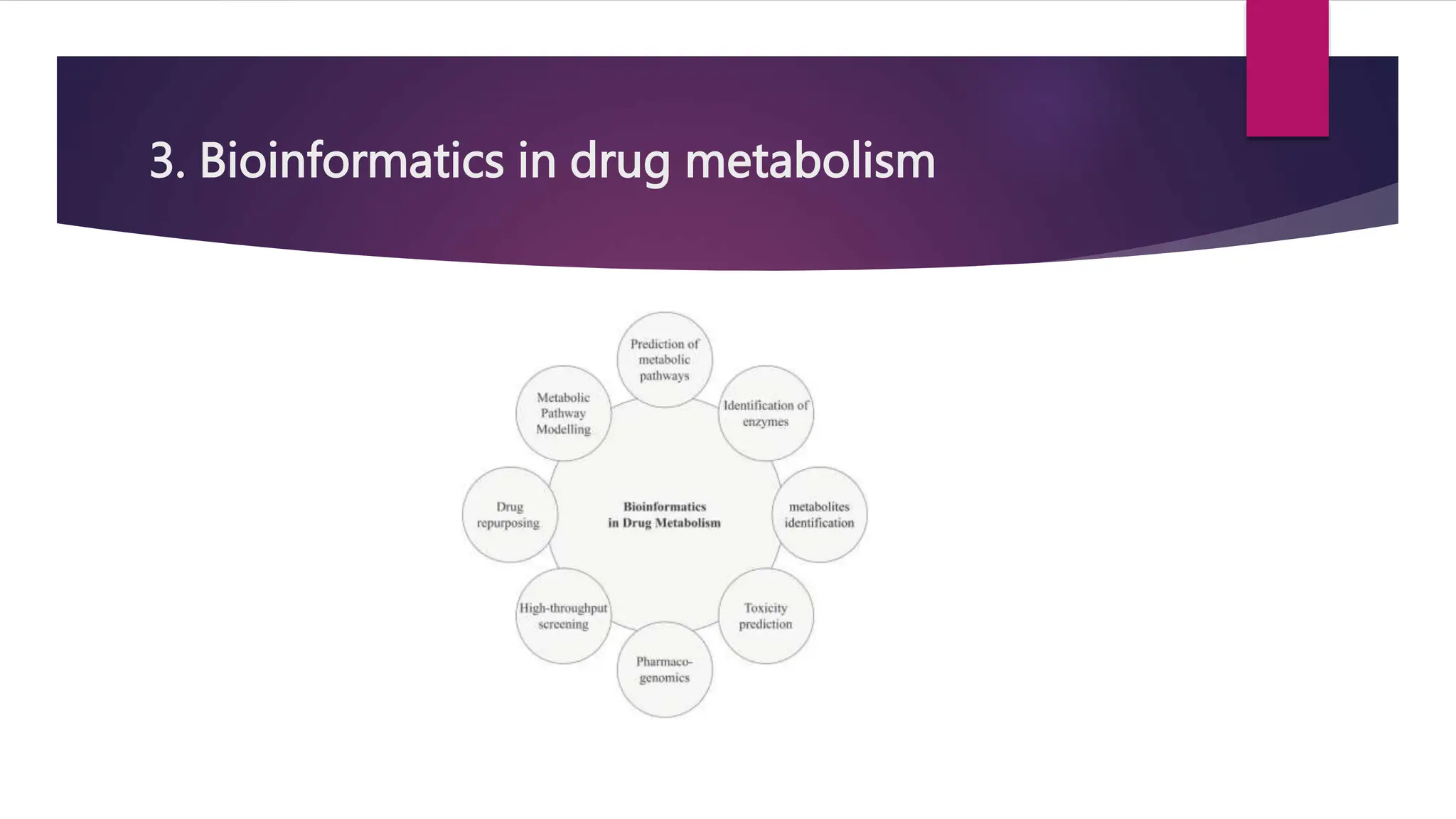
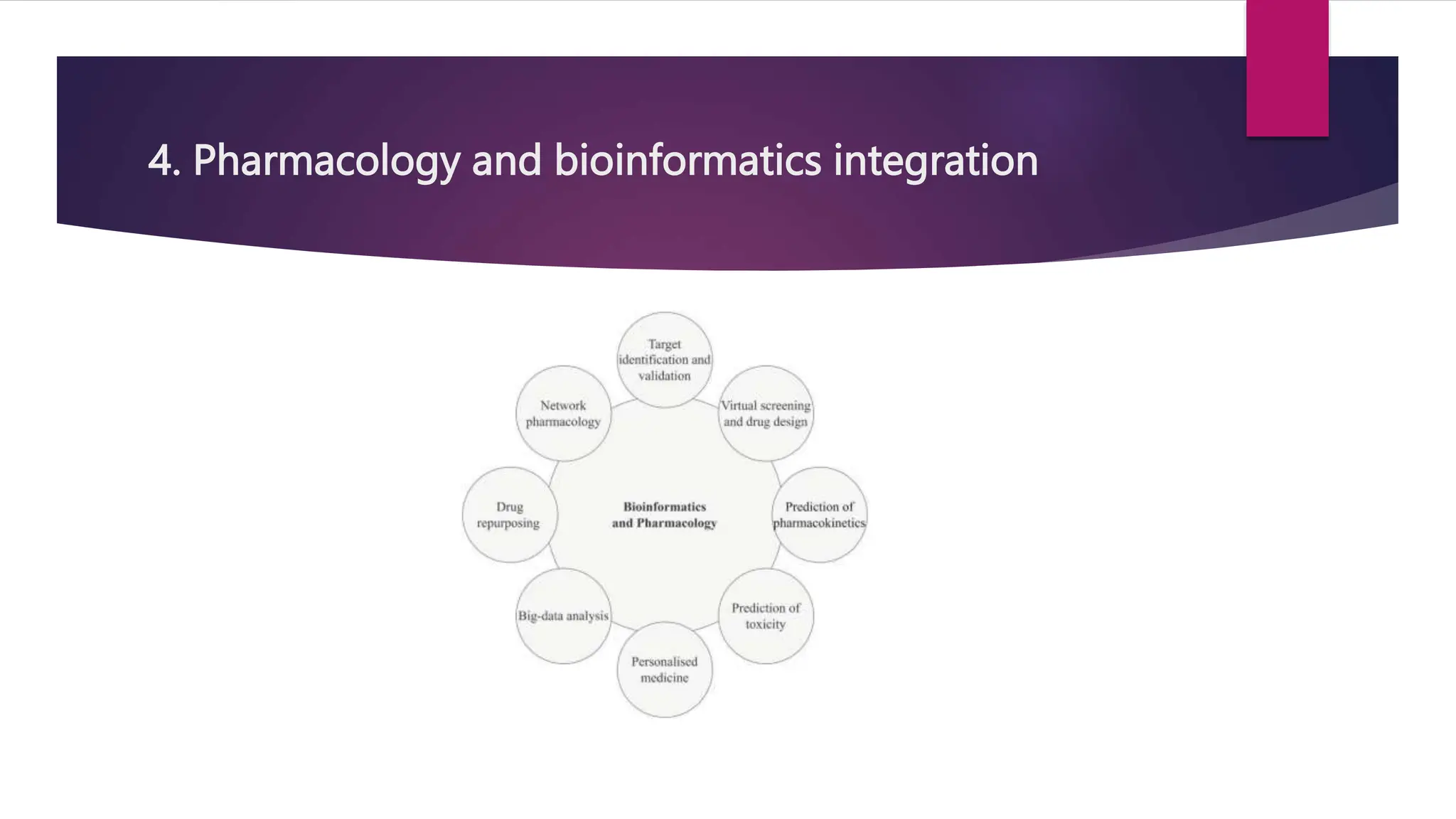
The document outlines bioinformatics as the application of computer technology to manage biological information, with goals including uncovering biological insights for fields like molecular medicine and agriculture. It discusses various software tools, the role of bioinformatics in drug discovery, target identification and validation, drug metabolism analysis, and toxicology assessments. Key contributions include improving drug candidate selection through data analysis and predictive modeling to enhance safety and efficacy.