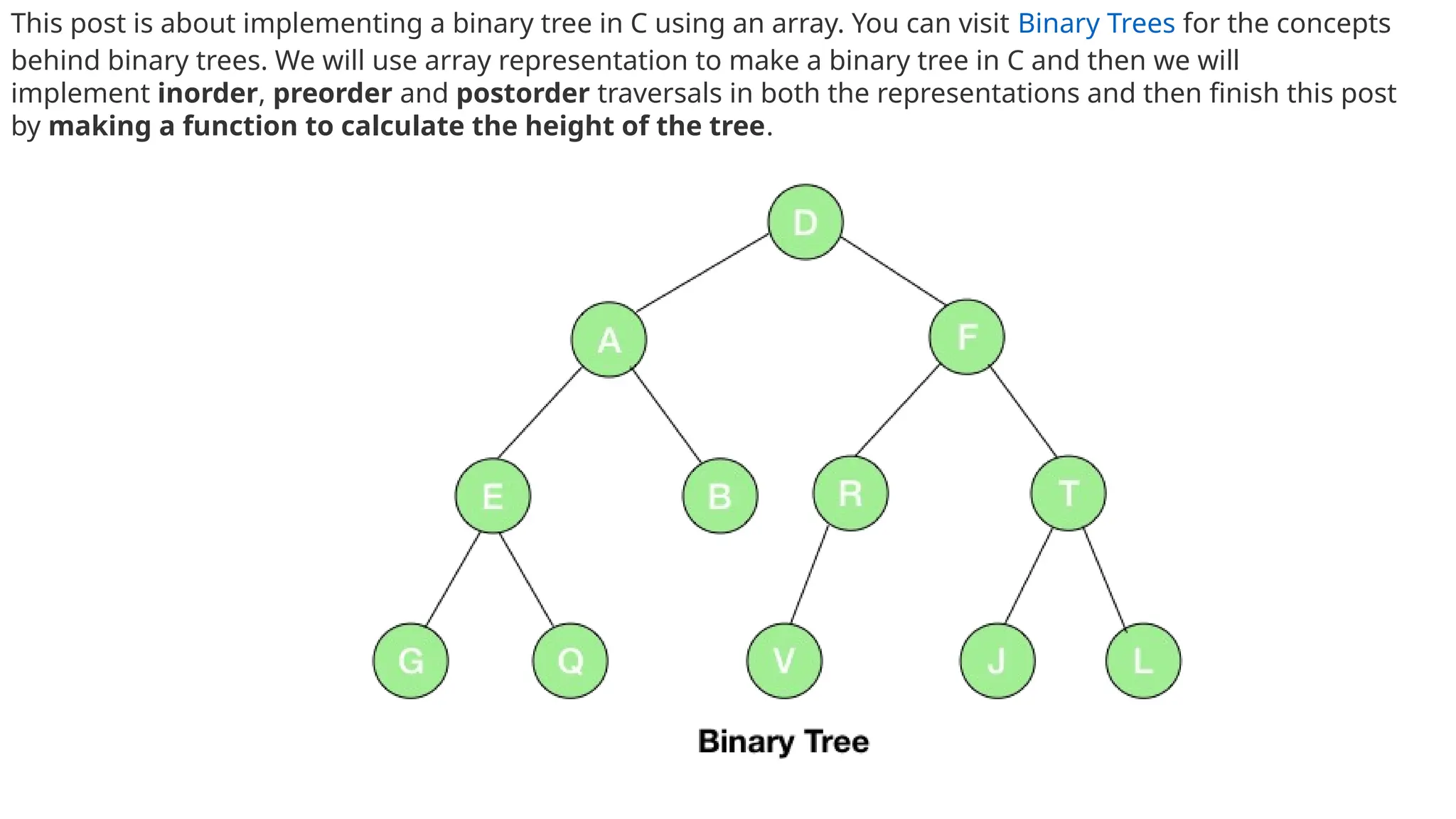
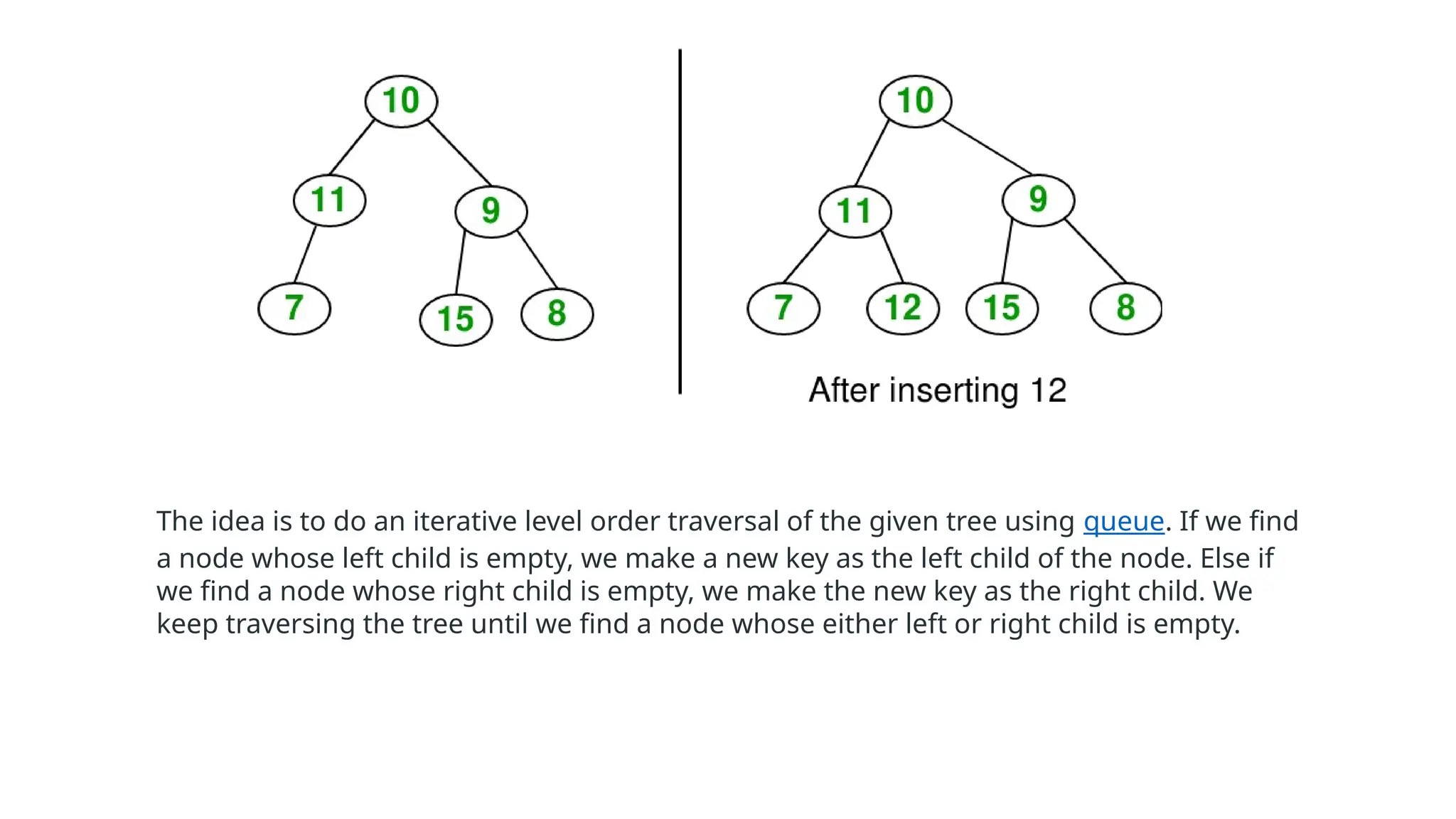
The document discusses the implementation of binary trees using arrays, explaining how an array can represent tree nodes with parent-child relationships. It covers operations such as insertion, deletion, and traversal methods including inorder, preorder, and postorder. Additionally, it addresses applications of binary trees in areas like data storage, expression evaluation, and memory allocation.