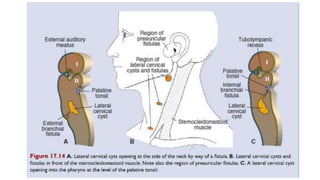
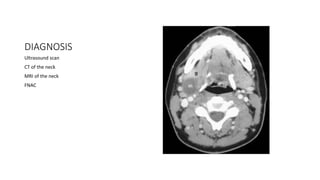
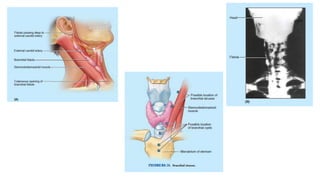
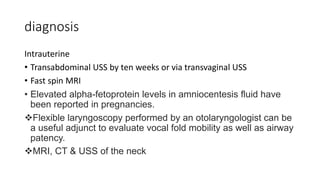
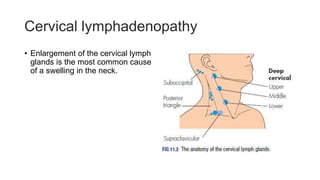
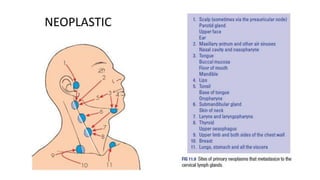
This document provides information on various neck masses including branchial cysts, branchial fistulas, cystic hygromas, carotid body tumors, and cervical lymphadenopathy. It describes the anatomy, etiology, clinical presentation, diagnosis and management of each condition. Branchial cysts are the most common congenital neck masses and usually present as soft, fluctuant swellings in the neck. Cystic hygromas are lymphangiomas that occur in the neck of newborns. Carotid body tumors develop in the carotid artery bifurcation and may cause cranial nerve palsies or Horner's syndrome. Surgical excision is the main treatment for branchial cysts, cystic hyg