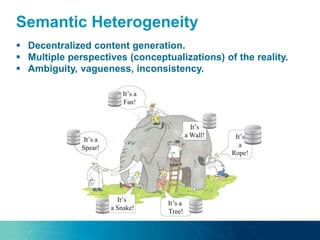
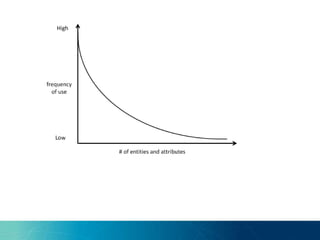
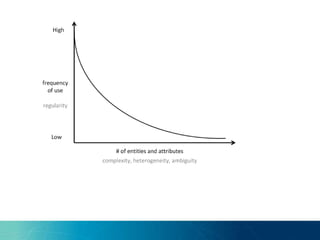
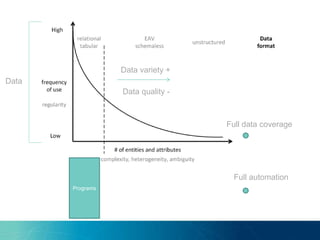
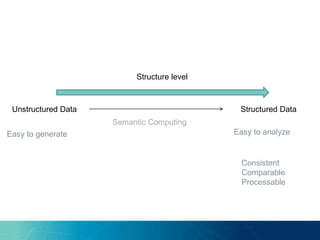
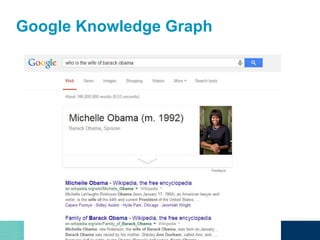
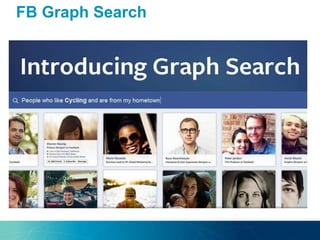
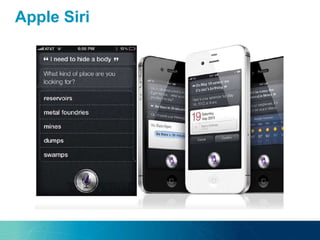
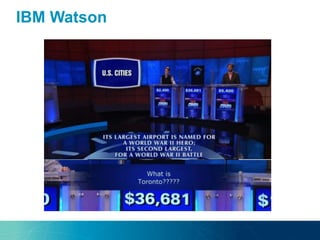
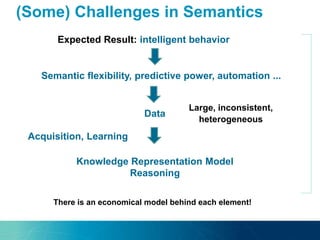
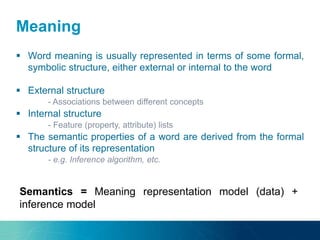
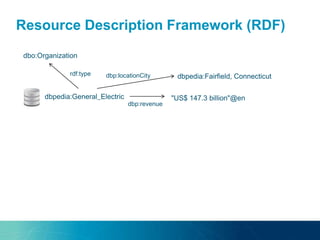
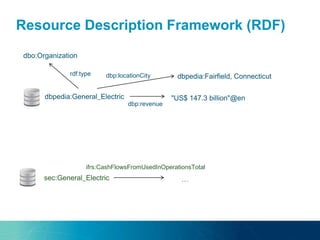
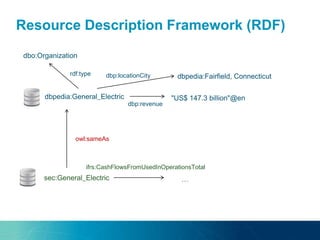
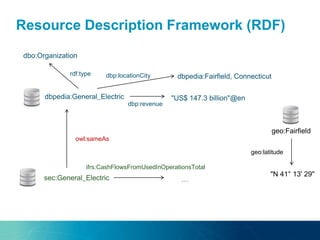
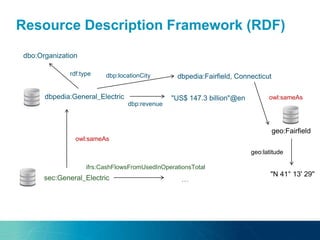
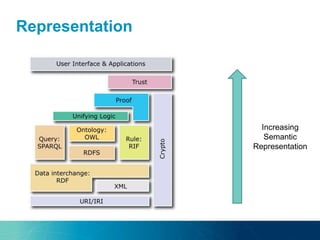
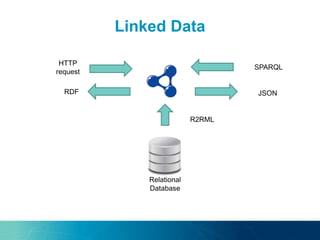
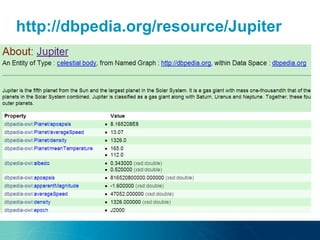
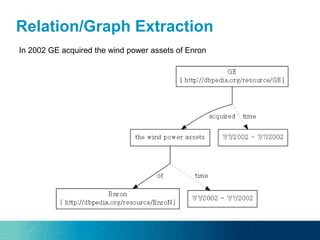
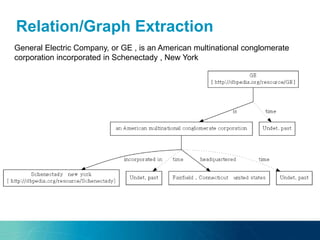
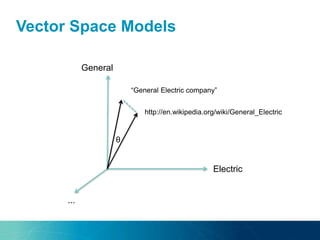
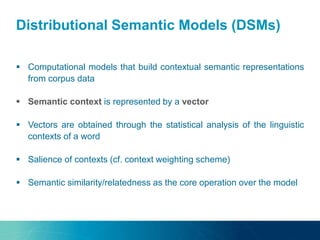
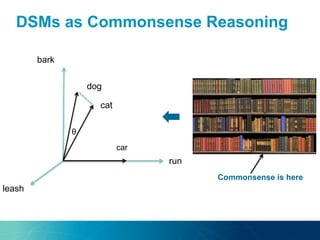
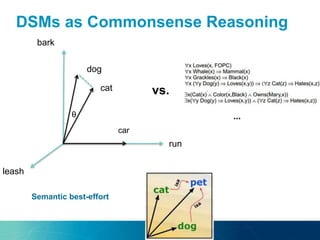
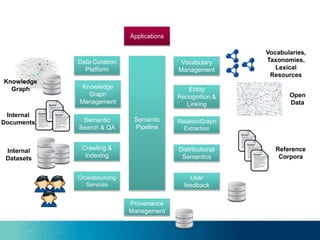
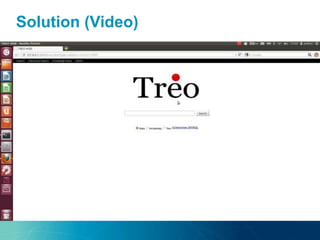
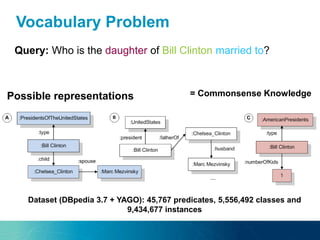
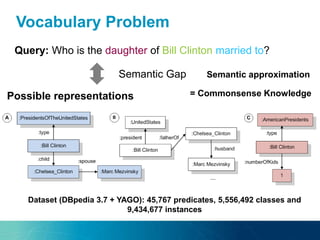
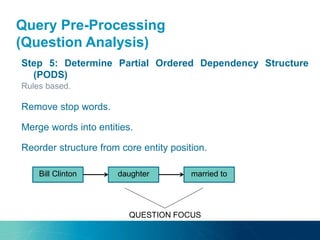
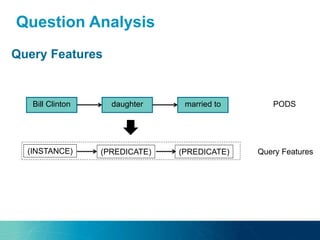
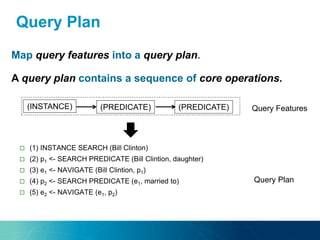
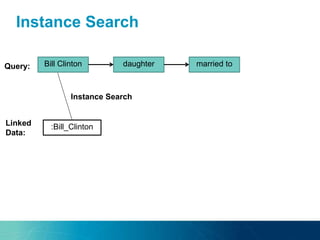
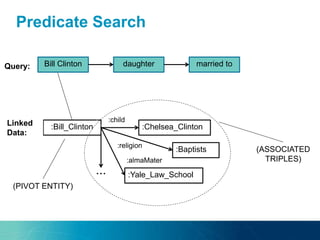
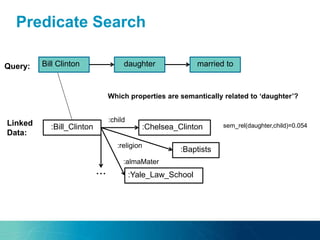
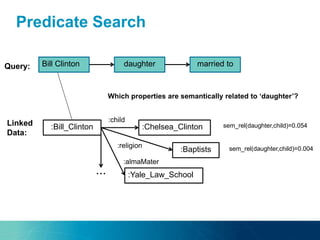
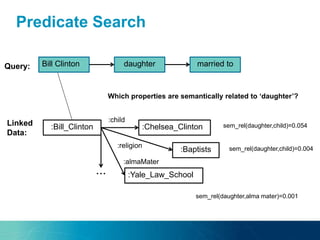
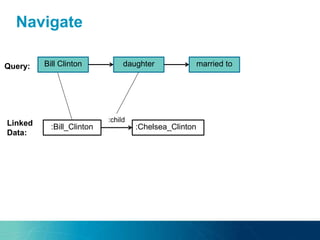
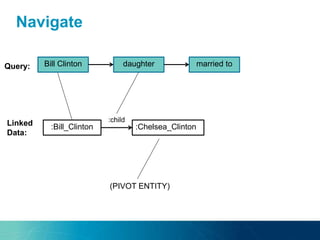
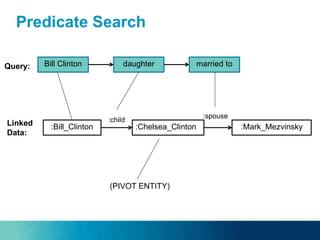
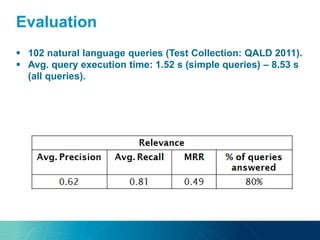
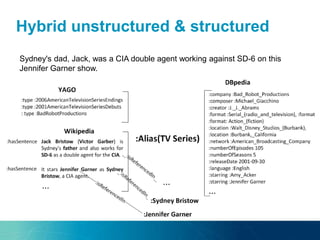
The document discusses the challenges and opportunities of managing data variety in the big data era through semantic computing. It highlights issues such as data quality, representation, and processing, along with current technologies that address these challenges. A case study on the Treo QA system illustrates the application of semantic technologies in querying knowledge graphs.