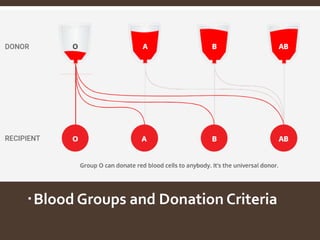
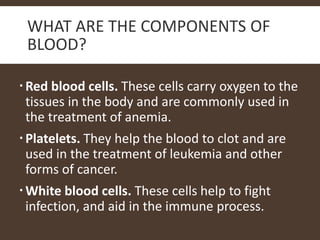
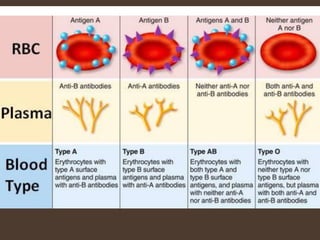
The document explains blood banking, defined as the process of ensuring the safety of donated blood for transfusions. It outlines donor criteria, types of donations, and the testing procedures to screen for infections. Additionally, it details the components of blood and their uses, storage durations for blood products, and necessary equipment for blood collection.