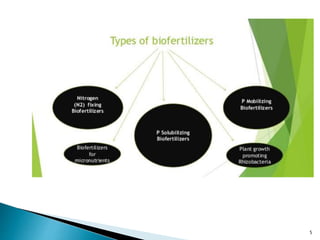
1. The document discusses various microorganisms that can be used as biofertilizers, including nitrogen-fixing bacteria like Rhizobium, Azospirillum, and Azotobacter, as well as phosphate-solubilizing bacteria and mycorrhizal fungi.
2. It provides details on the nitrogen fixation process and describes important diazotrophic bacteria.
3. Mycorrhizal fungi form mutualistic relationships with plant roots and help increase nutrient absorption, especially of phosphorus.