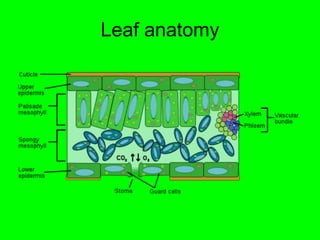
Leaves are specialized plant organs for photosynthesis. They consist of a petiole, lamina, epidermis, and mesophyll tissue. The epidermis is the outer layer that covers and protects the inner tissues. The mesophyll contains two types of tissues - palisade mesophyll with densely packed cells for photosynthesis, and spongy mesophyll with loosely packed cells that provide a surface for gas exchange. Transpiration is the process where water evaporates from the leaf surface and is an important part of photosynthesis, but the rate of transpiration is affected by environmental factors like light, temperature, humidity, and wind.