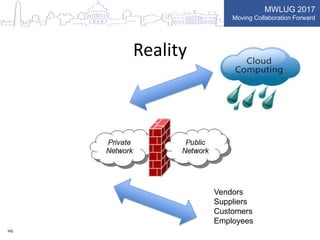
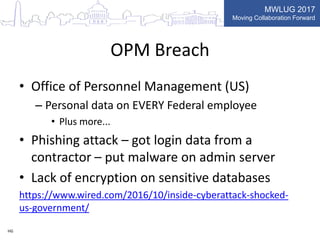
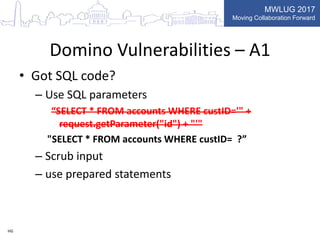
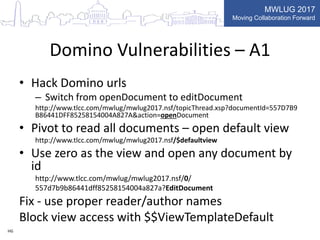
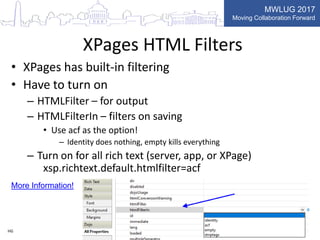
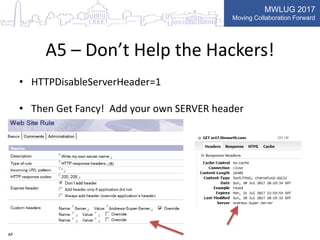
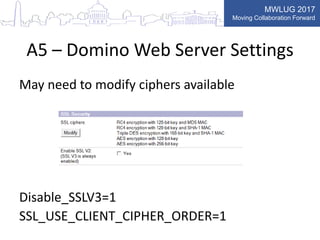
This document summarizes key points from a presentation on application security best practices. It discusses the top 10 security risks according to OWASP, relating each risk to potential vulnerabilities in Domino applications. For injection attacks, it notes risks from SQL injection and URL hacking. For authentication, it warns about weak password storage and session fixation. It provides tips for preventing cross-site scripting, sensitive data exposure, and cross-site request forgery. Overall, the presentation stresses the importance of input validation, access control, secure configuration, and keeping software up to date.