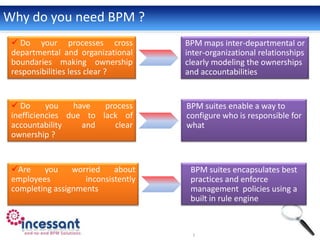
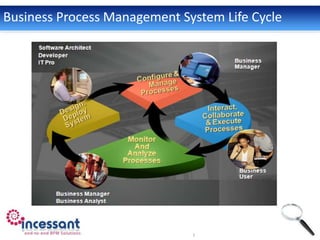
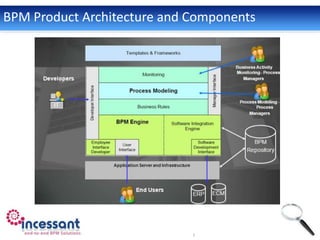
Business Process Management (BPM) involves modeling and automating cross-departmental business processes. BPM suites provide benefits like streamlined operations, improved efficiency, end-to-end visibility, compliance, agility, and accountability. The BPM lifecycle includes modeling, deployment, execution, monitoring, and optimization of processes. Key components of BPM suites include a process engine to execute models, a process modeler to design processes, a business rules engine, and business activity monitoring for oversight. BPM is applicable across industries like healthcare, travel, manufacturing, and more.