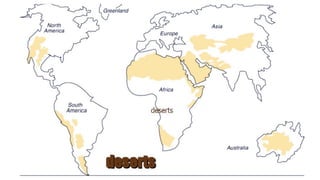
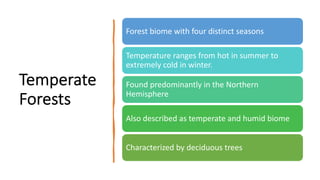
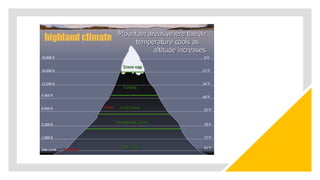
The document outlines various terrestrial biomes, their characteristics, and the importance of conservation due to human impact. It discusses five to ten different biome classifications, including aquatic, desert, forest, grassland, and tundra, detailing their climates and typical vegetation. Additionally, it describes specific habitats like floodplains and wetlands, emphasizing their ecological significance.