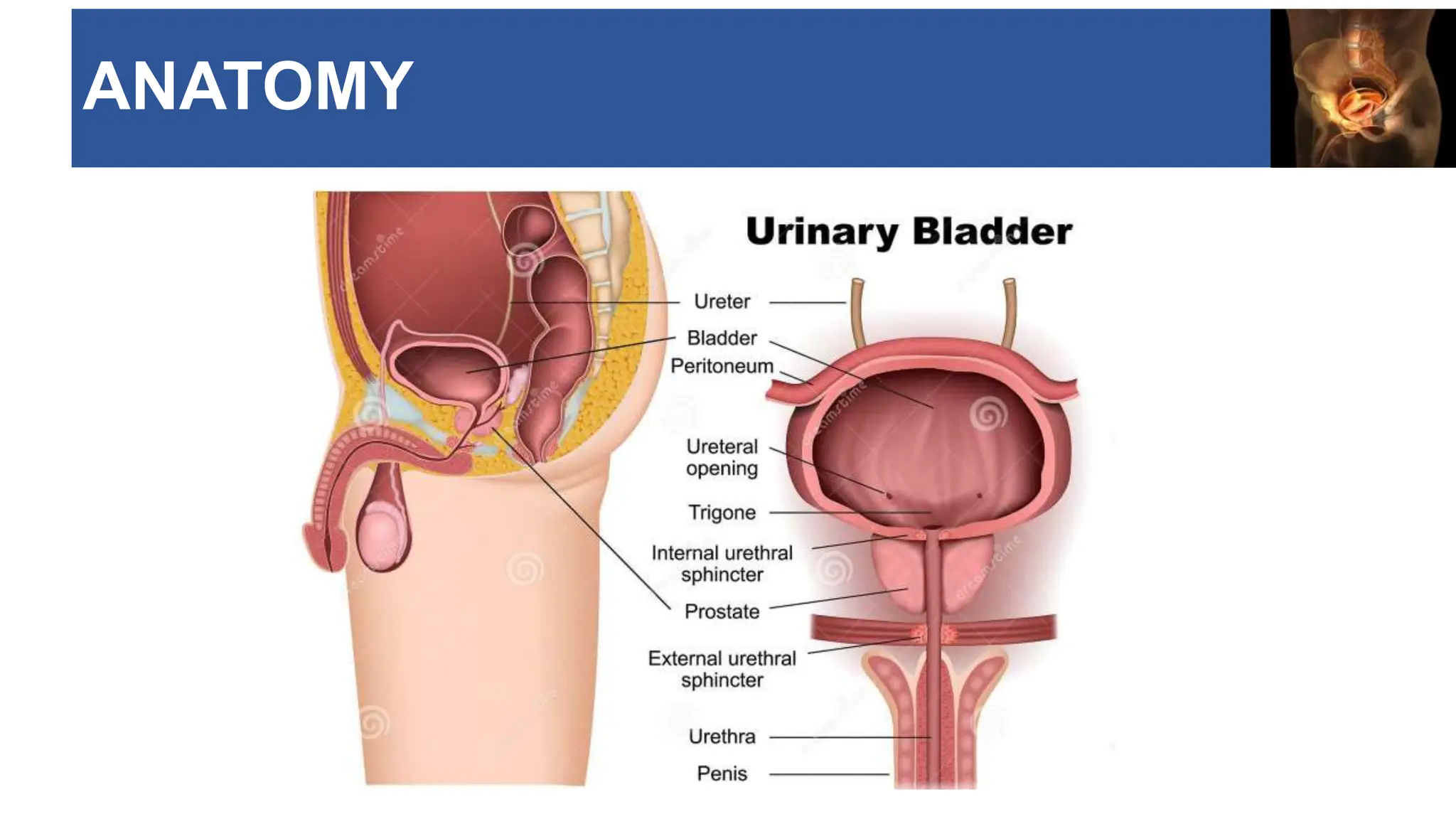
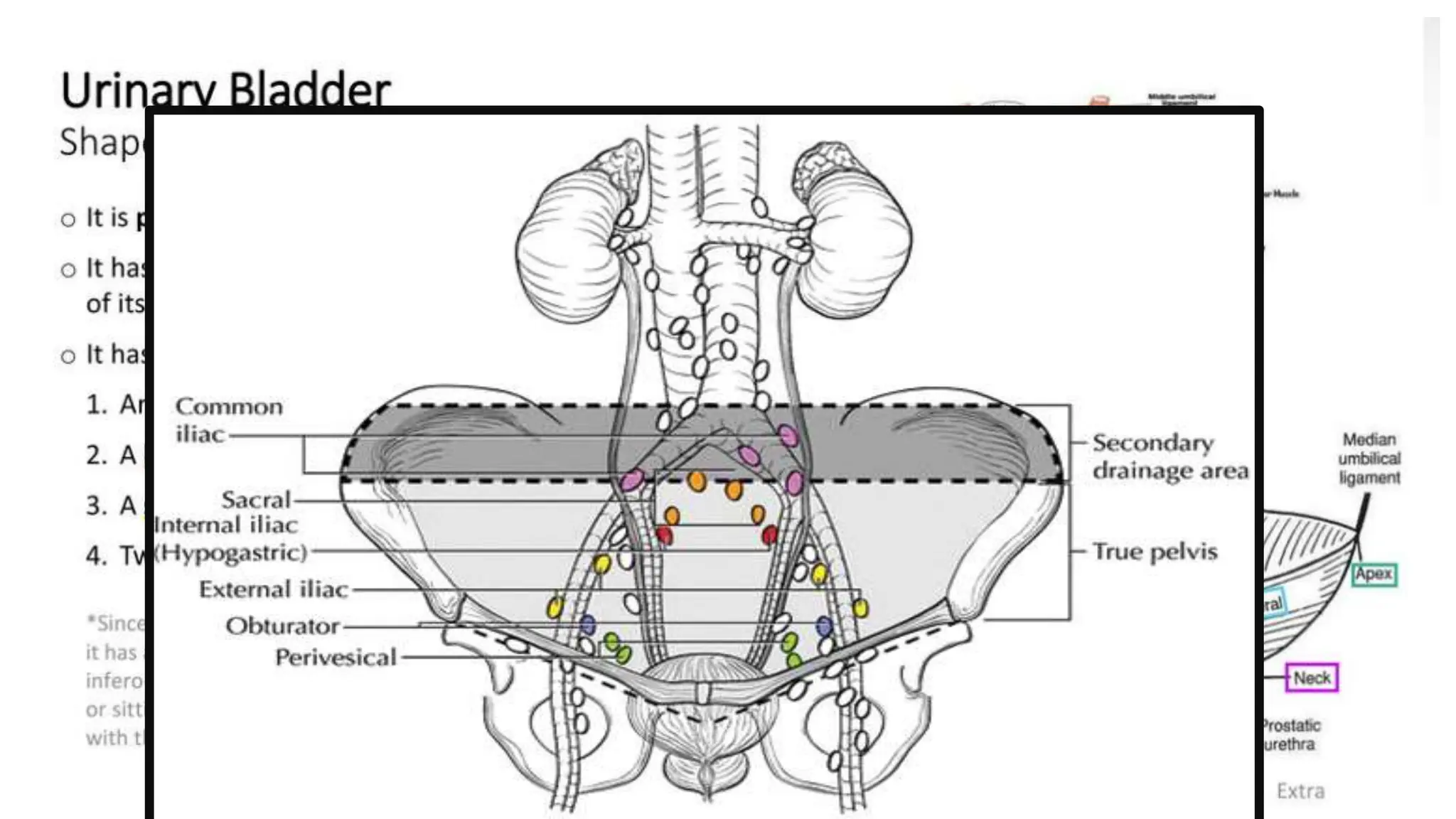
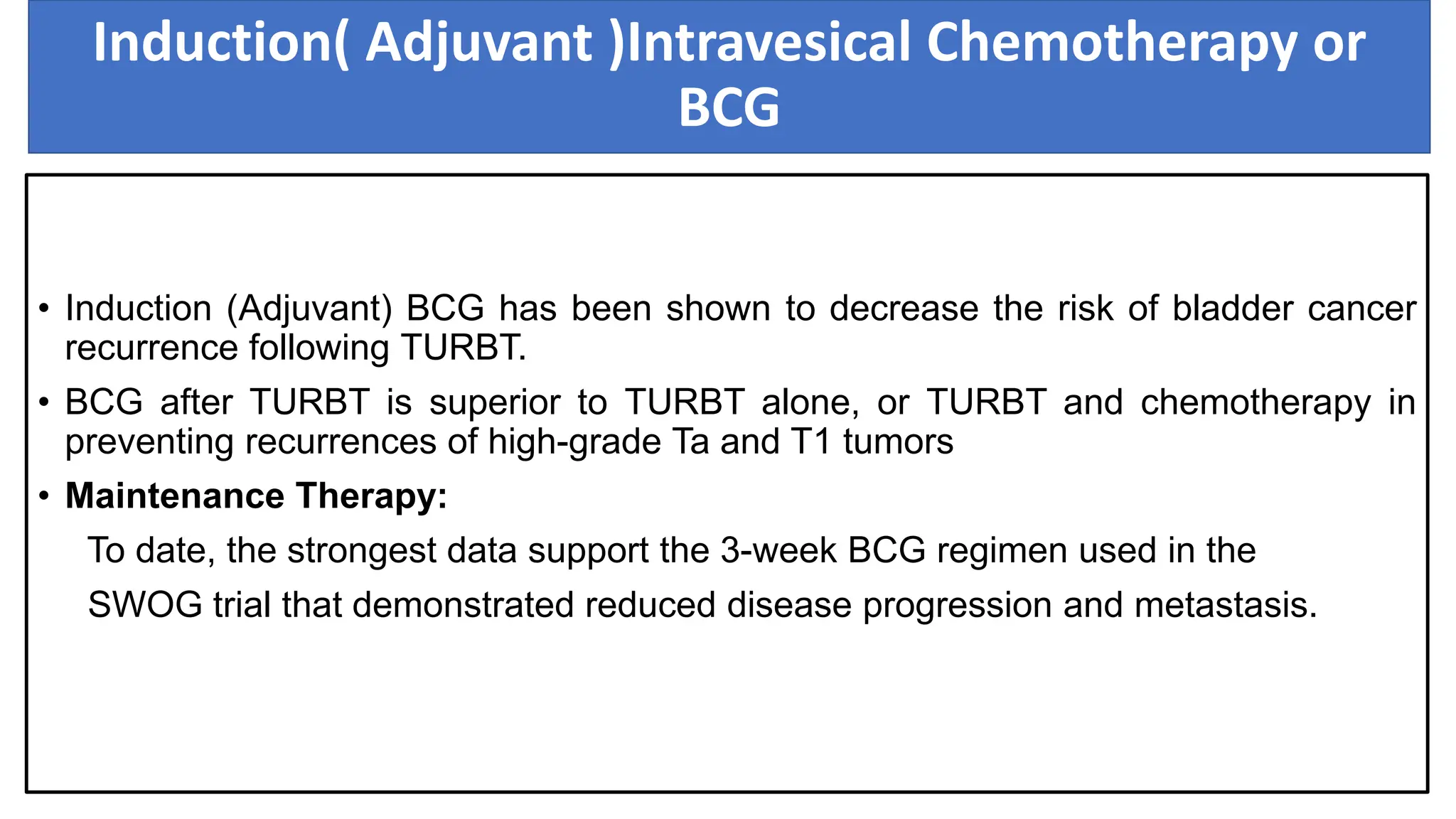
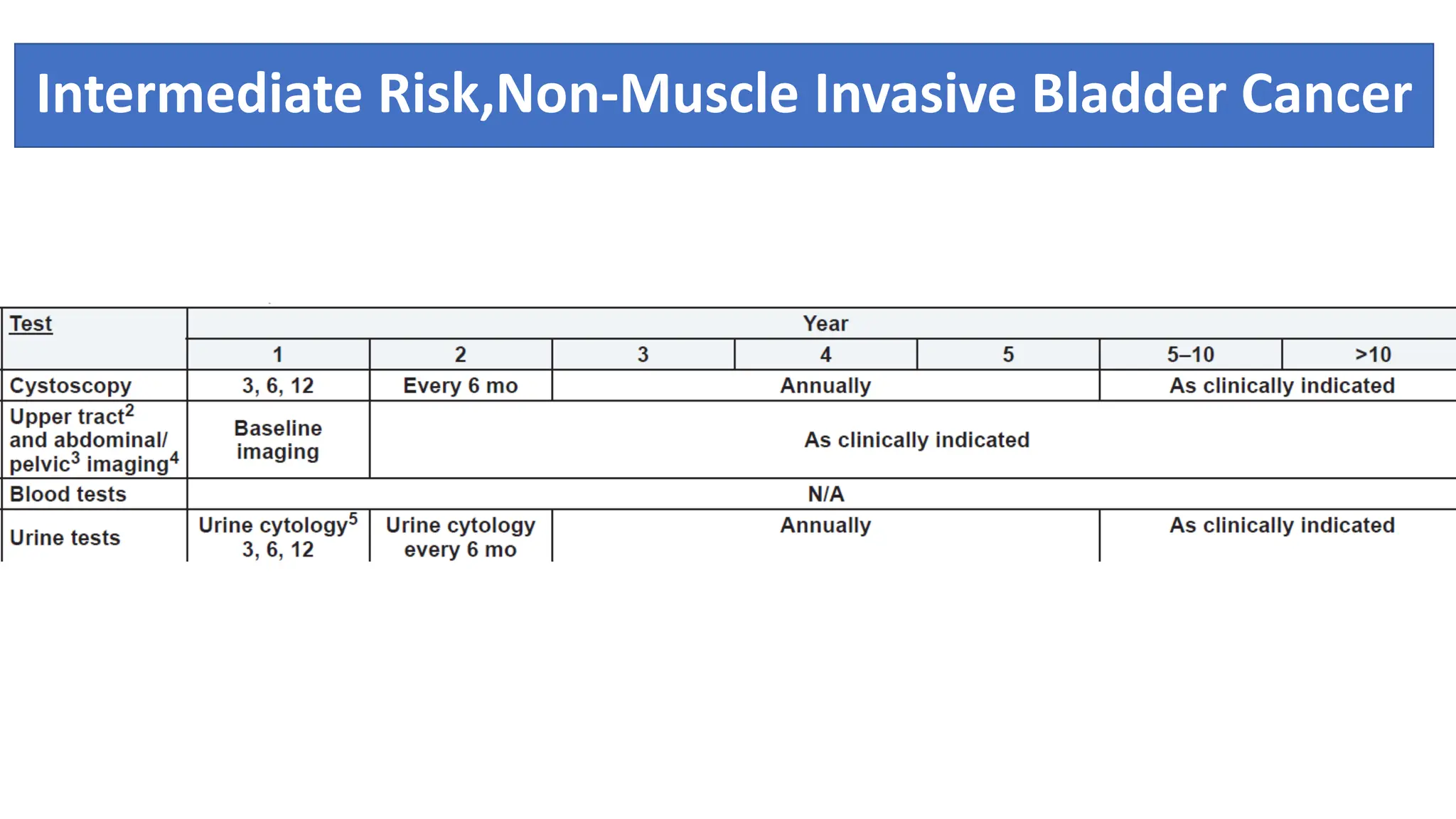
The document provides an extensive overview of urinary bladder carcinoma, detailing its anatomy, epidemiology, clinical presentation, staging, histology, and management strategies. It outlines the risk factors, diagnostic workup, treatment options for non-muscle invasive and muscle-invasive bladder cancers, as well as the role of newer therapies like pembrolizumab. Additionally, the document emphasizes the importance of timely intervention and comprehensive treatment plans to improve patient outcomes.
















![Workup
• Full blood count
• Biochemical profile
• Prostate-specific antigen (if indicated)
• Urine cytologic examination
• Flexible cystoscopy
• Imaging of the urothelium (e.g., ultrasound,
intravenous urogram, or computed tomography [CT]
urogram)
Patients with muscle-invasive bladder
cancer (MIBC) will require detailed cross-sectional staging
with CT or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the
chest, abdomen, and pelvis. If there are any features
suggestive of bone metastasis (e.g., raised alkaline
phosphatase, bone pain), an isotope bone scan will be
indicated in addition](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/caurinarybladder-240428105704-51be6a2b/75/Ca-Urinary-Bladder-anatomy-to-management-19-2048.jpg)


![Pathways to Muscle-Invasive and Non–Muscle-
Invasive Bladder Cancer
• Most cases (70% to 80%) present with non–muscle-invasive bladder
cancer(NMIBC, stage Ta, T1, and carcinoma in situ [Tis]), which is rarely
lethal, but shows a high recurrence rate of 50% to 70% after treatment by
transurethral resection of the bladder tumor (TURBT).
• In about 10% to 20% of patients with NMIBC, the disease progresses to
muscle invasion (=T2 lesions)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/caurinarybladder-240428105704-51be6a2b/75/Ca-Urinary-Bladder-anatomy-to-management-22-2048.jpg)










































![Systemic Chemotherapy
• A meta-analysis of 11 completed randomized trials of neoadjuvant chemotherapy for
invasive bladder cancer (3,005 patients) demonstrated a 5% OS benefit at 5 years (HR,
0.86; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.77 to 0.95; P = .003), supporting the role for
platinum-based combination neoadjuvant chemotherapy(standard MVAC).
• MVAC is administered in 28-day cycles, with starting doses of methotrexate 30 mg/m2
(days 1, 15, and 22), vinblastine 3mg/m2 (days 2, 15, and 22), doxorubicin 30 mg/m2
(day 2), and cisplatin 70 mg/m2 (day 2)
• Toxic effects of MVAC include neutropenia, anemia, thrombocytopenia, stomatitis,
nausea, and fatigue](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/caurinarybladder-240428105704-51be6a2b/75/Ca-Urinary-Bladder-anatomy-to-management-67-2048.jpg)









![Neoadjuvant chemotherapy in invasive bladder cancer. Update of a systematic review and meta-analysis of individual
patient data advanced bladder cancer (ABC) meta-analysis collaboration. Advanced Bladder Cancer(ABC)
Meta-analysis Collaboration, Eur Urol 48:202-205, 2005.
Update in 2005 [EAU 2005]
• Absolute OS benefit of 6.5% (95% CI 1-9%, from 45-50%)
• Significant DFS benefit (HR 0.78, 95% CI 0.71-0.86,
p<0.0001) with 9% improvement in 5 years
• Platinum combination significantly better than platinum single
agent](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/caurinarybladder-240428105704-51be6a2b/75/Ca-Urinary-Bladder-anatomy-to-management-77-2048.jpg)

