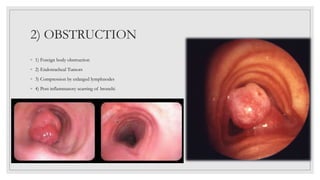
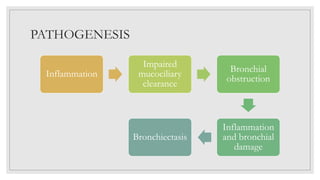
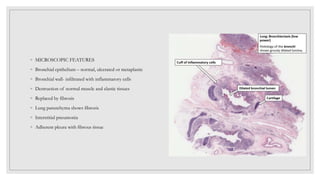
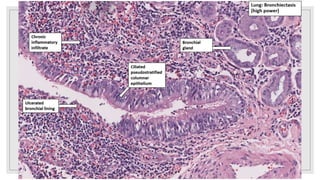
Bronchiectasis is characterized by abnormal and irreversible dilation of the bronchi due to inflammatory damage, caused primarily by endobronchial obstruction and infections. Contributing factors include hereditary conditions, tumors, airway obstruction, and complications from other respiratory disorders. Clinical features comprise a persistent productive cough, thick sputum, and airway obstruction, with treatment focusing on antimicrobial therapy, hygiene maintenance, and clearing secretions.