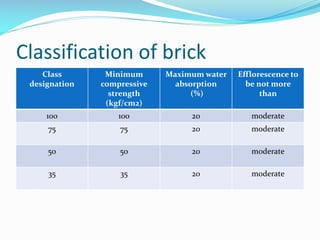
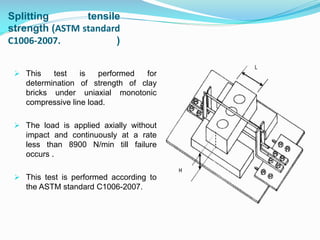
This document defines masonry and brick masonry. Masonry is made of small building units like clay, shale, concrete or stone that are set in mortar. Brick masonry consists of bricks laid together with mortar and is a popular building material. Bricks come in various sizes and strengths and are classified based on compressive strength and water absorption. Mortar is used to bind the bricks and is typically made of water, cement or lime, and sand. Various tests are performed on bricks and brick masonry assemblies to test properties like efflorescence, water absorption, compressive strength, and bond strength. Brick masonry provides benefits like low maintenance, fire resistance, insulation, and structural load