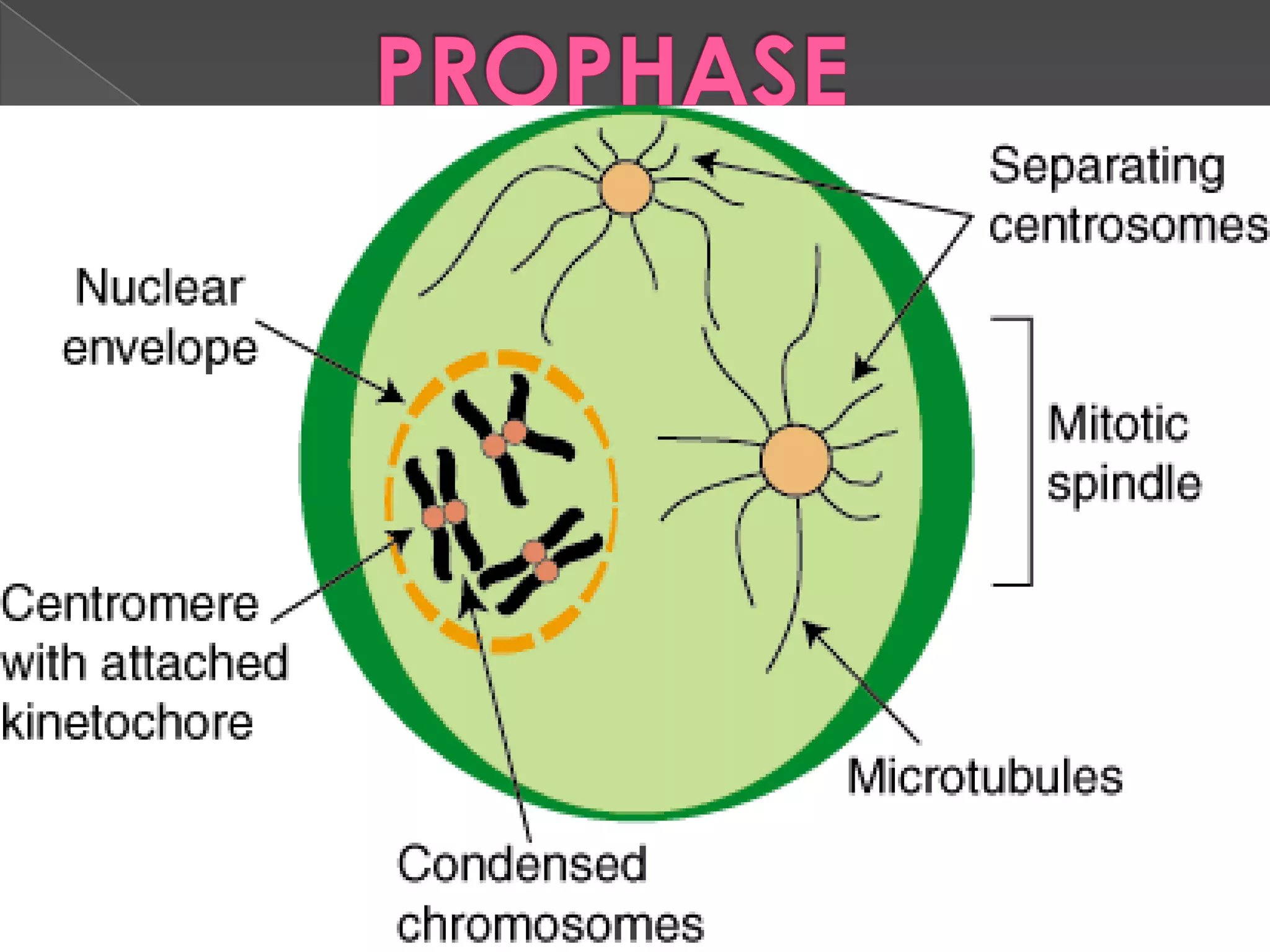
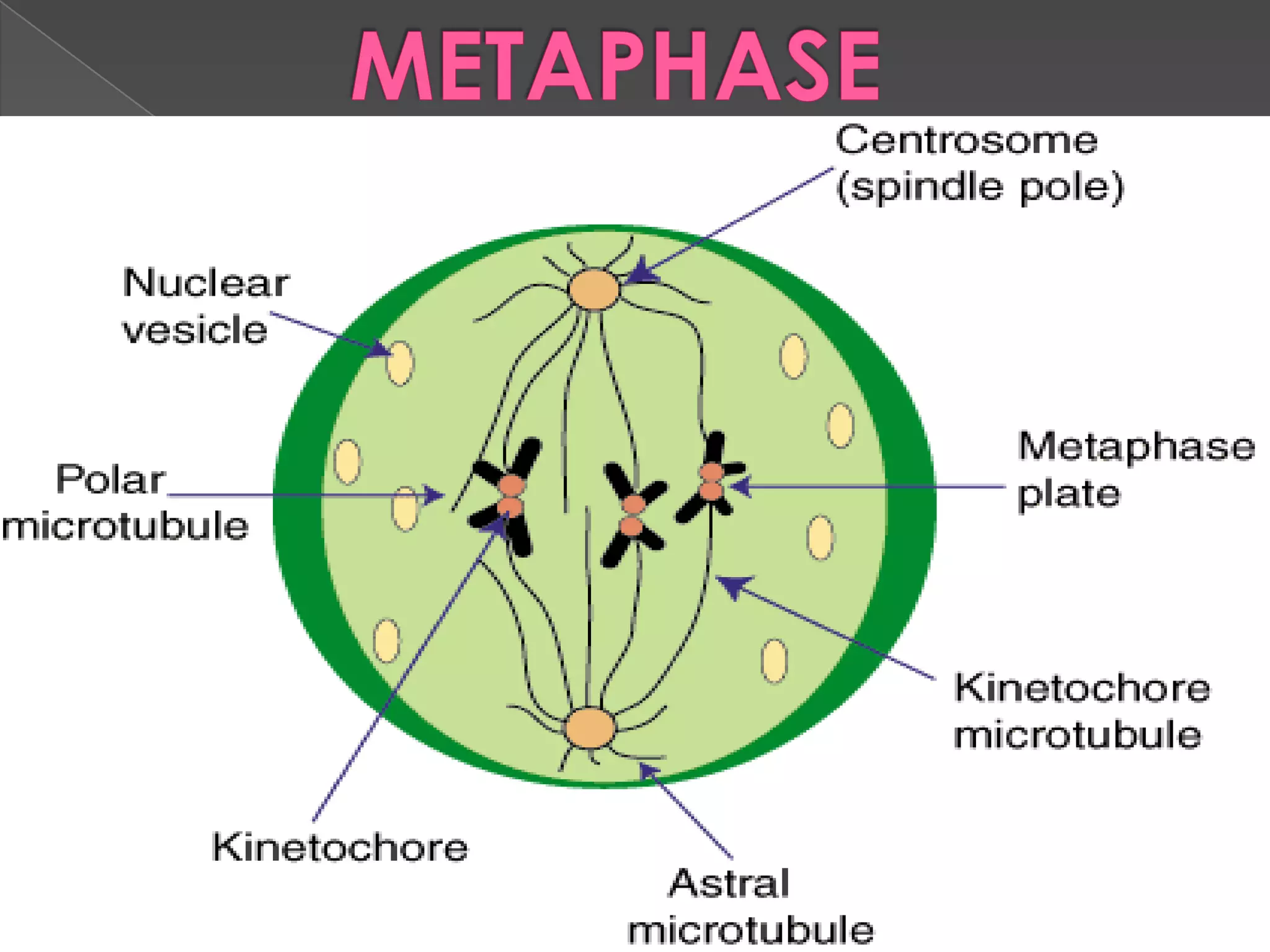
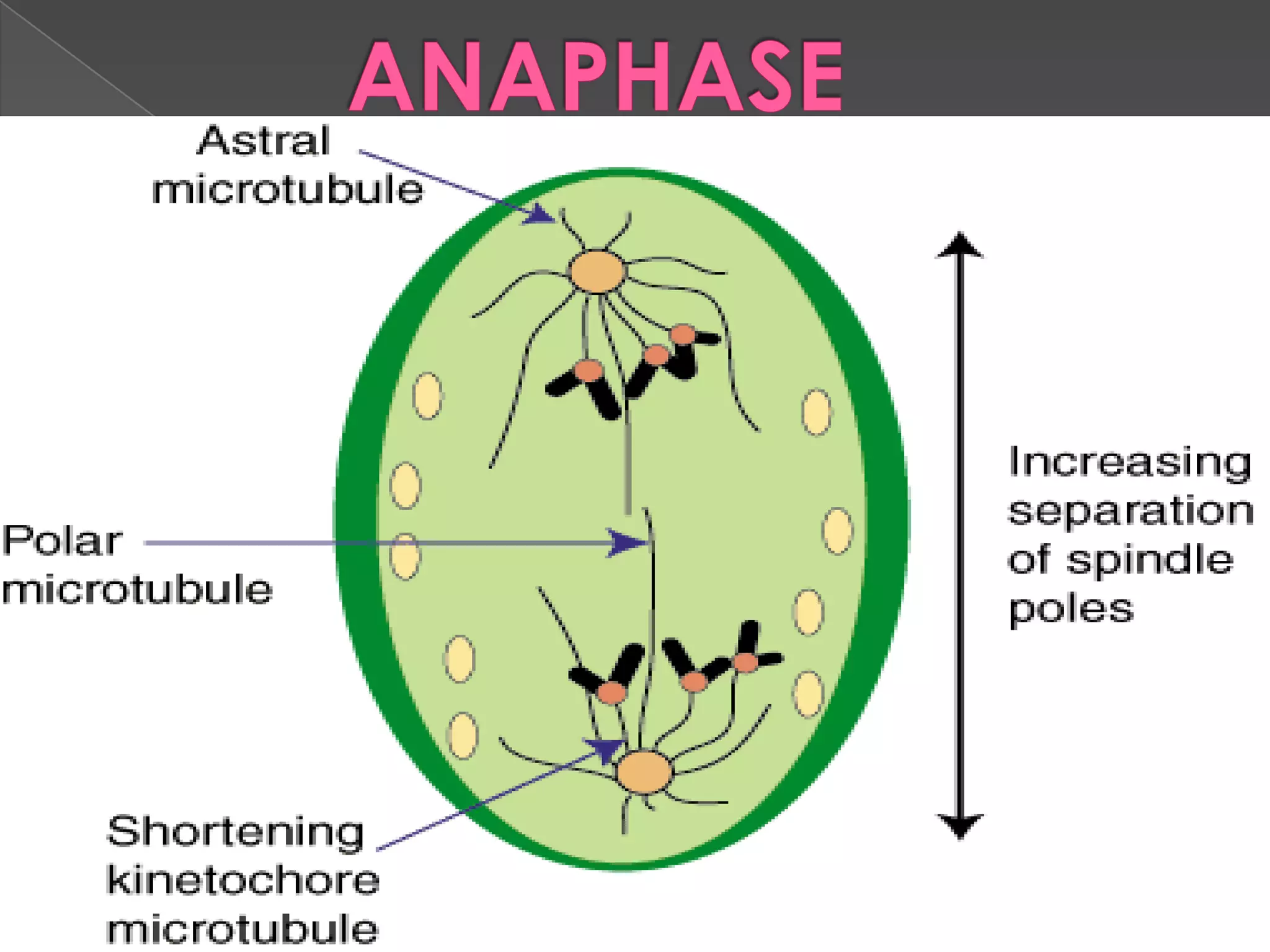
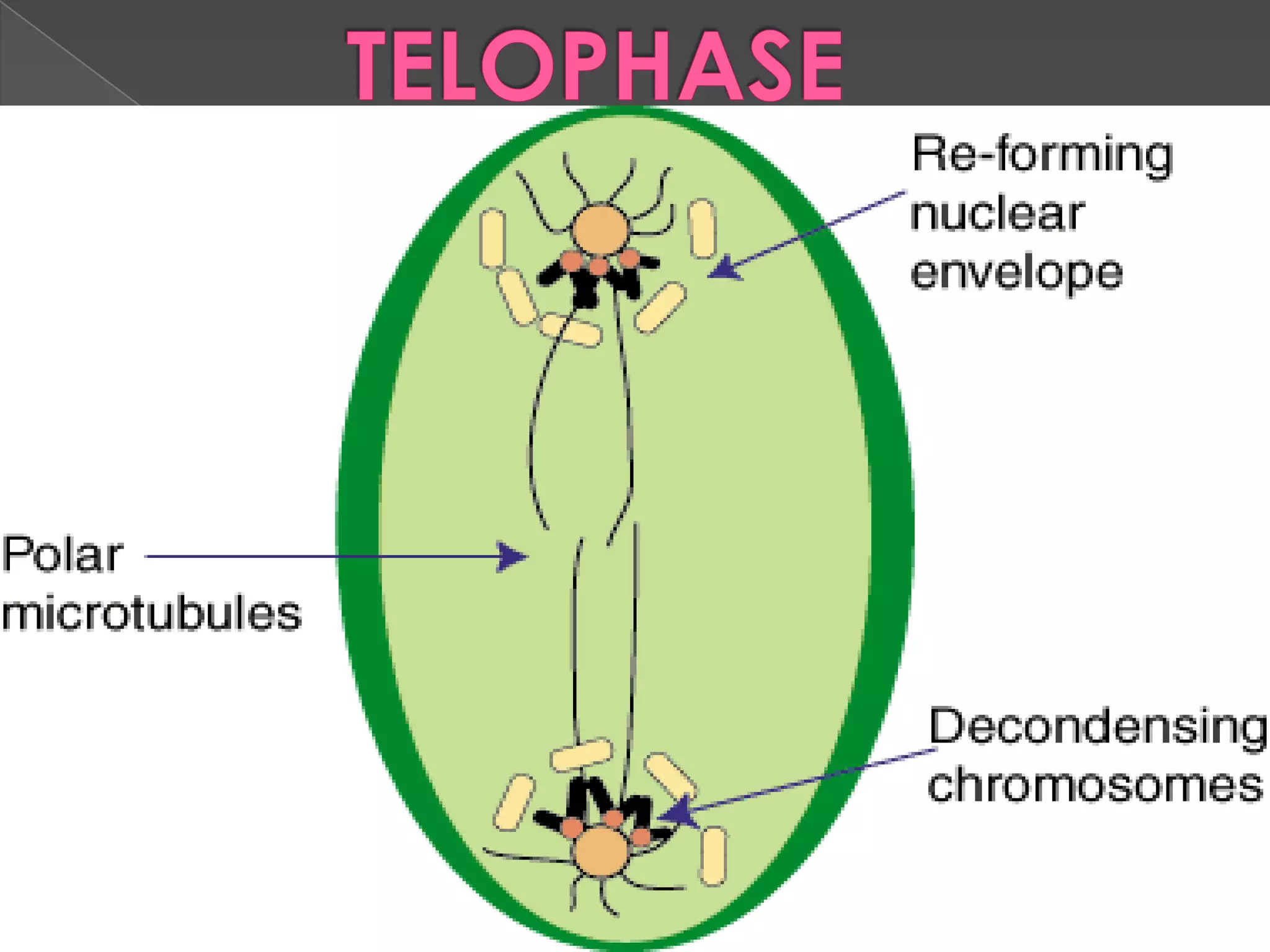
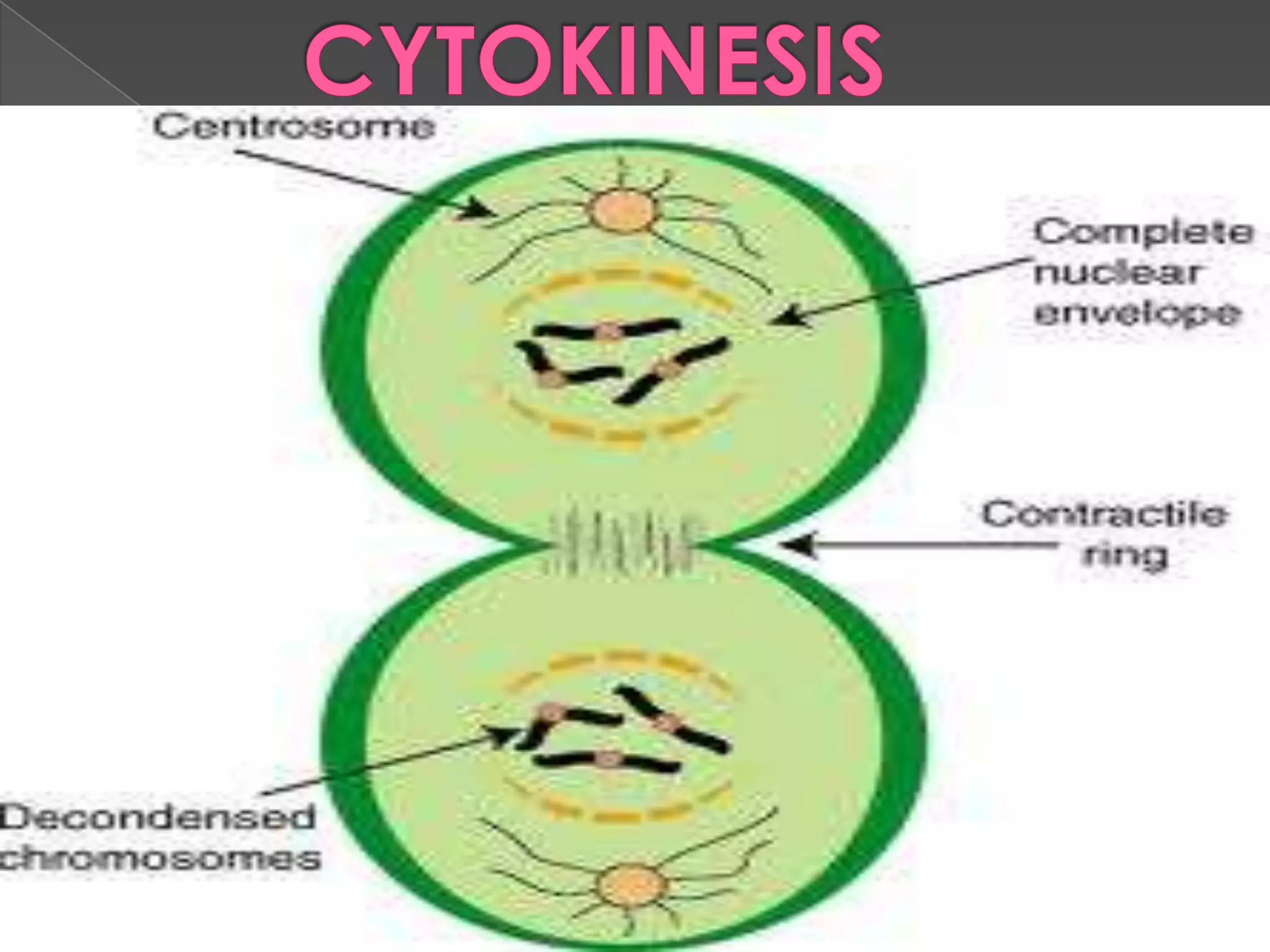
Mitosis is the process where a eukaryotic cell separates its chromosomes and divides into two identical daughter cells. It involves karyokinesis, where the nucleus and chromosomes divide, and cytokinesis, where the cytoplasm and cell membrane divide. First, the chromosomes condense and duplicate. Then, the nuclear envelope breaks down and mitotic spindles form to separate the chromosomes. The chromosomes align at the metaphase plate and then separate into the two daughter cells during anaphase. Finally, in telophase, the two new daughter nuclei form and the cell membrane pinches the cell in two through cytokinesis. Mitosis plays an important role in growth, tissue repair, and asexual reproduction in organisms.