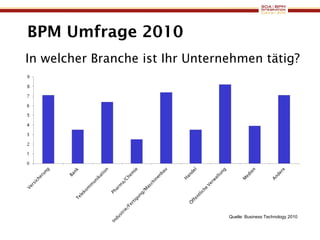
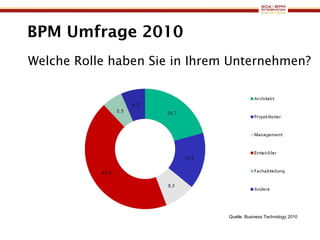
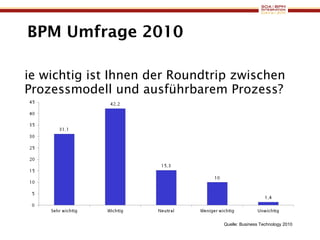
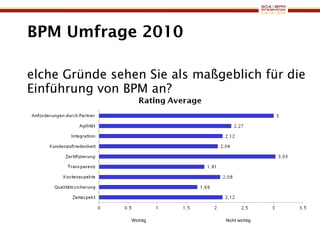
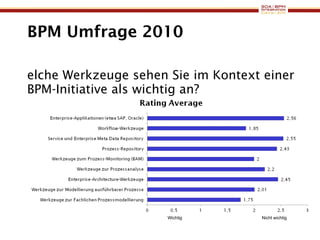
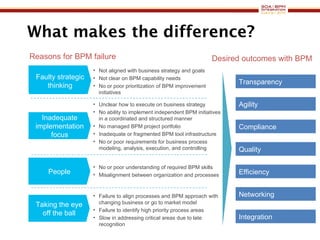
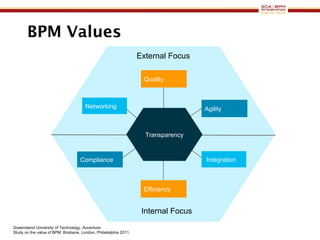
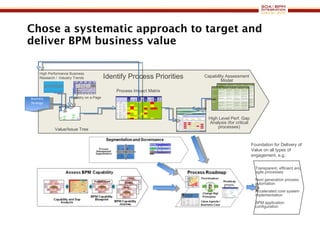
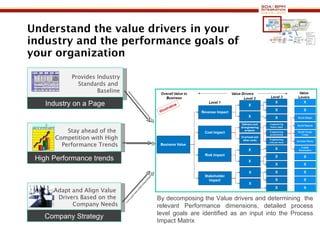
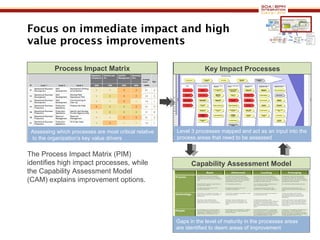
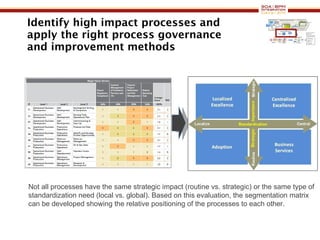
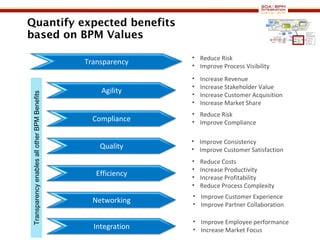
The document discusses business process management (BPM) business value and case studies. It introduces Dr. Matthias Ziegler from Accenture and Jürgen Kress from Oracle who will discuss identifying and delivering high value through BPM. Example case studies include using BPM at a retail company to reduce product returns and at a justice ministry to track citizen request lead times.