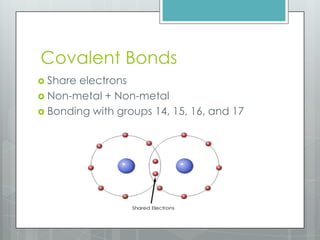
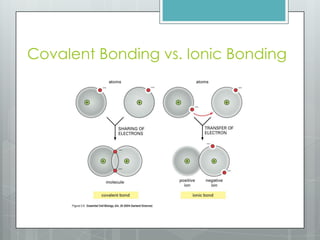
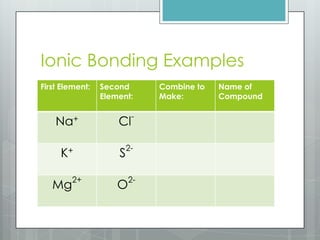
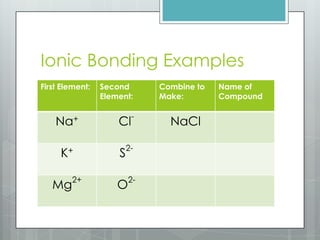
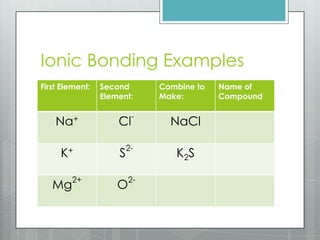
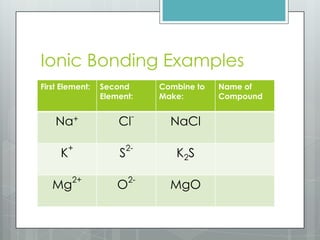
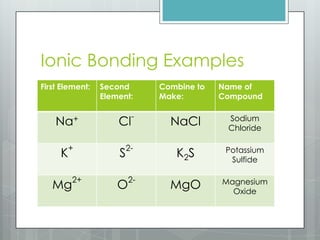
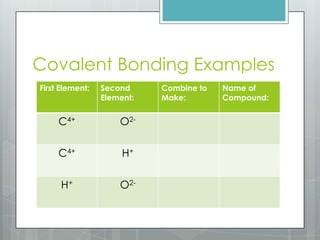
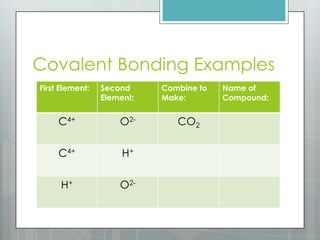
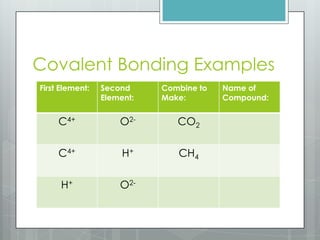
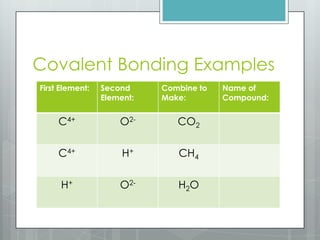
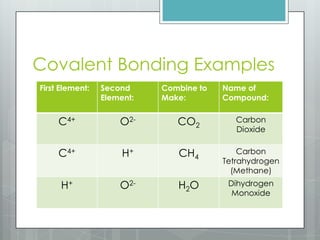
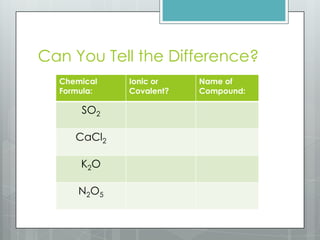
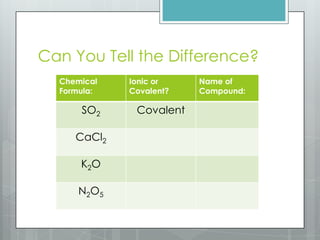
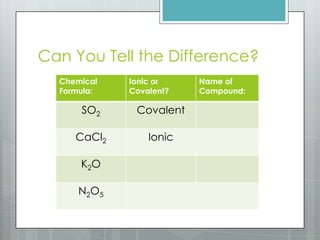
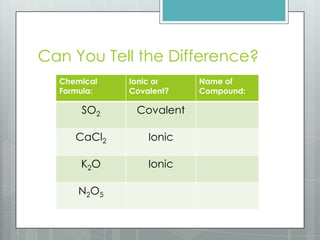
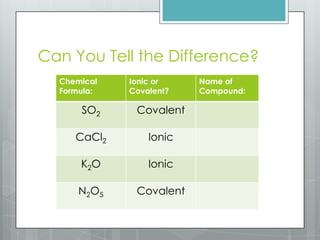
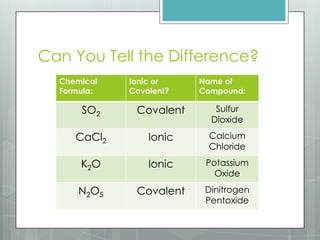
This document discusses chemical bonding and the two main types: ionic and covalent bonding. Ionic bonding involves the transfer of electrons between atoms to form ions, while covalent bonding involves the sharing of electrons between atoms. Examples of ionic compounds include sodium chloride, potassium sulfide, and magnesium oxide. Examples of covalent compounds include carbon dioxide, methane, and water. The document provides tables to illustrate ionic and covalent bonding examples and how to determine the type of bonding and name compounds based on their chemical formulas.