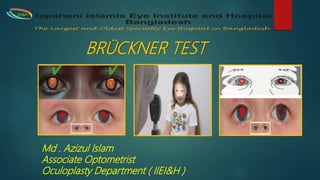
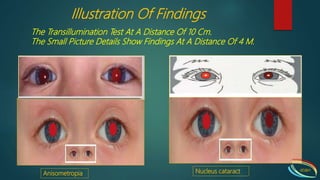
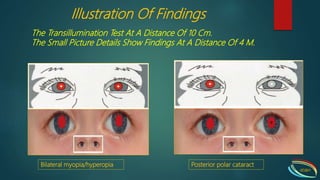
The Brückner test is used to diagnose amblyopia and strabismus in young children. It involves simultaneously illuminating both eyes from 1 meter away with a bright light source like a direct ophthalmoscope. The test evaluates the position and brightness of the corneal light reflex and fundus reflex in each pupil. A darker reflex in the fixing eye indicates strabismus. Conducting the test from both close and long distances can help detect refractive errors like anisometropia and myopia. Abnormal findings may include unequal pupil sizes, displaced light reflexes, or differences in pupil brightness between the eyes.