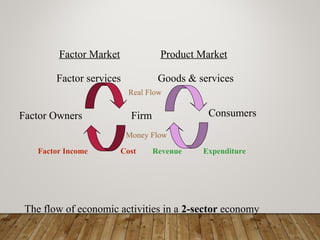
This document provides an overview of national income accounting. It defines key terms like gross national product (GNP), gross domestic product (GDP), real GNP, and per capita GNP. It also describes the three approaches to measuring national income: the income approach, output approach, and expenditure approach. Finally, it discusses the merits and limitations of using national income statistics to analyze and compare economic performance across countries.