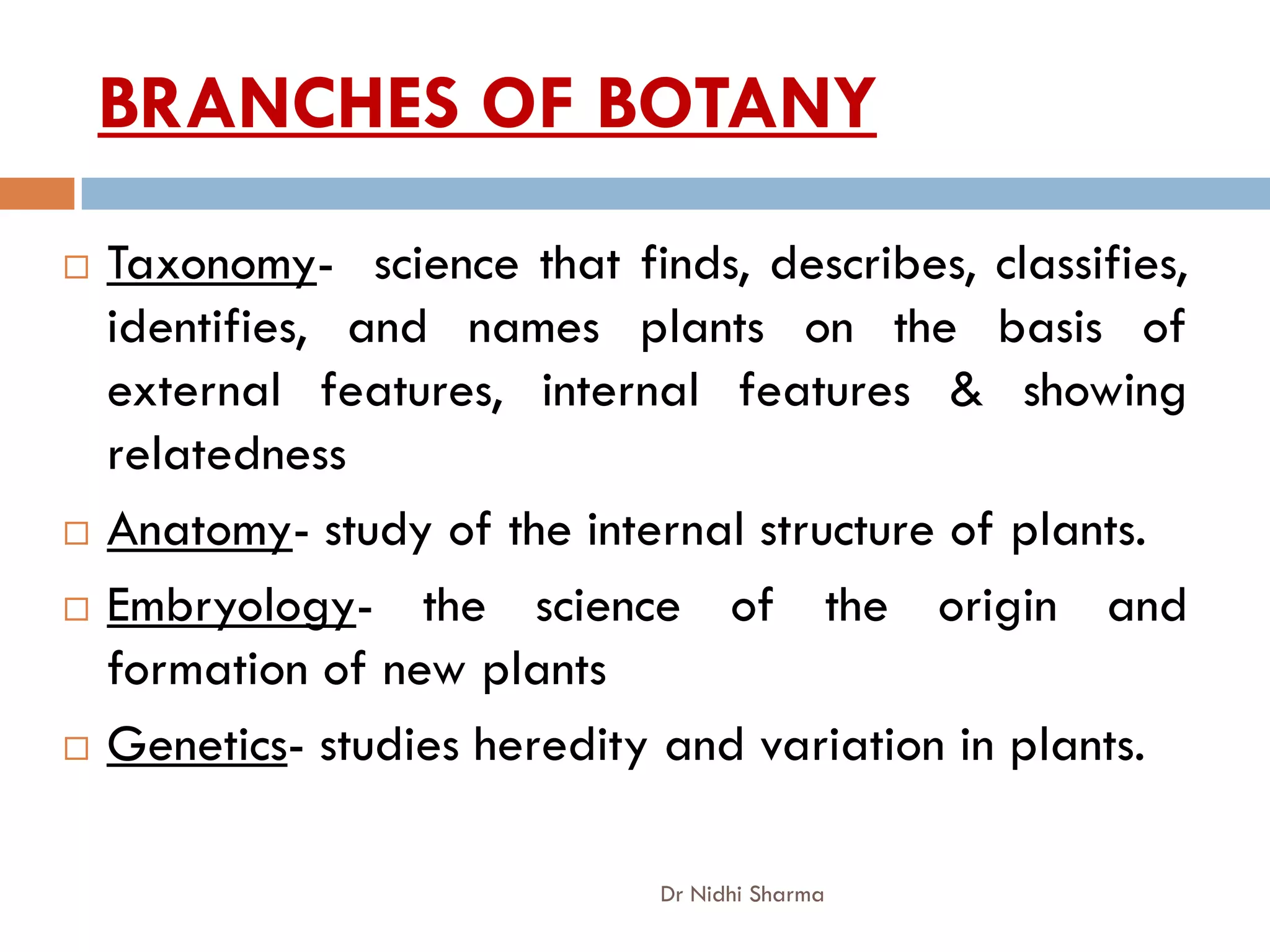
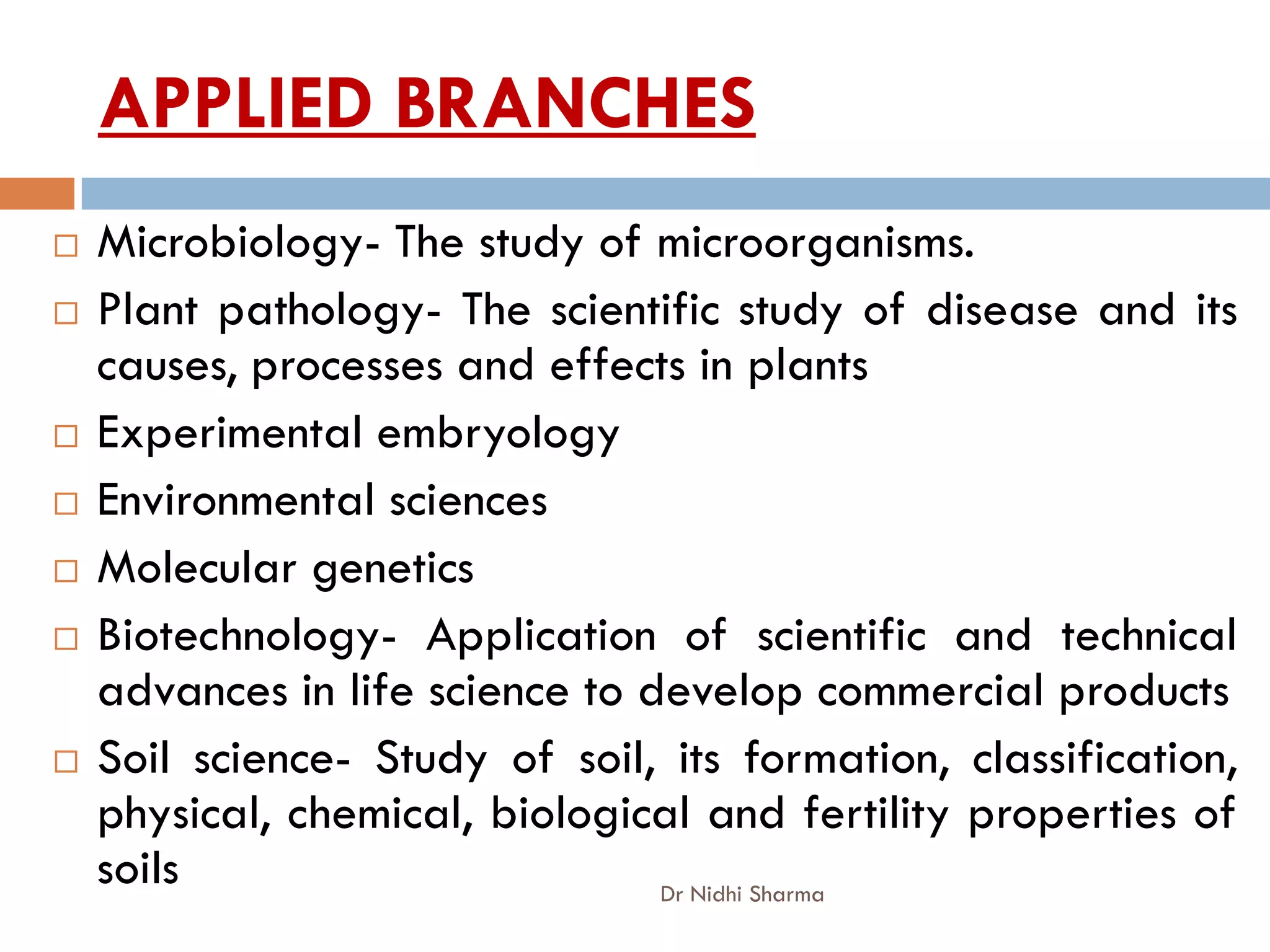
Botany is the study of plants. It includes the study of bacteria, viruses, fungi, algae, bryophytes, pteridophytes, gymnosperms and angiosperms. Some key points covered in the document include:
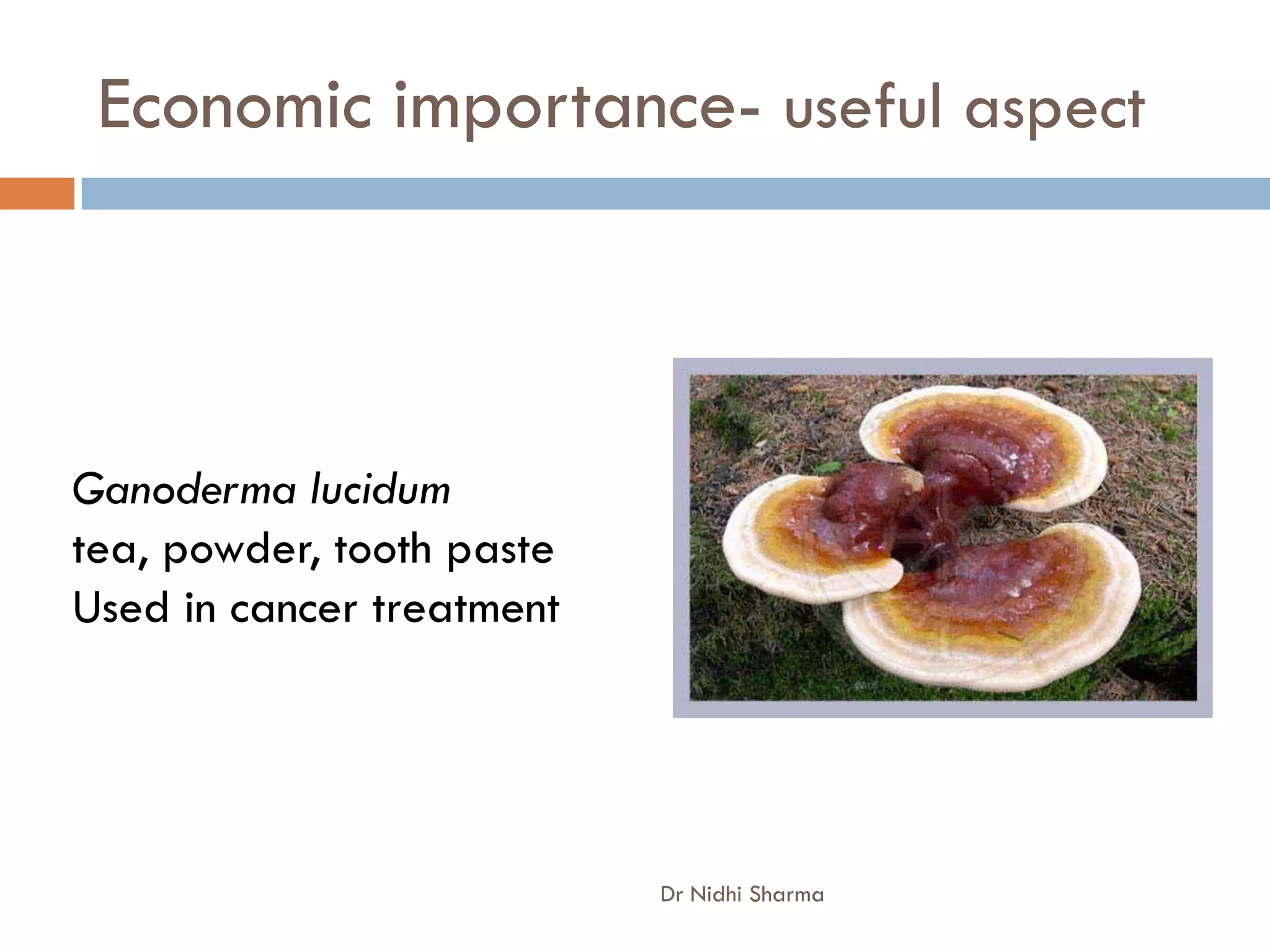
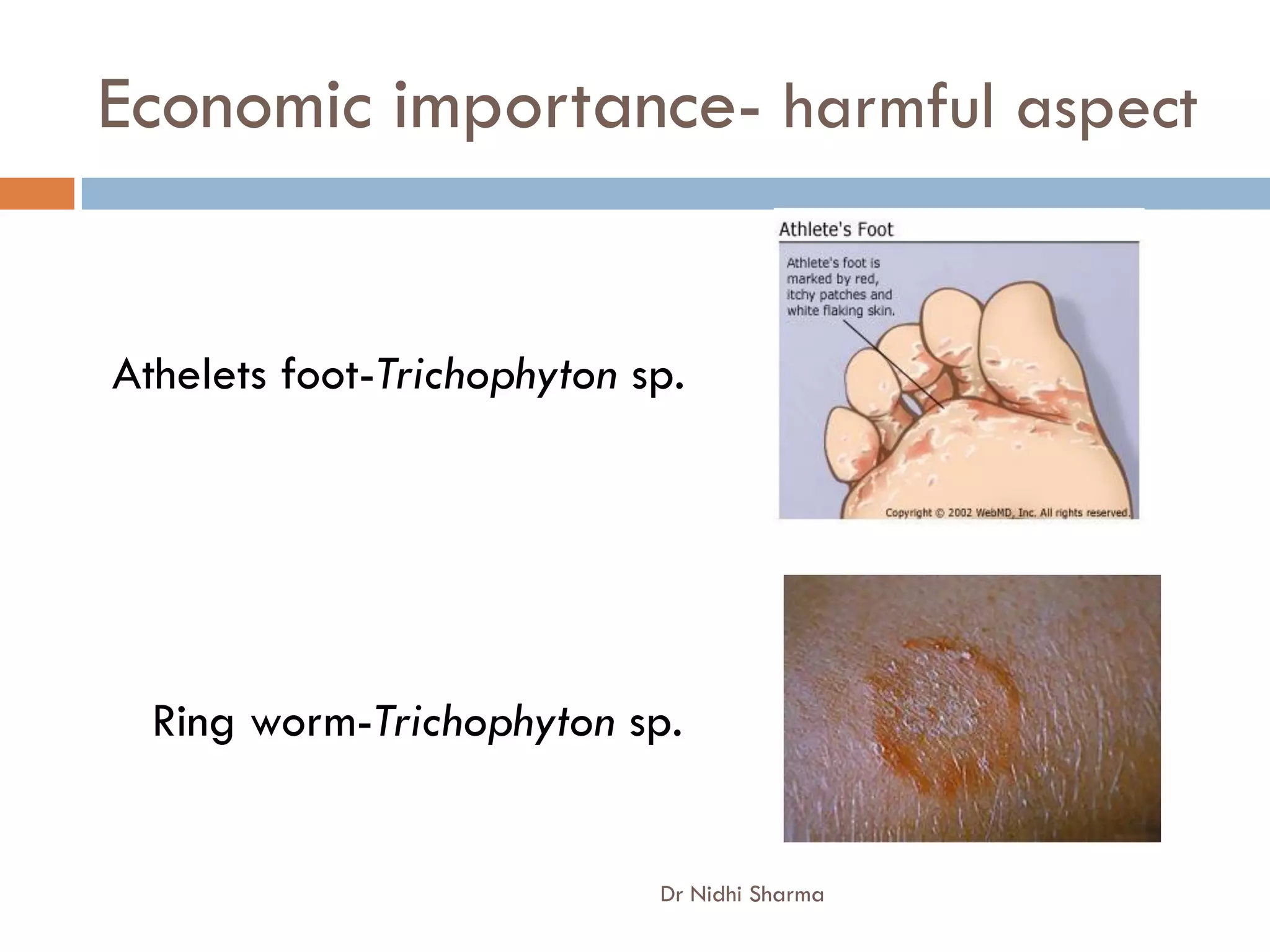
- Bacteria and fungi have economic importance as both harmful and useful organisms. They are involved in food production and cause diseases.
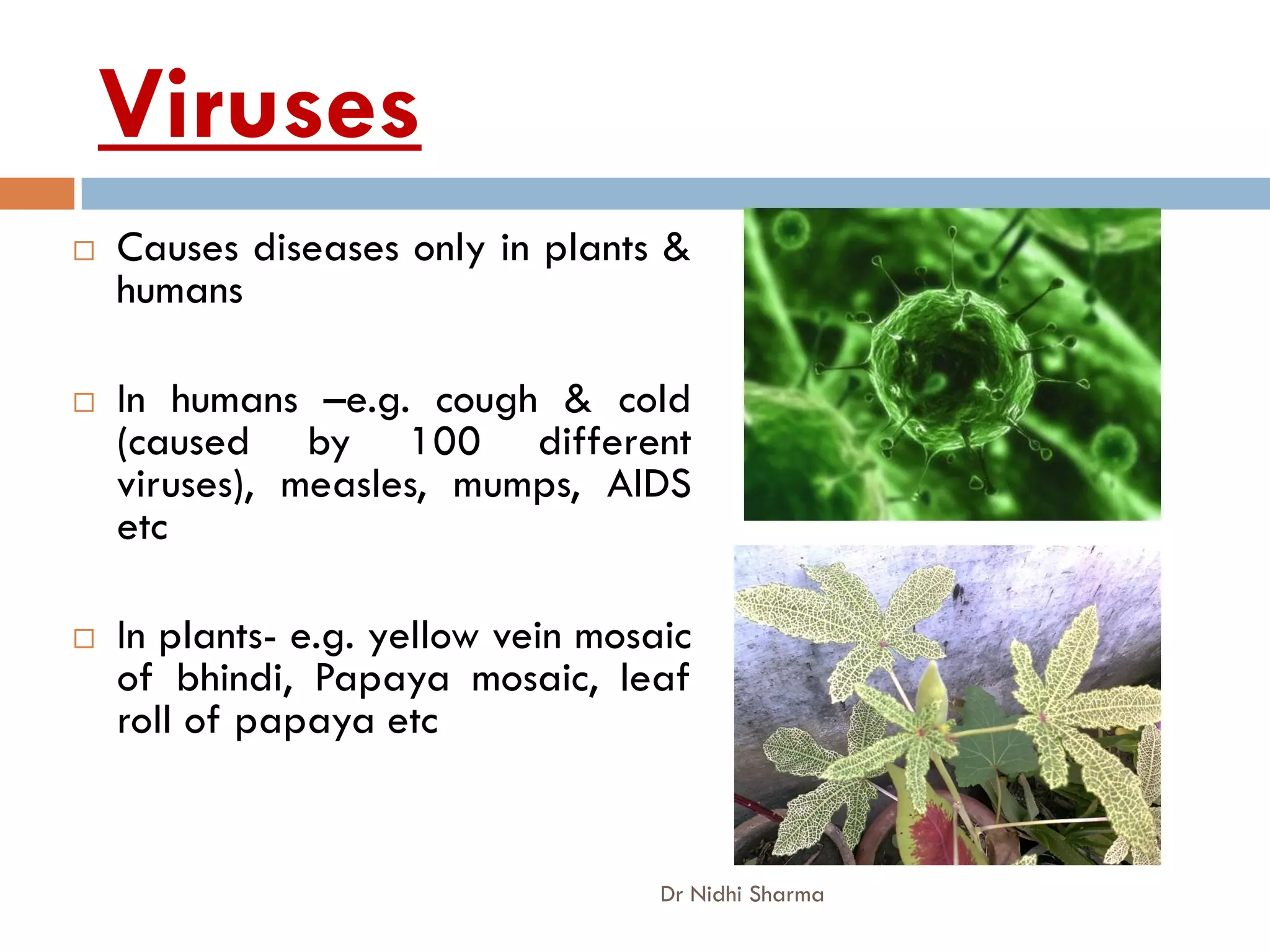
- Viruses only infect plants and humans, causing diseases. Fungi grow on decaying organic matter and have edible and poisonous forms.
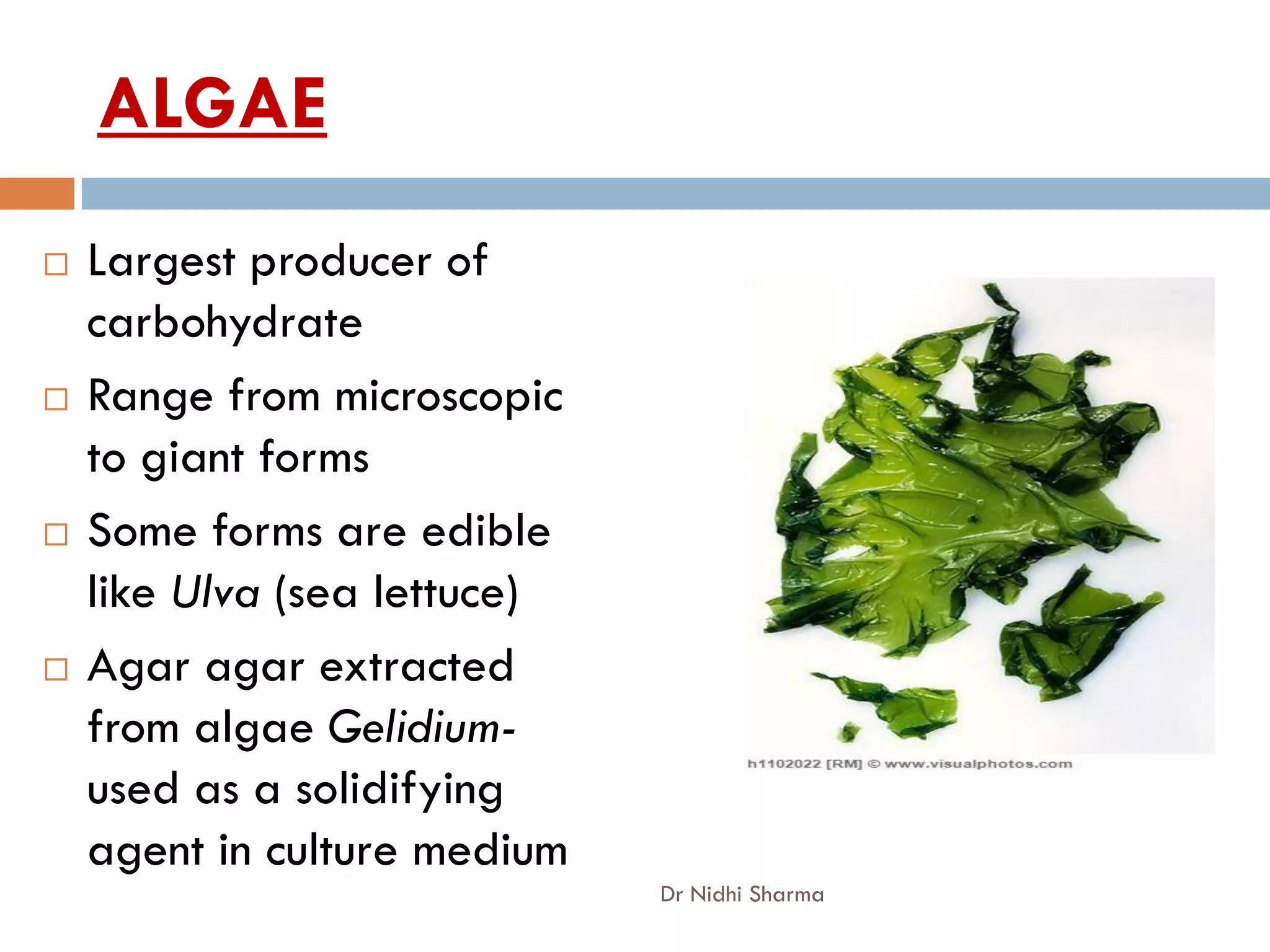
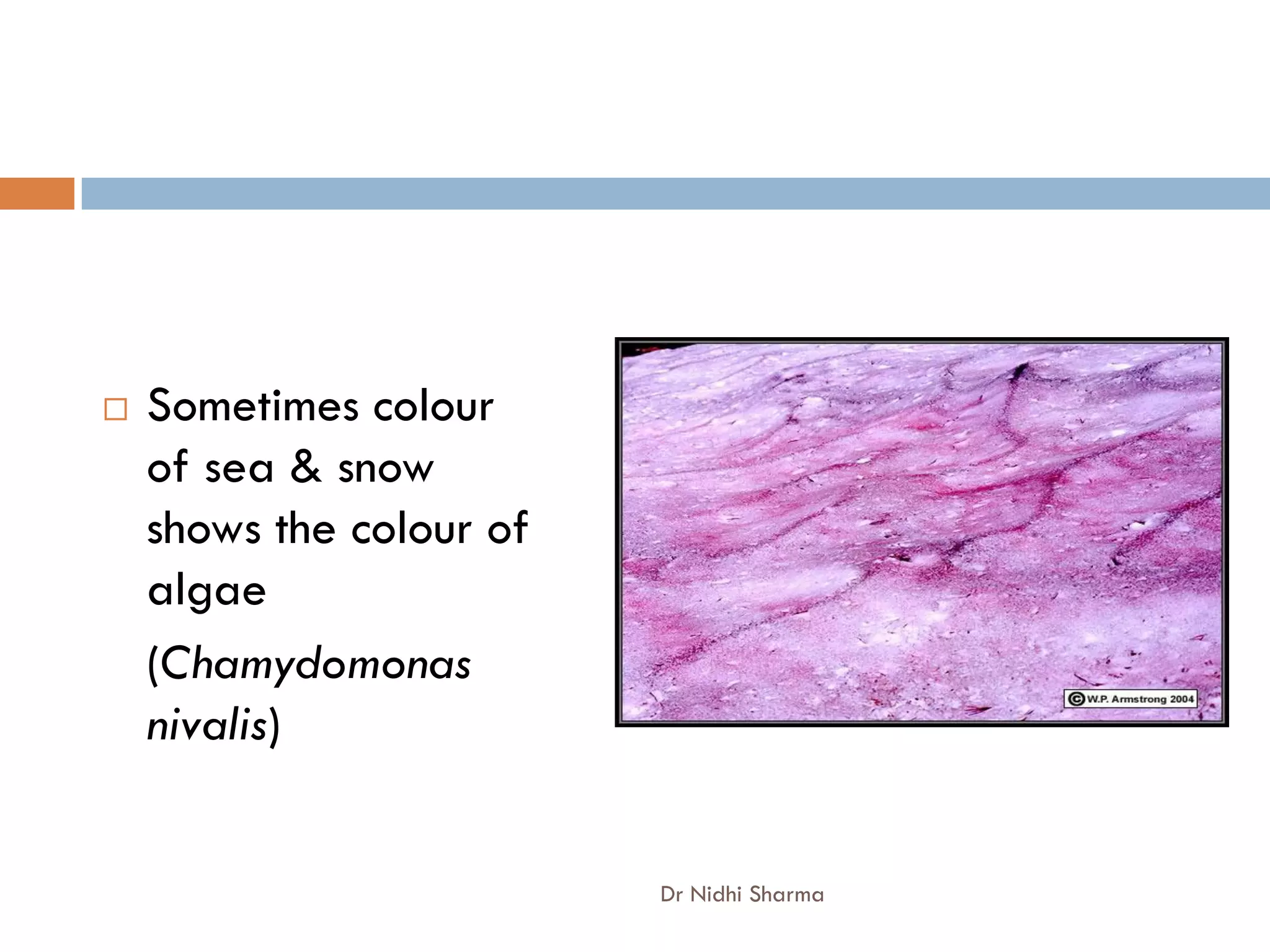
- Algae are important producers and are used as food and in industry. Bryophytes and pteridophytes include mosses and ferns