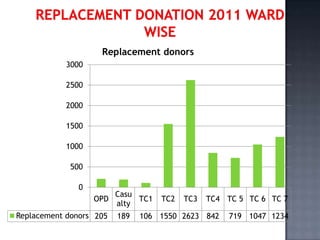
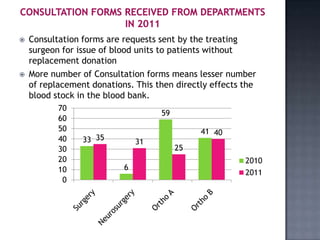
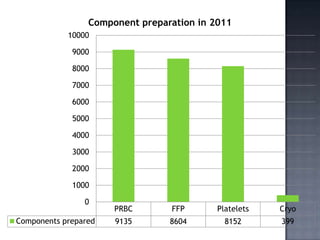
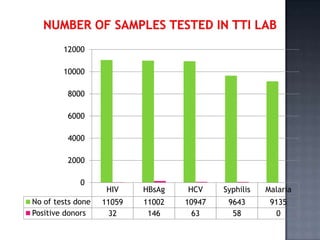
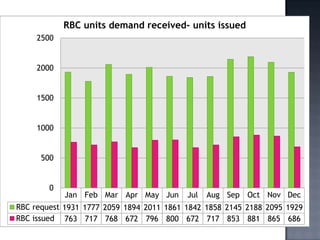
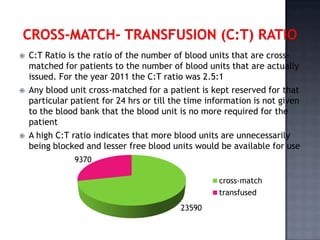
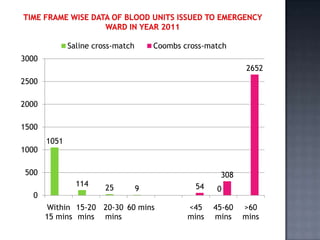
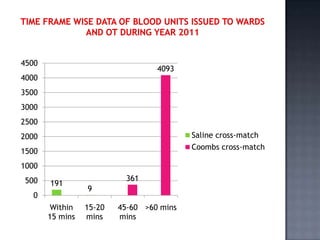
The blood bank in JPNA Trauma Centre was initially started in 2006 as a blood storage centre and became a full-fledged blood bank in 2008. Since then, it has been functioning as a blood bank that performs 100% component preparation. It obtains blood and components through both replacement and voluntary blood donations. In 2011, it collected 9,135 total donations, of which 7,848 were replacement donors and 1,339 were voluntary donors. It performs various tests on donated blood, prepares blood components, issues blood units based on demand, and conducts other activities required of a blood bank.