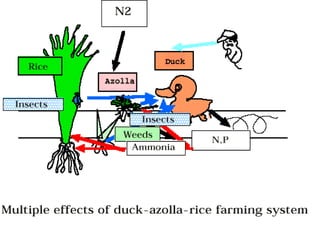
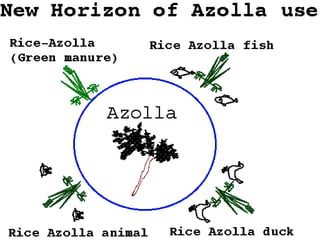
Azolla is an aquatic fern that fixes atmospheric nitrogen through a symbiotic relationship with cyanobacteria. It can be cultivated for use as a green manure in rice production systems. When applied to rice fields, azolla increases soil nitrogen levels and can reduce the need for nitrogen fertilizer by 30-40%, while increasing rice yields by 20-30%. Azolla contains 5% nitrogen and other nutrients and grows rapidly, multiplying to form a thick mat. It is usually applied to rice fields as a green manure before transplanting rice or grown together with rice in a dual cropping system to supply nitrogen over the growth period.