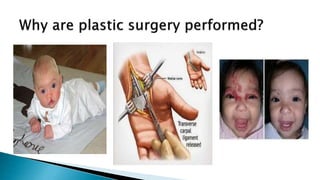
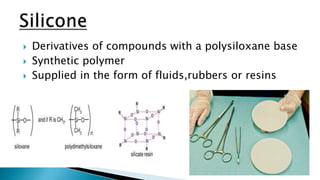
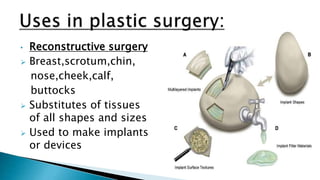
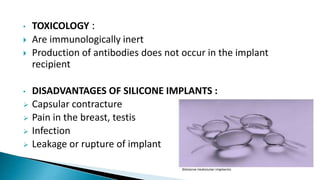
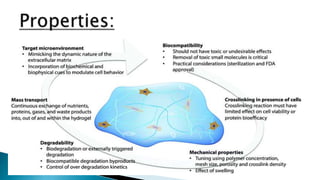
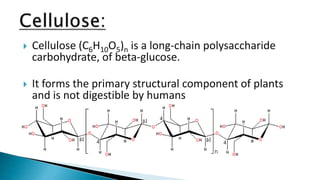
The document discusses various types of plastic surgeries, including cosmetic, reconstructive, and craniofacial surgeries, along with materials used for implants such as silicone and cellulose. It highlights the properties of these materials, including biodurability, biocompatibility, and toxicology, while mentioning potential disadvantages like capsular contracture and infection. Additionally, the text notes applications of these materials in medical devices and drug delivery.