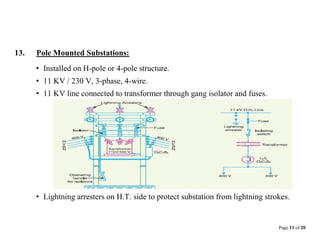
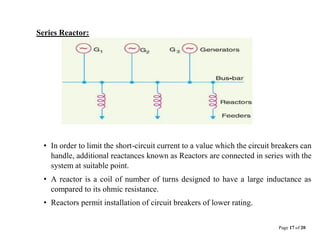
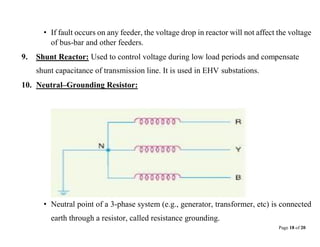
This document provides information about distribution substations, including their location, types, and key equipment. It discusses how substations are used to reduce transmission voltages and supply power to local distribution areas. The main types of substations covered are generating, primary grid, distribution, transformer, switching, power factor correction, frequency change, and converting substations. Key equipment found in substations includes power transformers, circuit breakers, buses, protective relays, and capacitors.