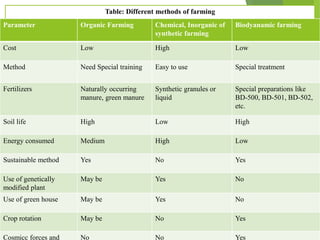
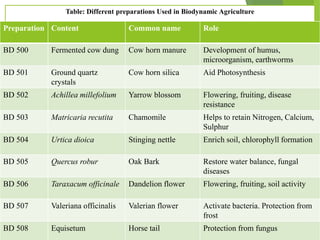
Biodynamic agriculture is a sustainable farming method that views the farm as a living organism and employs ecological practices to enhance soil fertility and plant growth, avoiding synthetic fertilizers and pesticides. This approach, developed by Rudolf Steiner, includes using natural composts, field sprays, and cosmic considerations to optimize agricultural processes. Biodynamic methods have demonstrated benefits in terms of soil health and crop quality compared to conventional farming, while also promoting biodiversity and ecological harmony.