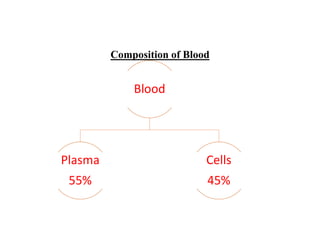
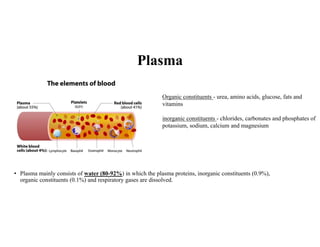
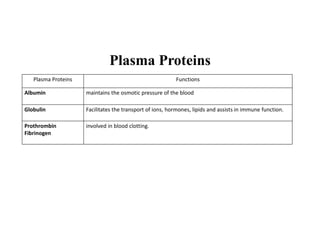
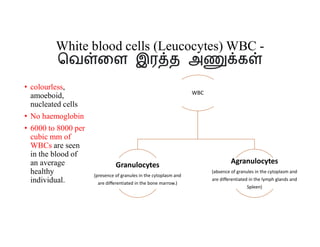
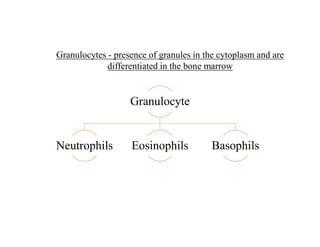
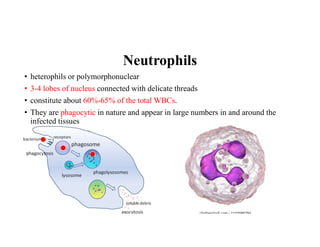
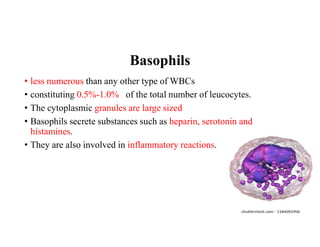
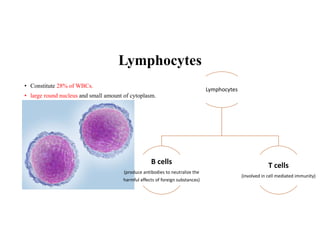
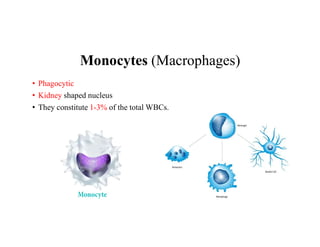
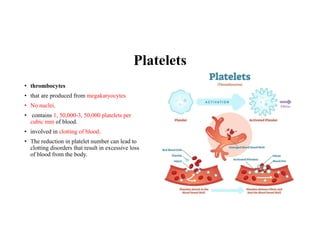
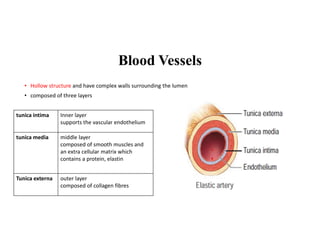
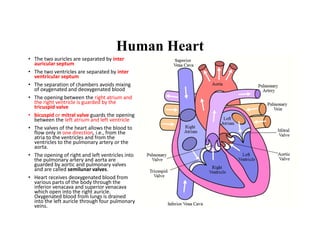
Blood is composed of plasma and formed elements including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. Plasma contains water, proteins, and other constituents. Red blood cells contain hemoglobin and transport oxygen. White blood cells help fight infection in different ways. Platelets help the blood clot. Blood circulates through arteries, capillaries, and veins, which have different structures suited to their functions in transporting blood and exchanging materials with tissues. The heart has four chambers and uses valves to pump blood through the body in two circuits, circulating oxygenated blood from the lungs and deoxygenated blood to the lungs.