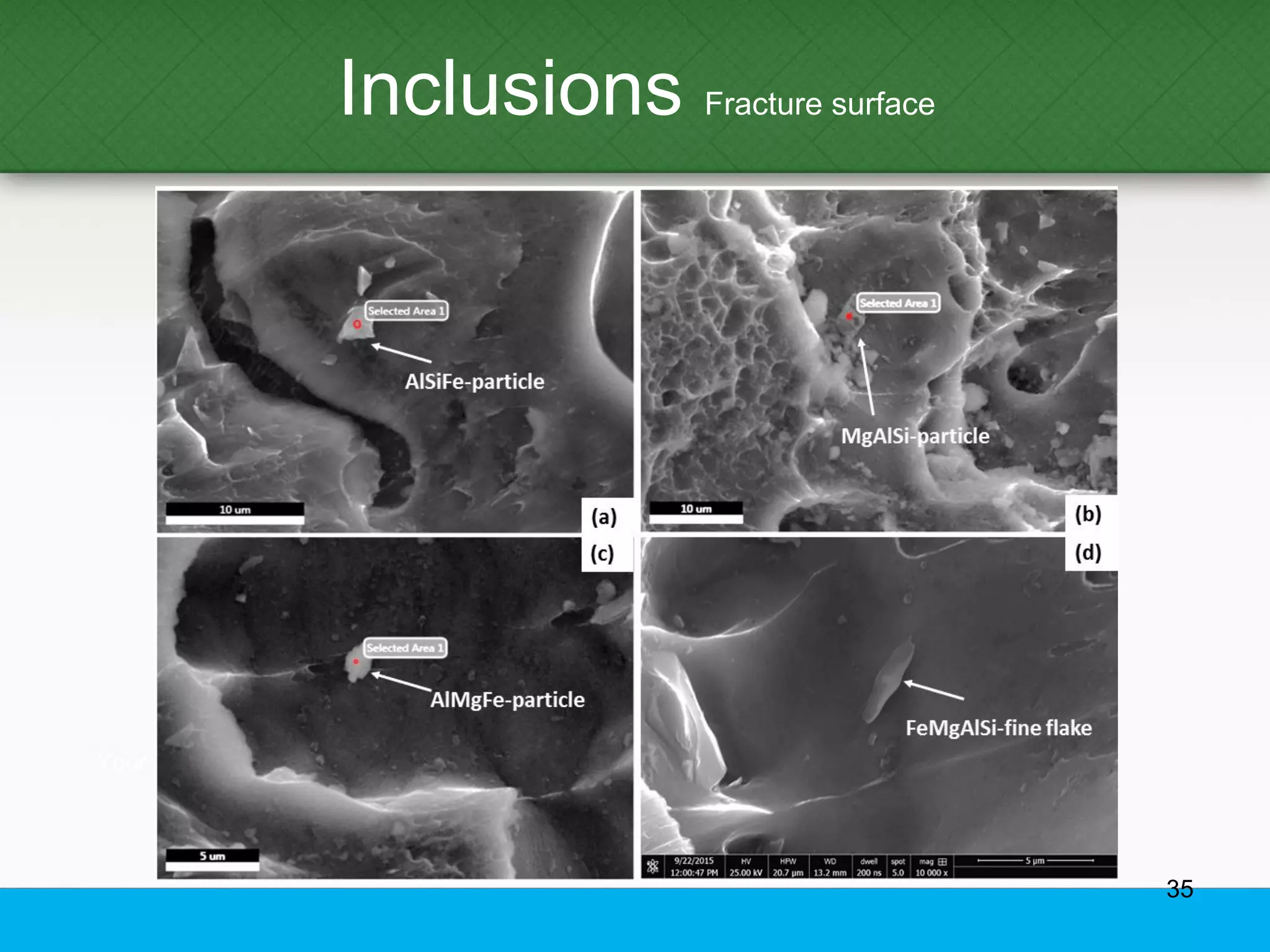
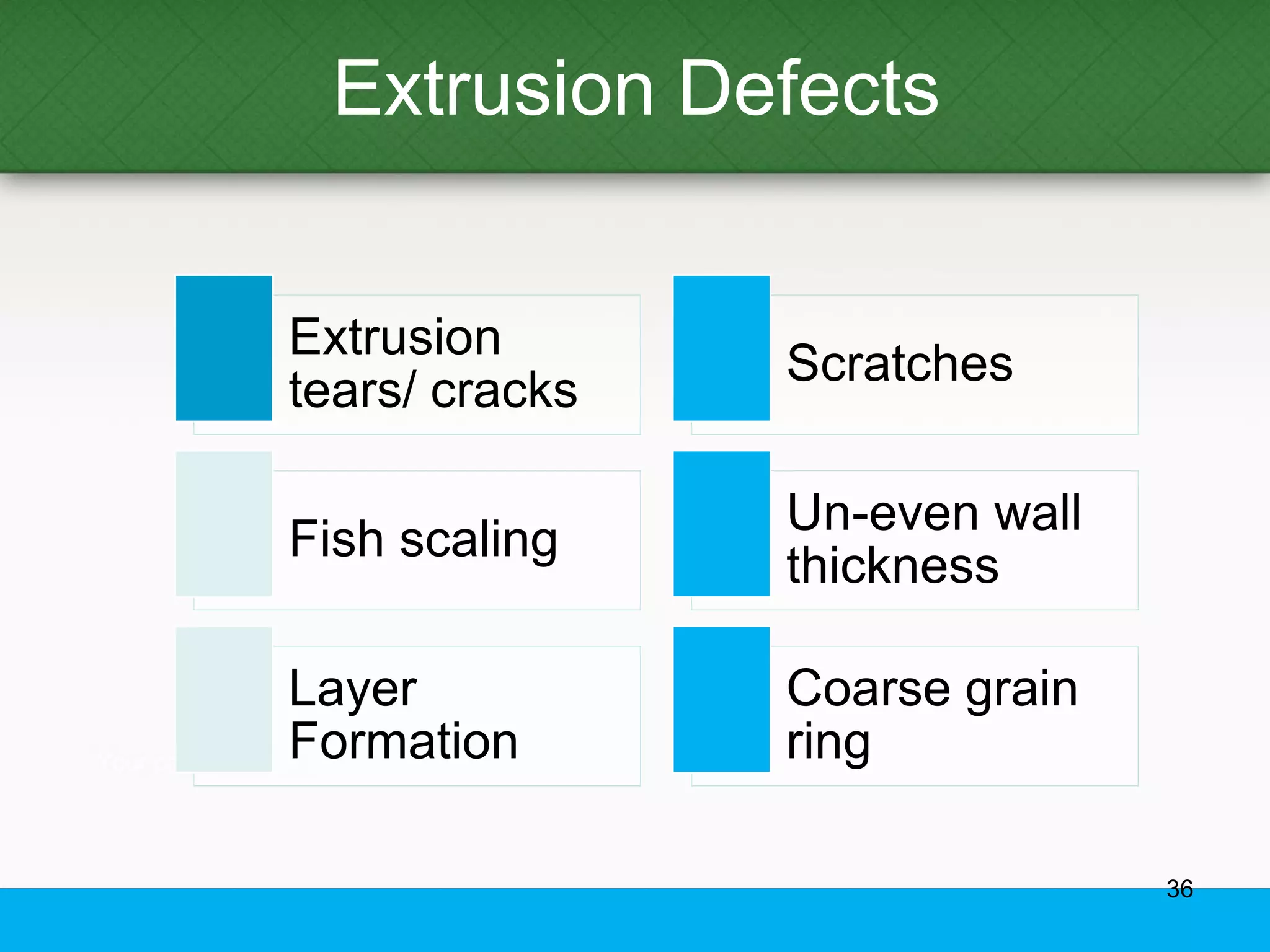
This document provides an overview of aluminum alloys, including their chemistry, classification system, applications, manufacturing processes, heat treatments, and common defects. It discusses the major alloying elements used in aluminum like copper, manganese, silicon, magnesium, and zinc. It also summarizes the various production methods for wrought aluminum alloys like extrusion and heat treating processes like annealing, solution heat treatment, and precipitation hardening. Finally, it outlines typical casting, extrusion, forging, and heat treatment defects seen in aluminum alloys.