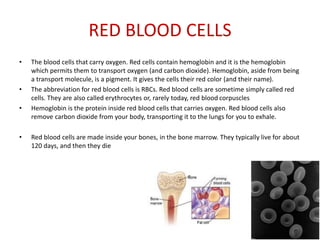
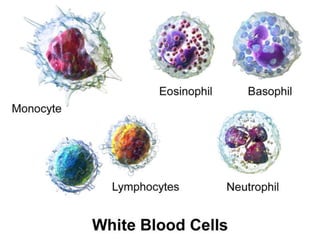
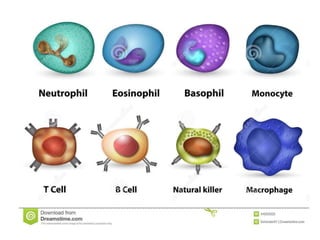
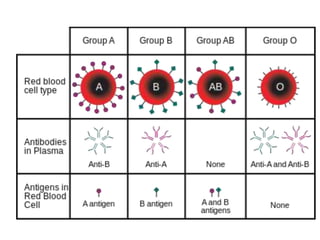
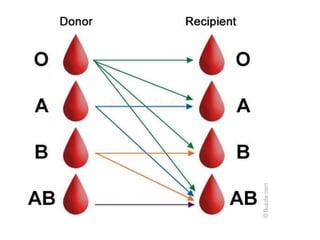
Blood has three main functions: transport, protection, and regulation. It transports gases, nutrients, hormones, heat, and waste throughout the body. Blood also protects the body through white blood cells that destroy pathogens and platelets that initiate clotting. Additionally, blood helps regulate pH, water balance, and other processes. Blood is composed of plasma, red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets, each with distinct roles in these important functions.