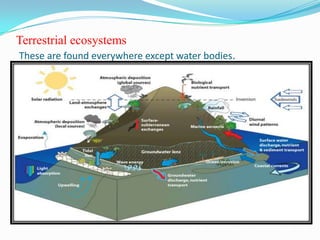
There are two main types of ecosystems: terrestrial and aquatic. Terrestrial ecosystems include forests, deserts, grasslands, and mountains. Forests have a high density of life. Deserts have scarce flora and fauna due to high heat, sunlight and low water. Grasslands mainly comprise grasses with some shrubs and trees and support many grazing animals. Mountains provide diverse habitats from alpine to coniferous forests. Aquatic ecosystems include marine and freshwater. Marine ecosystems cover most of the Earth's surface while freshwater ecosystems include lakes, rivers, and wetlands.