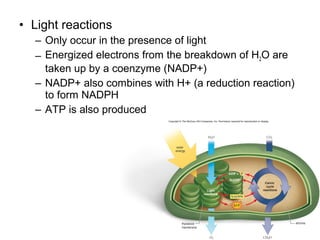
Photosynthesis involves two stages: the light-dependent reactions and the Calvin cycle. In the light reactions, solar energy is absorbed by pigments like chlorophyll and used to produce ATP and NADPH. In the Calvin cycle, ATP and NADPH fuel the reduction of carbon dioxide into carbohydrates like glucose. Photosynthesis is essential as it produces oxygen and food for all organisms on Earth.