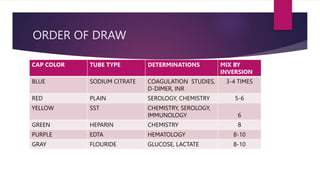
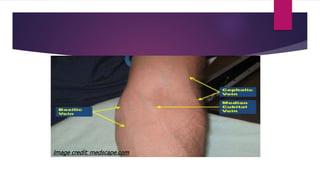
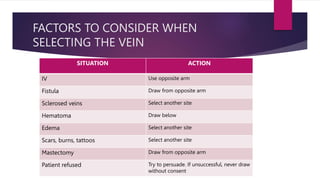
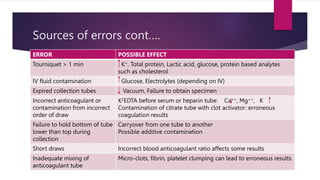
Phlebotomy is the procedure of inserting a needle into a vein to collect blood for laboratory testing. It involves selecting a suitable vein, such as the median cubital or cephalic veins in the arm, applying a tourniquet, cleaning the skin with antiseptic, inserting the needle at a 30 degree angle, collecting the blood into tubes, removing the tourniquet and applying pressure to stop bleeding. Factors like patient identification, tube type and order of draw, mixing of tubes, and sources of error must be considered to obtain accurate test results and avoid complications.