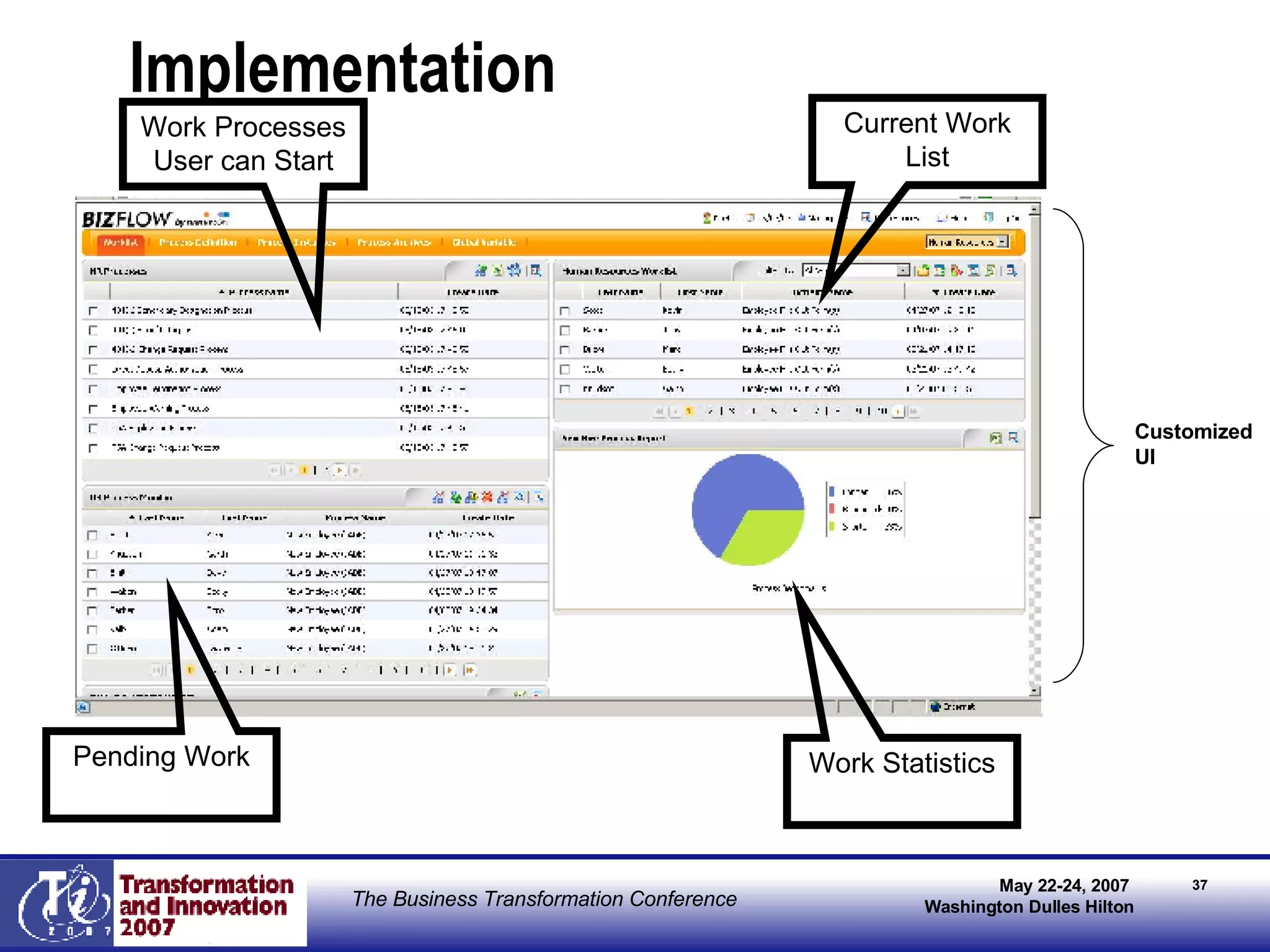
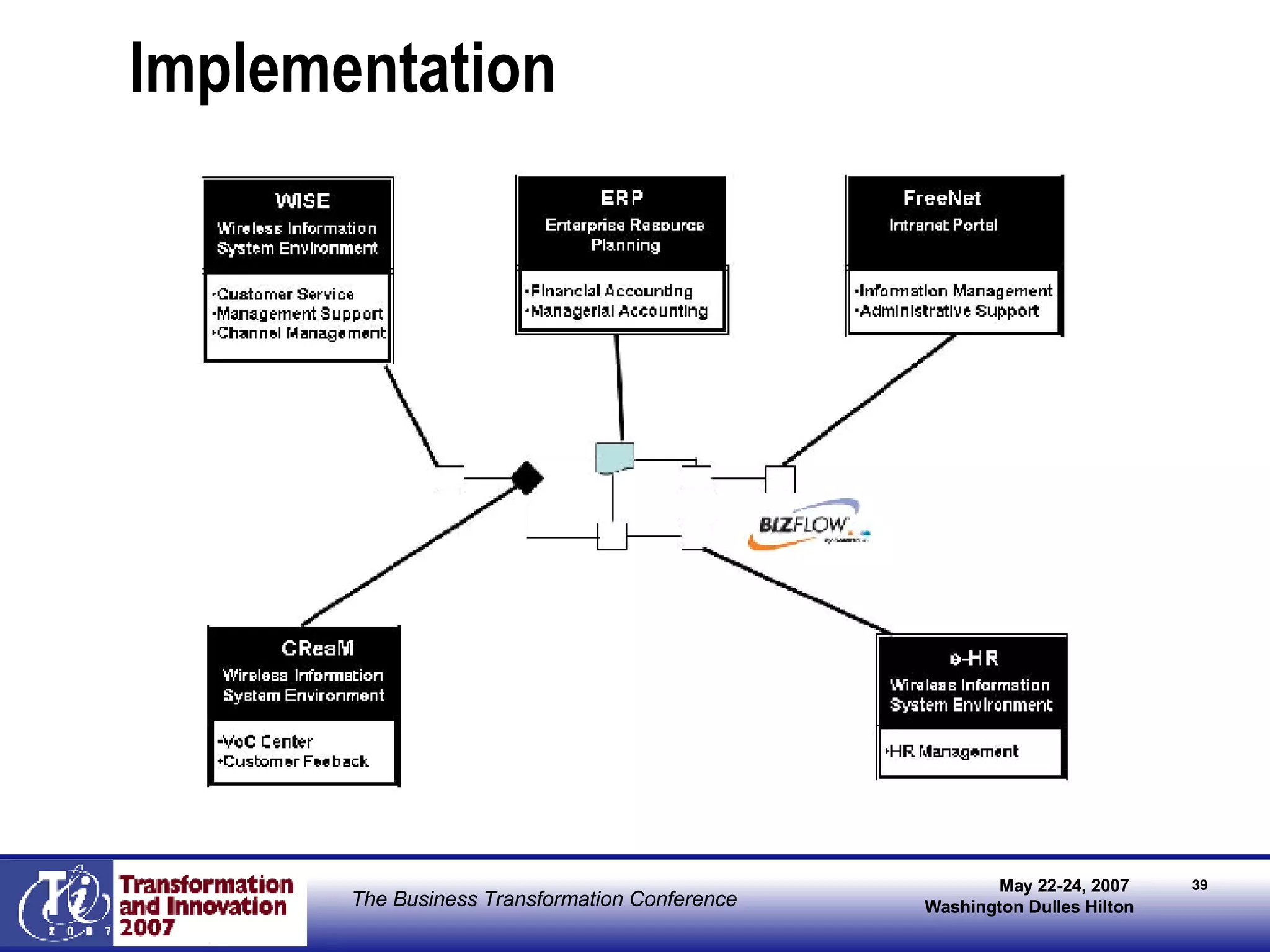
The document outlines Robert Cain's presentation on BPM (Business Process Management) innovation in telecommunications, focusing on KTF's strategy to improve customer care and operational efficiency through BPM systems. It details the goals, barriers, and key strategies for implementing BPM, including process standardization, automation, and enhancing collaboration among teams. The expected outcomes include reduced cycle times, improved customer service, and sustained innovation in the organization.







































![Thank Y Robert Cain Director of Product Management HandySoft Global Corporation Contact Information: 703-442-5600 [email_address] ou Thank Y ou](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/the-fundamentals-of-bpm-innovation-in-telecommunications3861/75/The-Fundamentals-Of-BPM-Innovation-In-Telecommunications-58-2048.jpg)