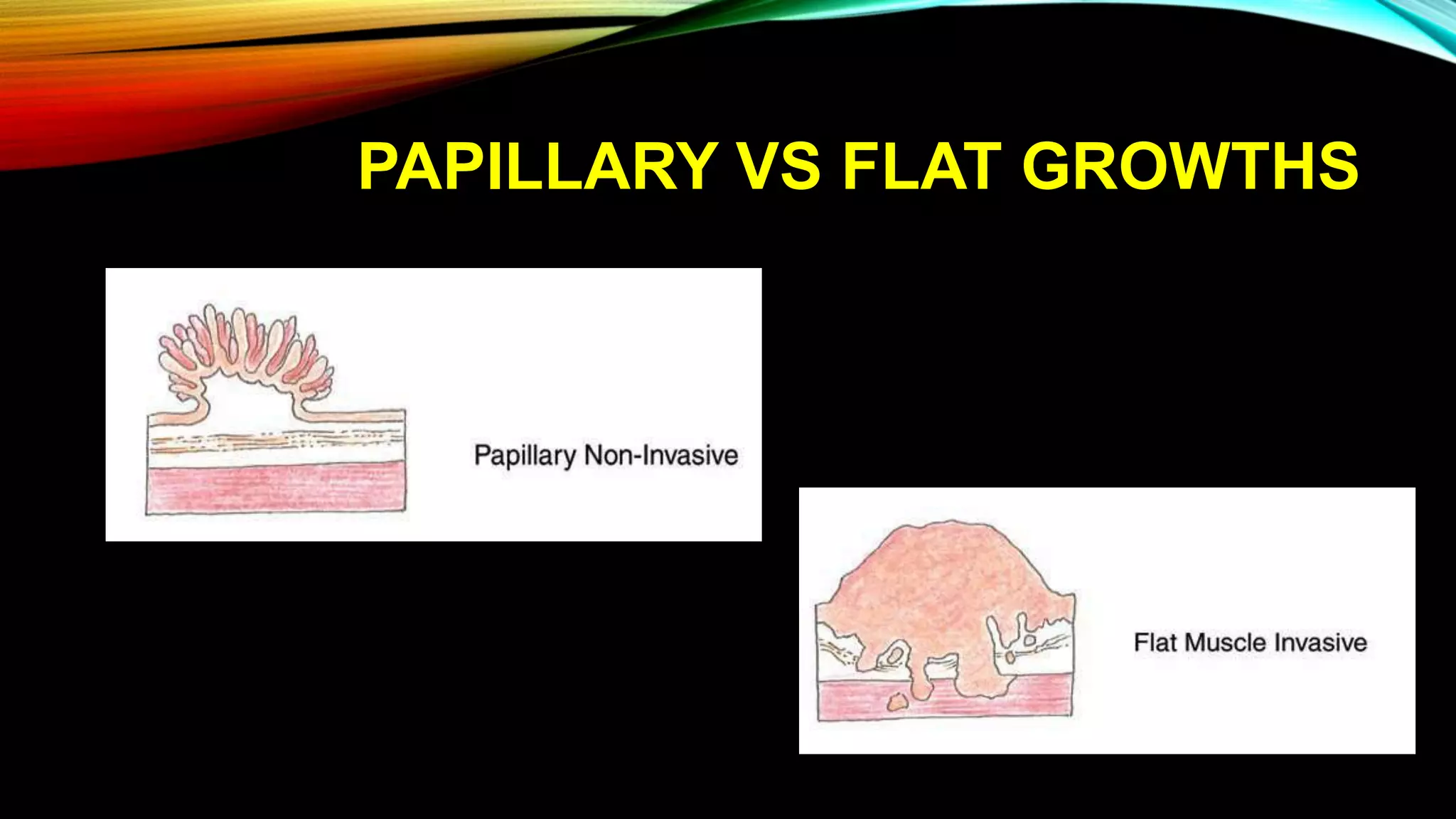
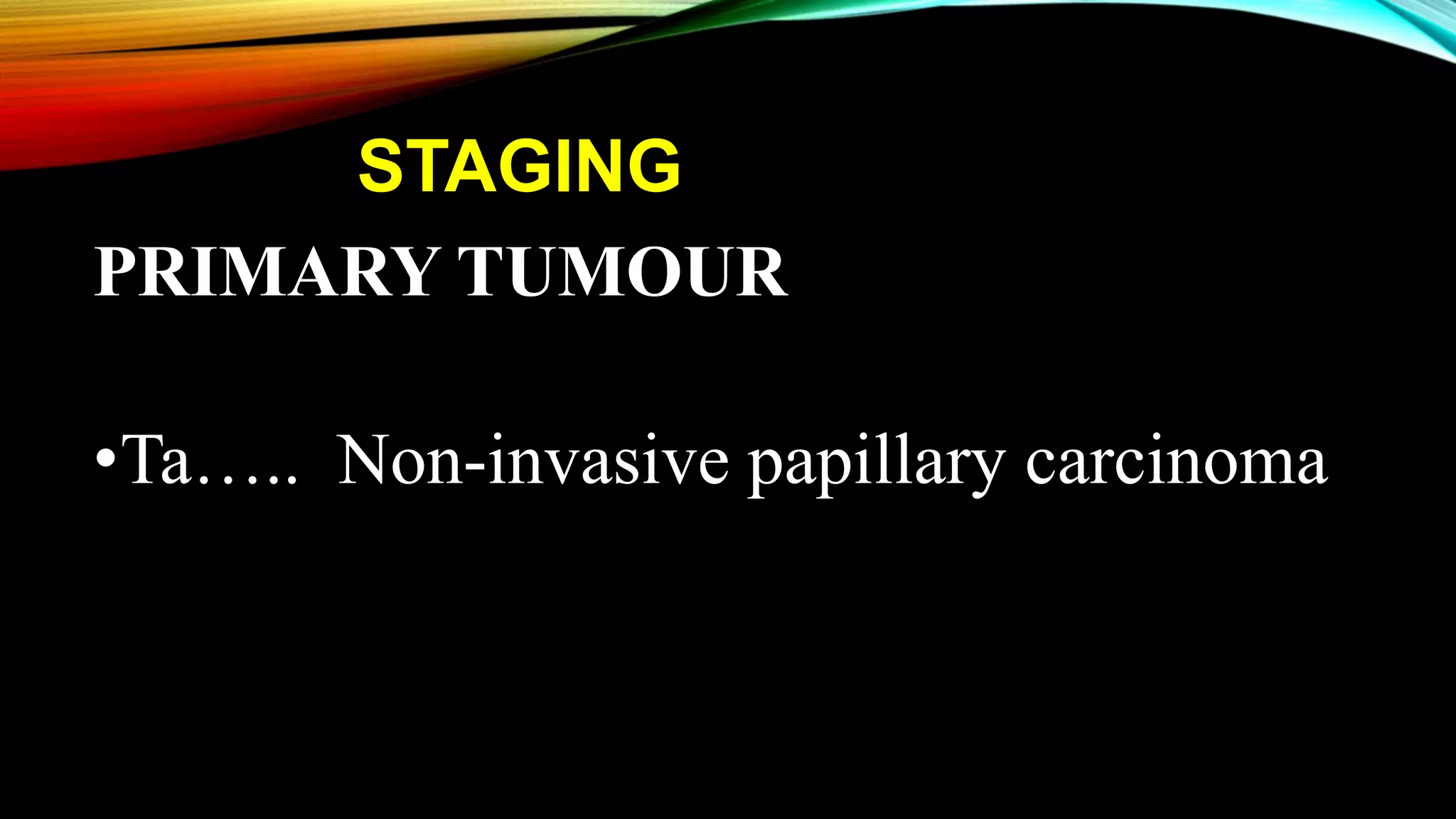
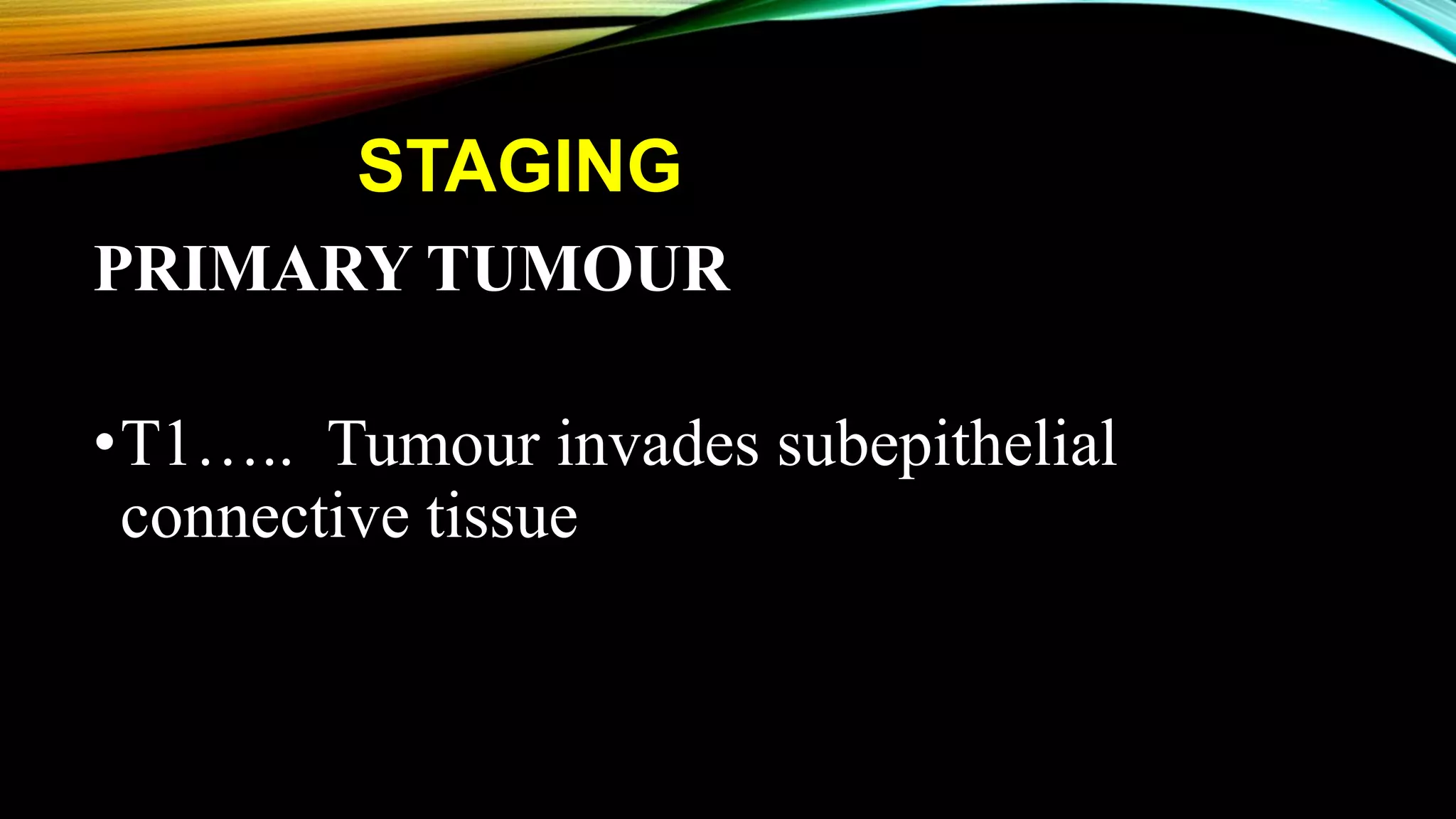
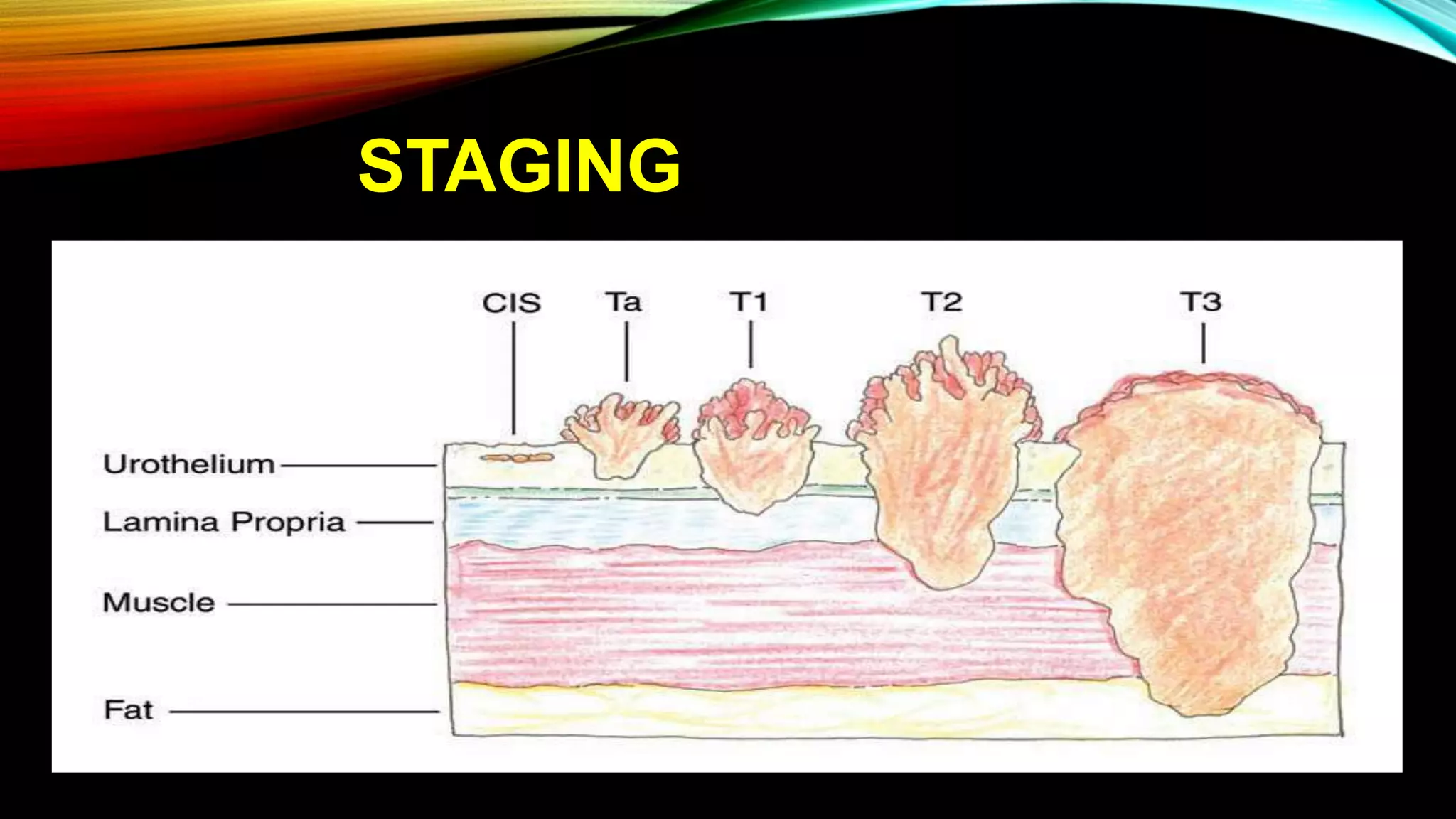
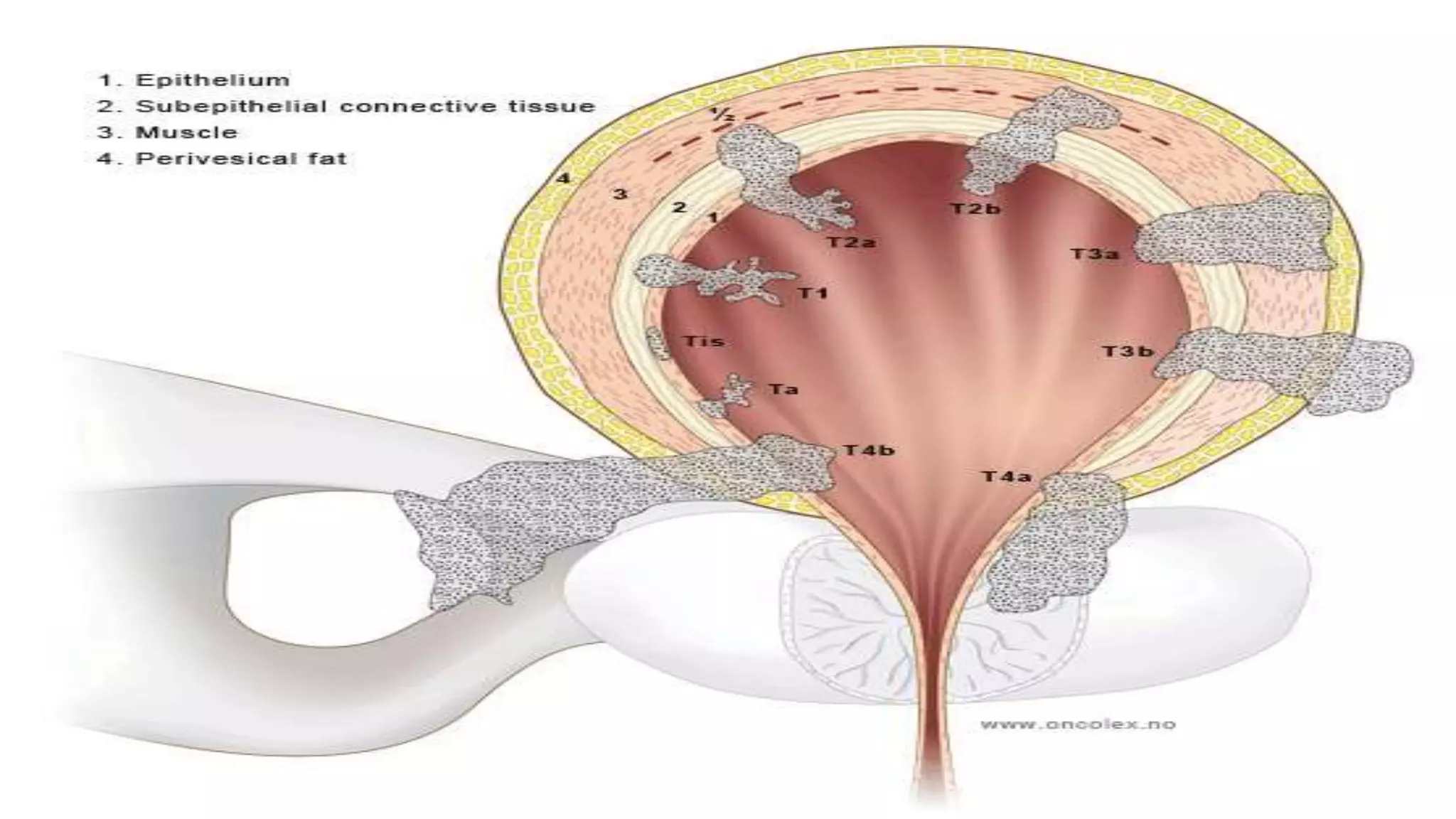
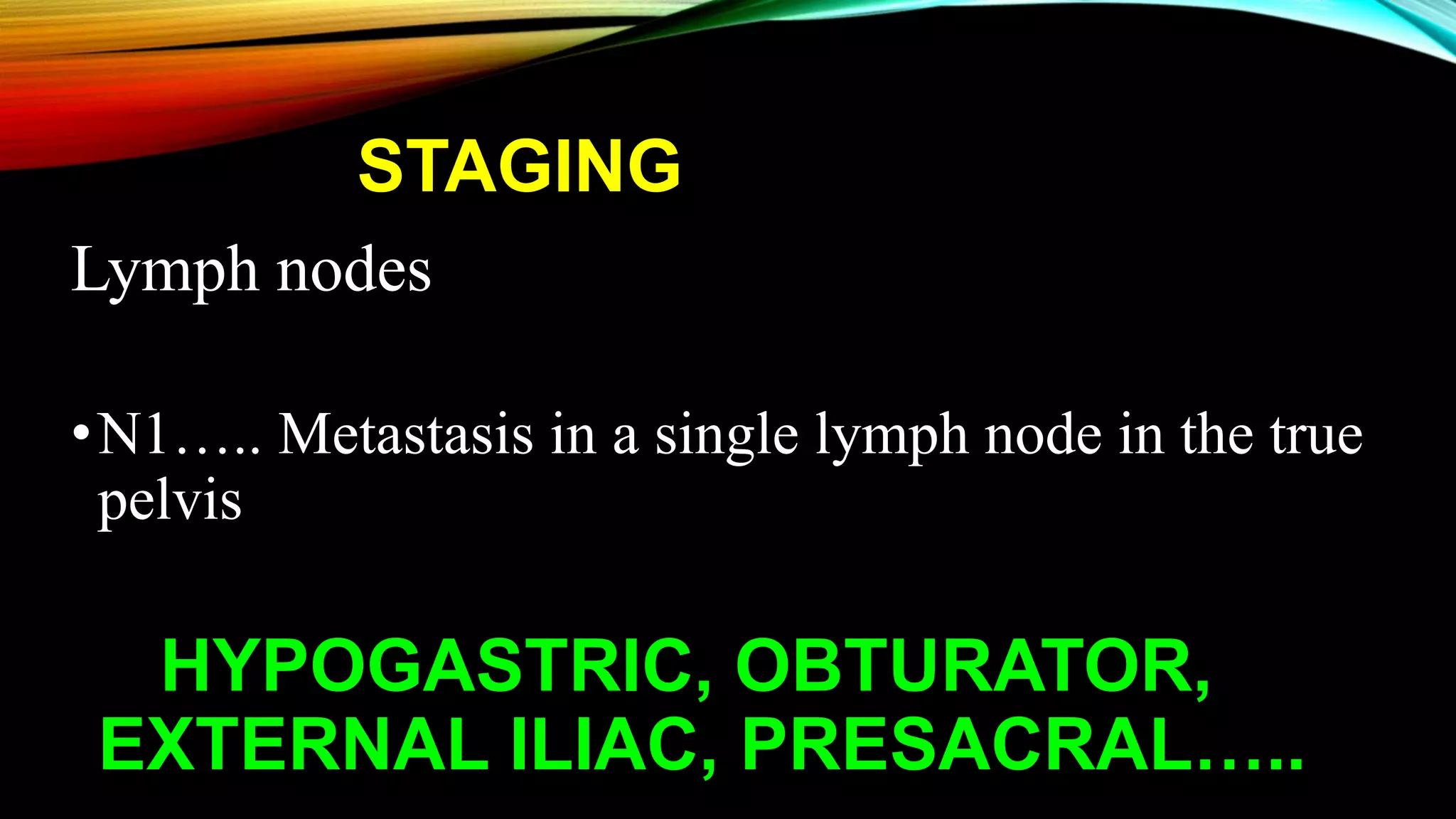
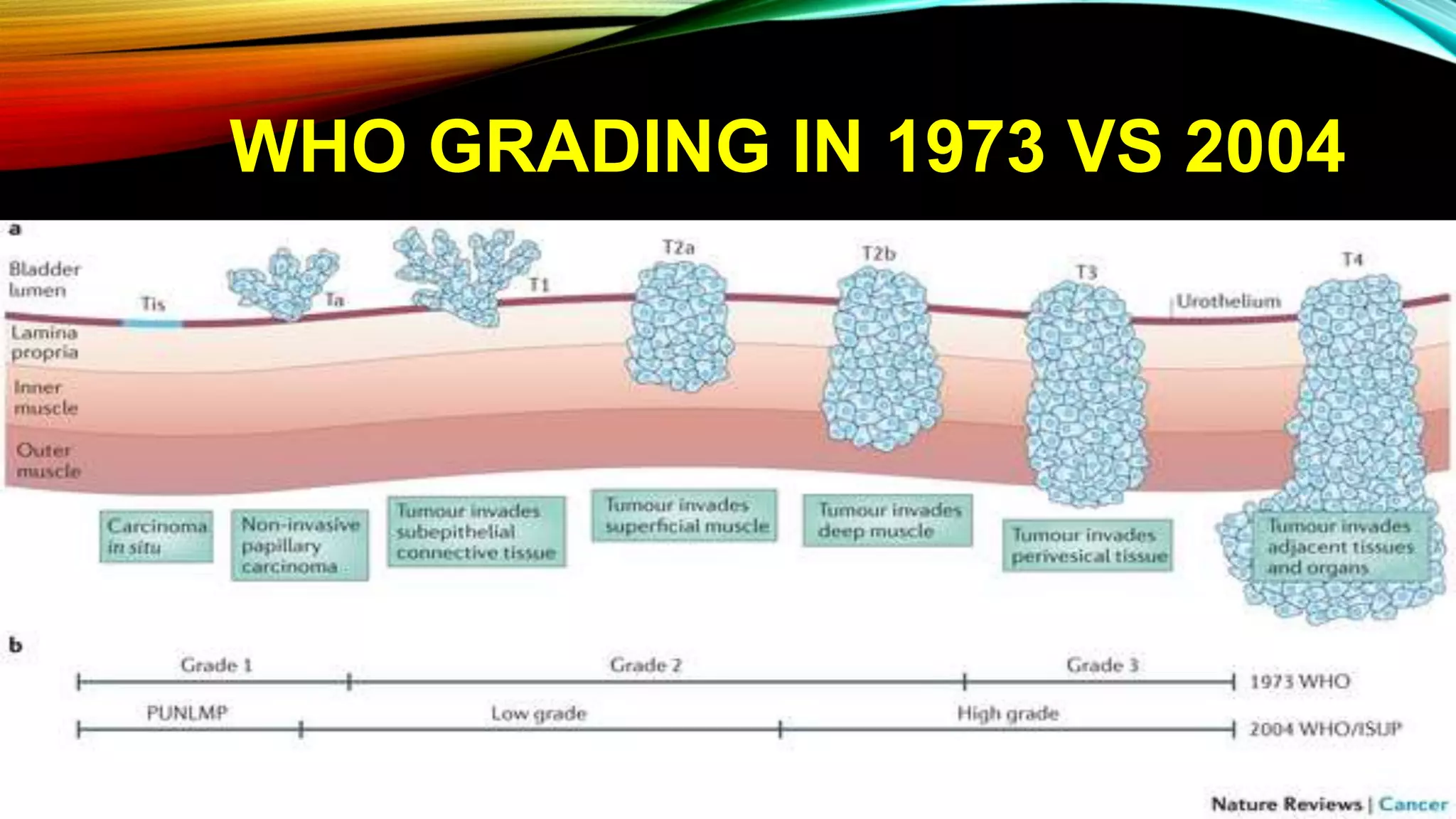
The document outlines the clinical features and staging of urinary bladder carcinoma, highlighting hematuria as a common symptom and the importance of staging for treatment options and prognosis. It details the various stages of the disease, grading of tumors according to WHO guidelines, and the high recurrence rate of bladder cancer, emphasizing risk factors for recurrence and disease progression. Additionally, it covers metastasis patterns and unusual sites for transitional cell carcinoma (TCC).