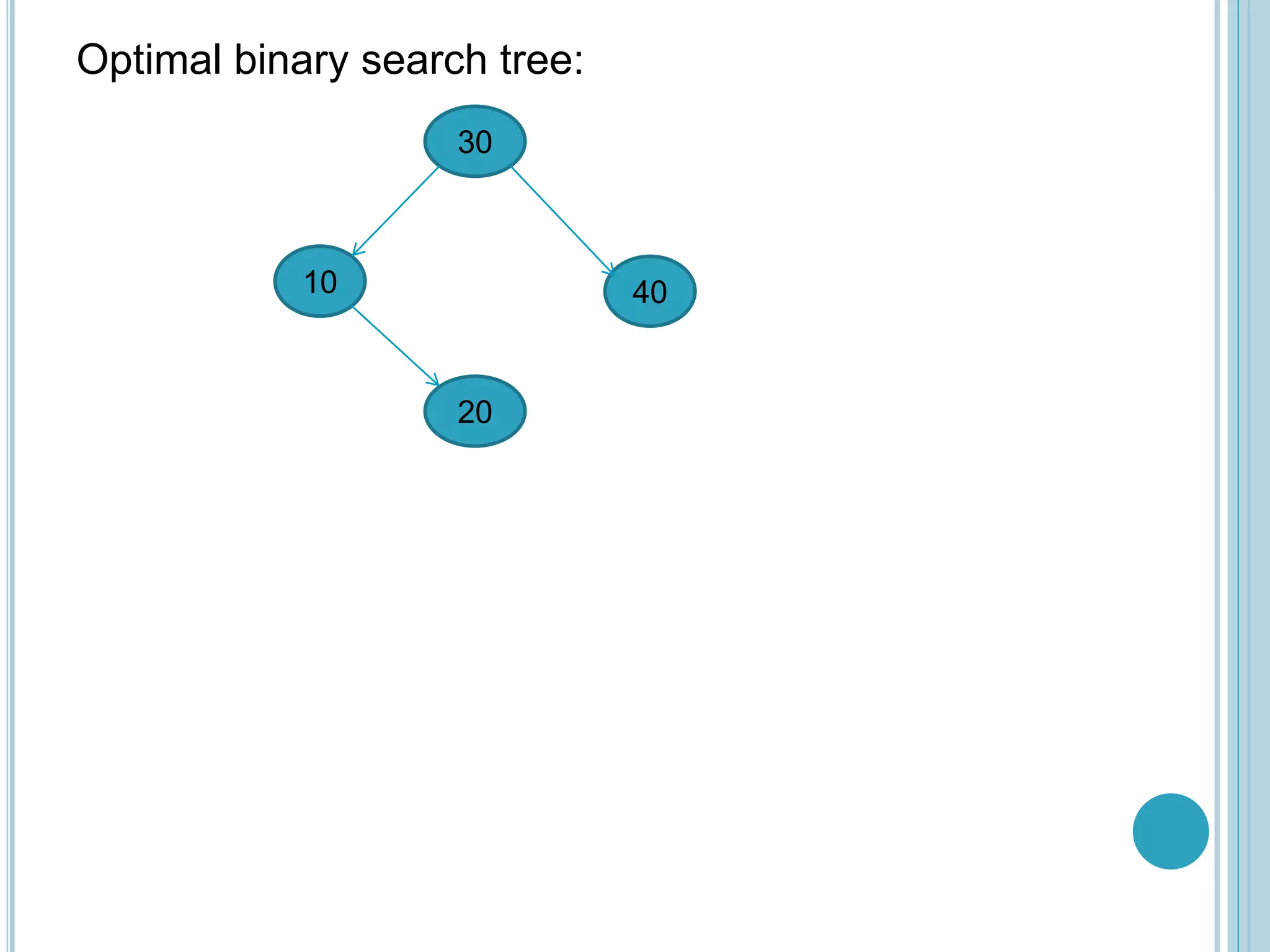
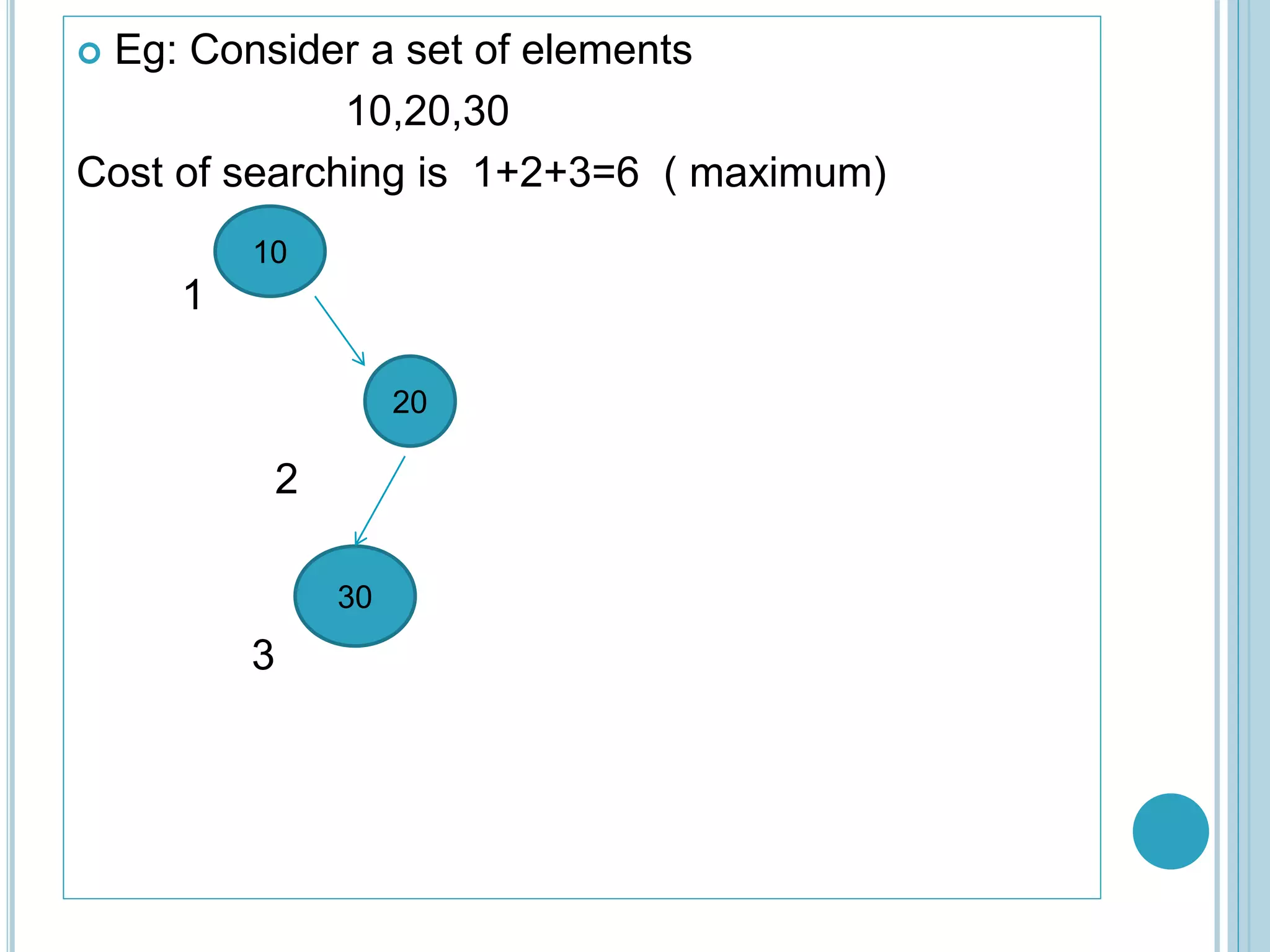
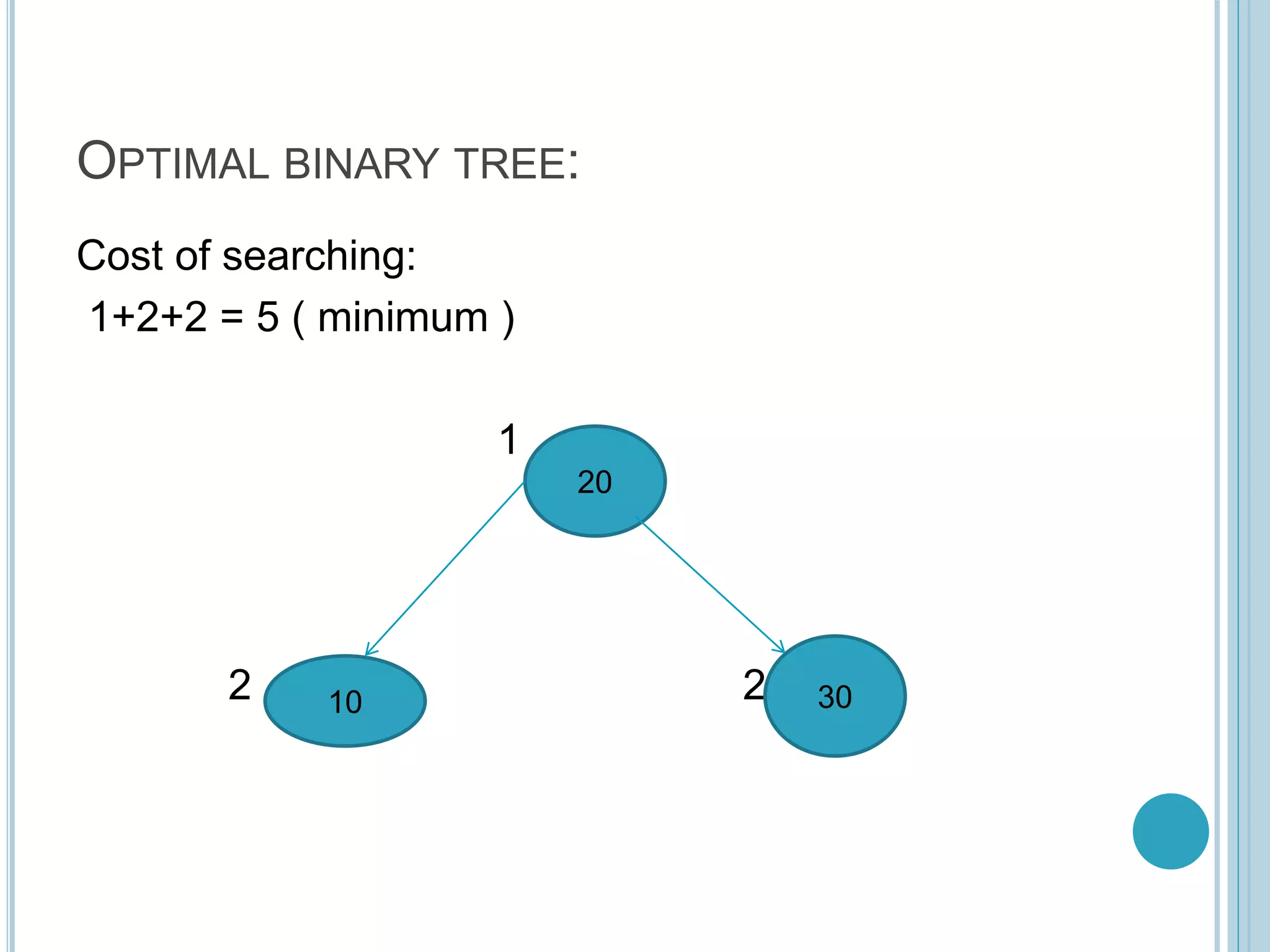
The document discusses optimal binary search trees. It begins by defining binary trees and binary search trees, noting that binary search trees require that left child nodes be less than the parent and right child nodes be greater. It then explains that an optimal binary search tree arranges elements in a binary structure to minimize search costs. The document provides an example comparing search costs between different binary tree structures. It outlines the optimal binary search tree algorithm, which calculates costs c[i,j] of reaching nodes i through j recursively to find the lowest cost tree structure.








![ Step 1: Consider the cost of reaching the same node
c[0,0]=0
c[1,1]=0
c[2,2]=0
c[3,3]=0
C[4,4]=0
Step2: Consider the cost of reaching one node
• c[0,1]=4
• c[1,2]=2
• c[2,3]=6
• c[3,4]=3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/optimalbinarysearchtreepptseminar-220911083541-c9ea17d4/75/Optimal-Binary-Search-tree-ppt-seminar-pptx-11-2048.jpg)
![ Step 3: Consider cost of reaching 2 nodes distance
c[0,2], c[1,3] , c[2,4]
c[i,j]= min{ c[i,k-1] + c[k,j] + w[i,j]}
Where k=1 ( rootnode)
c[0,2]= min { c[0,0]+c[1,2]+w[0,2],c[0,1]+c[2,2]+w[0,2]}
=min{ 0+2+6, 4+0+6}
=min{8,10}
C[0,2]=81
c[1,3]= min { c[1,1]+c[2,3]+w[1,3],c[1,2]+c[3,3]+w[1,3]}
=min{ 0+6+8,2+0+8}
=min{14,10}
C[1,3]=103](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/optimalbinarysearchtreepptseminar-220911083541-c9ea17d4/75/Optimal-Binary-Search-tree-ppt-seminar-pptx-12-2048.jpg)
![ c[2,4]= min { c[2,2]+c[3,4]+w[2,4],c[2,3]+c[4,4]+w[2,4]}
=min{ 0+3+9, 6+0+9}
=min{12,15}
C[2,4]=123
Step 4: Consider the cost of reaching 3 nodes.
c[0,3]= min {
c[0,0]+c[1,3]+w[0,3],c[0,1]+c[2,3]+w[0,3],c[0,2]+c[3,3]+12}
=min{ 0+10+12,4+6+12,8+0+12}
=min{22,22,20}
C[0,3]=203](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/optimalbinarysearchtreepptseminar-220911083541-c9ea17d4/75/Optimal-Binary-Search-tree-ppt-seminar-pptx-13-2048.jpg)
![ c[1,4]= min {
c[1,1]+c[2,4]+w[1,4],c[1,2]+c[3,4]+w[1,4],c[1,3]+
c[4,4]+w[1,4]}
=min{ 0+12+11,2+3+11,10+0+11}
=min{23,16,21}
C[1,4]=163
Step 5: Consider the cost of reaching 4 nodes.
c[0,4]= min {
c[0,0]+c[1,4]+w[0,4],c[0,1]+c[2,4]+w[0,4],c[0,2]+c[3,
4]+w[0,4],c[0,3]+c[4,4]+w[0,4]}
=min{ 31,31,26,35}
=min{22,22,20}
C[0,4]=263](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/optimalbinarysearchtreepptseminar-220911083541-c9ea17d4/75/Optimal-Binary-Search-tree-ppt-seminar-pptx-14-2048.jpg)