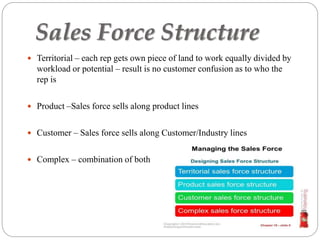
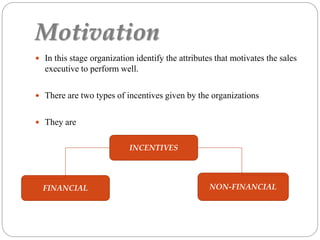
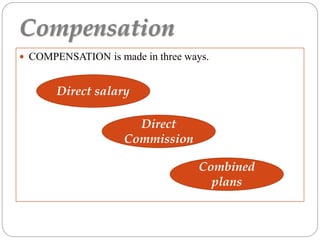
The document discusses sales force management. It covers several topics in 3 sentences or less each: introduction to sales and its reputation; types of sales organizations and sizes; objectives of a sales force like prospecting and selling; strategies for reps to work with customers; common structures like territorial and product based; determining size based on workload and call frequency; recruitment, selection, training, supervision, motivation, evaluation, and compensation of sales forces.