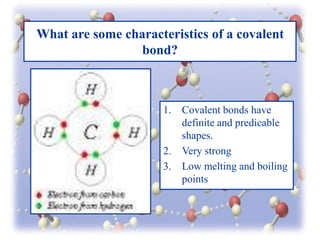
This document provides an overview of different types of bonds between atoms including ionic bonds, covalent bonds, and metallic bonds. It discusses the characteristics of each type of bond such as ionic bonds being crystalline, having high melting points, and being able to conduct electricity when molten. Covalent bonds are described as having definite shapes and being very strong. Molecular substances, network solids, polar vs. nonpolar covalent bonds, and coordinate covalent bonds are also summarized. Polyatomic ions and the geometric arrangements of electron pairs in molecules are defined. The document concludes with a review of the material presented.