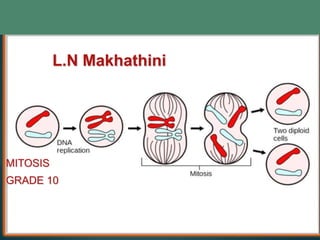
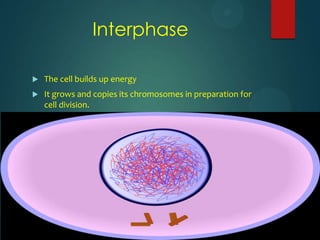
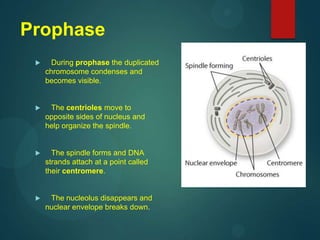
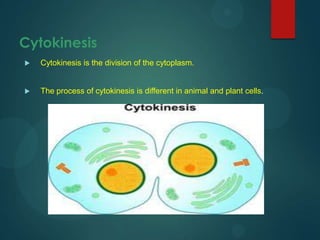
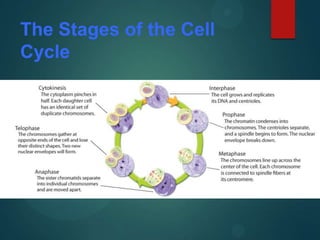
This document discusses mitosis and defines it as the process where a cell duplicates its genetic material and divides into two identical daughter cells. It describes the important cell structures involved like chromatids, centromeres, and centrioles. The stages of mitosis - interphase, prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase, and cytokinesis - are explained in detail. Cytokinesis, the final stage where the cytoplasm splits into the two daughter cells, differs between animal and plant cells.