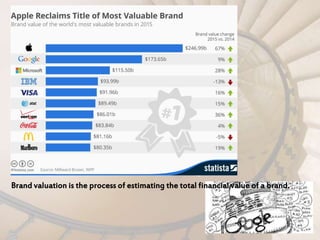
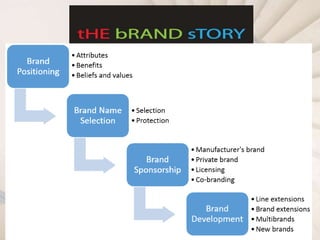
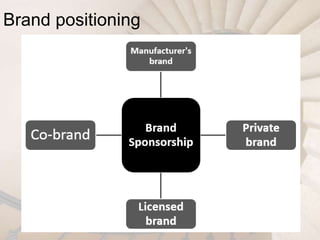
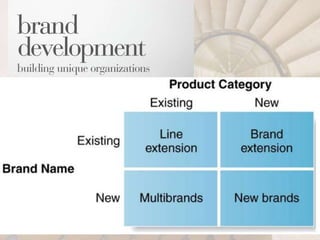
This document outlines key concepts to be learned about branding decisions for a marketing management project. It will cover defining what a brand and branding are, the major branding decisions including positioning, name selection, and development. Branding consists of strategic decisions to differentiate a brand, establish relevance with customers, build brand knowledge and esteem. Proper branding positions the brand in customers' minds based on attributes, benefits or beliefs, and develops brand equity through strong customer perceptions and loyalty over time.