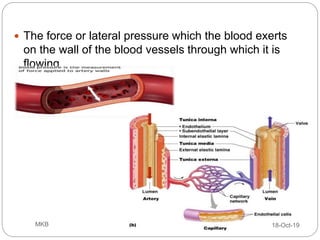
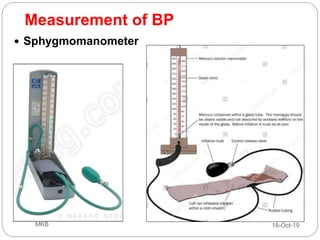
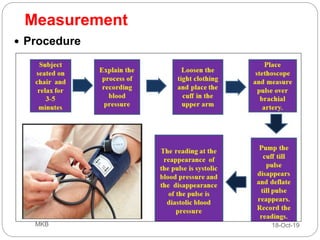
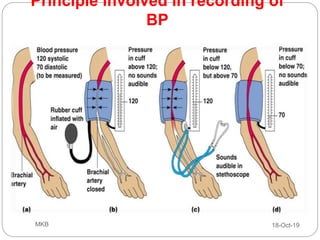
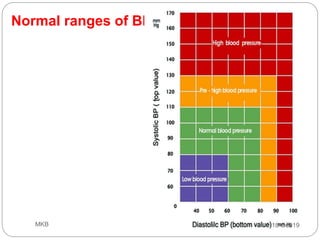
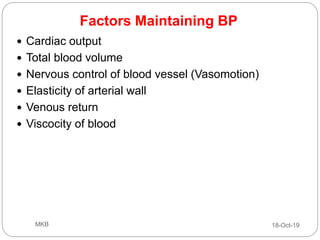
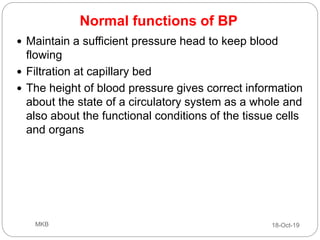
The document provides an overview of blood pressure (BP), including its measurement, normal ranges, and factors affecting it. It discusses high blood pressure (hypertension) and low blood pressure (hypotension), their causes, symptoms, and prevention and treatment strategies. Key aspects include the importance of BP for circulatory health and various contributing factors to BP changes.