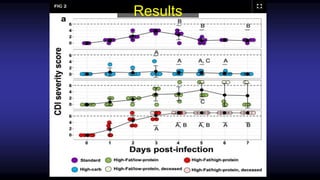
A study found that a high-fat, high-protein "Atkins-type" diet worsened Clostridium difficile infection (CDI) in mice, while a high-carbohydrate diet protected against CDI. Mice fed the Atkins-type diet had the worst CDI outcomes and 100% mortality rate, while those on a high-carbohydrate diet were protected from CDI despite antibiotic treatment. The study suggests popular high-fat, high-protein weight loss diets may increase CDI risk by reducing protective gut bacteria and increasing amino acids that promote C. difficile growth.